ppt
... take the n(search-key value, pointer) pairs (including the one being inserted) in sorted order. Place the first n/2 in the original node, and the rest in a new node. let the new node be p, and let k be the least key value in p. Insert (k,p) in the parent of the node being split. If the paren ...
... take the n(search-key value, pointer) pairs (including the one being inserted) in sorted order. Place the first n/2 in the original node, and the rest in a new node. let the new node be p, and let k be the least key value in p. Insert (k,p) in the parent of the node being split. If the paren ...
Improving Lookup Time Complexity of Compressed Suffix Arrays
... compressed suffix arrays given by Grossi et al. Grossi et al. 2003 . We use multi-ary wavelet trees Ferragina et al. 2007 to implement function Ψ of the first level of the recursive decomposition in compressed suffix arrays that was previously implemented using binary wavelet trees, and maintain the ...
... compressed suffix arrays given by Grossi et al. Grossi et al. 2003 . We use multi-ary wavelet trees Ferragina et al. 2007 to implement function Ψ of the first level of the recursive decomposition in compressed suffix arrays that was previously implemented using binary wavelet trees, and maintain the ...
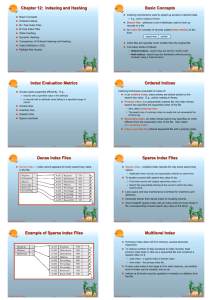
12: Indexing and Hashing
... take the n(search-key value, pointer) pairs (including the one being inserted) in sorted order. Place the first n/2 in the original node, and the rest in a new node. let the new node be p, and let k be the least key value in p. Insert (k,p) in the parent of the node being split. If the paren ...
... take the n(search-key value, pointer) pairs (including the one being inserted) in sorted order. Place the first n/2 in the original node, and the rest in a new node. let the new node be p, and let k be the least key value in p. Insert (k,p) in the parent of the node being split. If the paren ...
Example of Sparse Index Files
... created. In this case, the first search-key value appearing in the new block is inserted into the index. ! Multilevel insertion (as well as deletion) algorithms are simple ...
... created. In this case, the first search-key value appearing in the new block is inserted into the index. ! Multilevel insertion (as well as deletion) algorithms are simple ...
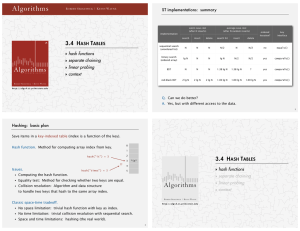
Algorithms
... http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.java http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.class http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.html ...
... http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.java http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.class http://www.cs.princeton.edu/introcs/13loop/Hello.html ...
6: linked lists
... // Add elements to the list list.addFirst("America"); // Add it to the beginning System.out.println("(1) " + list); list.addLast("Canada"); // Add it to the last of the list System.out.println("(2) " + list); list.addFirst("Russia"); // Add it to the first of the list System.out.println("(3) " + lis ...
... // Add elements to the list list.addFirst("America"); // Add it to the beginning System.out.println("(1) " + list); list.addLast("Canada"); // Add it to the last of the list System.out.println("(2) " + list); list.addFirst("Russia"); // Add it to the first of the list System.out.println("(3) " + lis ...
Linked list
... begin: returns an iterator addressing the first element in a list. pop_back:deletes the element at the end of a list. pop_front: deletes the element at the beginning of a list. push_back: adds an element to the end of a list. push_front: adds an element to the beginning of a list. ...
... begin: returns an iterator addressing the first element in a list. pop_back:deletes the element at the end of a list. pop_front: deletes the element at the beginning of a list. push_back: adds an element to the end of a list. push_front: adds an element to the beginning of a list. ...
Powerpoint - Chapters 16-18
... a trail of pointers, beginning at the first node. The time taken to access a node is linearly dependent on its position within the linked structure or O(n). From this discussion we conclude that the get and set methods are O(1) for an array implementation and O(n) for a linked implementation. ...
... a trail of pointers, beginning at the first node. The time taken to access a node is linearly dependent on its position within the linked structure or O(n). From this discussion we conclude that the get and set methods are O(1) for an array implementation and O(n) for a linked implementation. ...
Towards Optimal Range Medians - Department of Computer Science
... Our algorithm is based on the following key observation (see also Figure 1): Suppose we partition the elements in array A of length n into two smaller arrays: A.low which contains all elements with the n/2 smallest6 values in A, and A.high which contains all elements with the n/2 largest values. Th ...
... Our algorithm is based on the following key observation (see also Figure 1): Suppose we partition the elements in array A of length n into two smaller arrays: A.low which contains all elements with the n/2 smallest6 values in A, and A.high which contains all elements with the n/2 largest values. Th ...
03 Linked Lists
... Modifying a doubly-linked list usually requires changing more references, but is sometimes simpler because there is no need to keep track of the address of the previous node. In singly-linked list, this is required in delete and insert before operations. The extractLast operation is O(1) in doubly ...
... Modifying a doubly-linked list usually requires changing more references, but is sometimes simpler because there is no need to keep track of the address of the previous node. In singly-linked list, this is required in delete and insert before operations. The extractLast operation is O(1) in doubly ...
Answers to Selected Exercises
... Software engineering is a disciplined approach to the creation and maintenance of computer programs throughout their whole life cycle. Some software tools used in developing computer programs are text editors, compilers, assemblers, operating systems, and debugging programs. Goal 4 says, "Quality so ...
... Software engineering is a disciplined approach to the creation and maintenance of computer programs throughout their whole life cycle. Some software tools used in developing computer programs are text editors, compilers, assemblers, operating systems, and debugging programs. Goal 4 says, "Quality so ...
Implementations of stack menu driven program. Implementations of
... A stack is a restricted data structure, because only a small number of operations are performed on it. The nature of the pop and push operations also means that stack elements have a natural order. Elements are removed from the stack in the reverse order to the order of their addition. Therefore, th ...
... A stack is a restricted data structure, because only a small number of operations are performed on it. The nature of the pop and push operations also means that stack elements have a natural order. Elements are removed from the stack in the reverse order to the order of their addition. Therefore, th ...
pptx - Chair of Software Engineering
... “Find a member next of elements for which constraints contains no pair of the form [x, next]” sorted.extend (next) “Remove next from elements, and remove from constraints any pairs of the form [next, y]” end ...
... “Find a member next of elements for which constraints contains no pair of the form [x, next]” sorted.extend (next) “Remove next from elements, and remove from constraints any pairs of the form [next, y]” end ...
Chapter11. Skip Lists and Hashing
... // max permissible chain level // max current nonempty chain // current number of elements // a large key // head node // tail node // last node seen on each level // needed for random numbers ...
... // max permissible chain level // max current nonempty chain // current number of elements // a large key // head node // tail node // last node seen on each level // needed for random numbers ...
Priority Queues
... case therefore occurs whenever we are looking for a key smaller than any key in the set. In the worst case, the number of iterations is therefore given by the following recurrence: f (n) = f (⌊n/2⌋) + 1 for n > 1. From Theorem 3.32, f (n) ∈ Θ(lg n). Therefore, Find runs in Θ(lg n) time. Let us now a ...
... case therefore occurs whenever we are looking for a key smaller than any key in the set. In the worst case, the number of iterations is therefore given by the following recurrence: f (n) = f (⌊n/2⌋) + 1 for n > 1. From Theorem 3.32, f (n) ∈ Θ(lg n). Therefore, Find runs in Θ(lg n) time. Let us now a ...
public boolean - University of Pittsburgh
... There are several reasons for this, from both the implementation (i.e. how to do it in the compiler and interpreter) point of view and the programmer (i.e. how to use it effectively) point of view However, it is sometimes useful to be able to access an object through more than one ...
... There are several reasons for this, from both the implementation (i.e. how to do it in the compiler and interpreter) point of view and the programmer (i.e. how to use it effectively) point of view However, it is sometimes useful to be able to access an object through more than one ...