comparison study of sorting techniques in static data structure anwar
... enviable, whilst, it is premised that the sorting techniques eliminate ambiguities with less effort. Therefore, this study investigates the functionality of a set of sorting techniques to observe which technique to provide better efficiency in terms of sorting data. Therefore, five types of sorting ...
... enviable, whilst, it is premised that the sorting techniques eliminate ambiguities with less effort. Therefore, this study investigates the functionality of a set of sorting techniques to observe which technique to provide better efficiency in terms of sorting data. Therefore, five types of sorting ...
linked lists
... to the node (before the one to be removed, or before the insertion point) already, is a constant-time operation. While one can "delete" an element from an array in constant time by somehow marking its slot as "vacant", this causes fragmentation that impedes the performance of iteration. Moreover, ar ...
... to the node (before the one to be removed, or before the insertion point) already, is a constant-time operation. While one can "delete" an element from an array in constant time by somehow marking its slot as "vacant", this causes fragmentation that impedes the performance of iteration. Moreover, ar ...
COMPARISON STUDY ON SORTING TECHNIQUES IN STATIC
... enviable, whilst, it is premised that the sorting techniques eliminate ambiguities with less effort. Therefore, this study investigates the functionality of a set of sorting techniques to observe which technique to provide better efficiency in terms of sorting data. Therefore, five types of sorting ...
... enviable, whilst, it is premised that the sorting techniques eliminate ambiguities with less effort. Therefore, this study investigates the functionality of a set of sorting techniques to observe which technique to provide better efficiency in terms of sorting data. Therefore, five types of sorting ...
06slide_Arrays_SingleDime
... To describe why arrays are necessary in programming (§6.1). To declare array reference variables and create arrays (§§6.2.1-6.2.2). To initialize the values in an array (§6.2.3). To access array elements using indexed variables (§6.2.4). To declare, create, and initialize an array using an array ini ...
... To describe why arrays are necessary in programming (§6.1). To declare array reference variables and create arrays (§§6.2.1-6.2.2). To initialize the values in an array (§6.2.3). To access array elements using indexed variables (§6.2.4). To declare, create, and initialize an array using an array ini ...
ACM SIGCSE 2003: Multimedia Construction Projects
... At very end, create a two-branched list to start on trees. ...
... At very end, create a two-branched list to start on trees. ...
on queue - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... time, because to remove the tail node, I need to access the previous node. The only way you can to do in this kind of list is to start from the beginning and move all the way to the right till you get to the tail node. Then you will be able to access the previous node. What is problem in removing in ...
... time, because to remove the tail node, I need to access the previous node. The only way you can to do in this kind of list is to start from the beginning and move all the way to the right till you get to the tail node. Then you will be able to access the previous node. What is problem in removing in ...
MIT 6.851 Advanced Data Structures
... Left and Right slabs containing points and rectangles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76 ...
... Left and Right slabs containing points and rectangles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76 ...
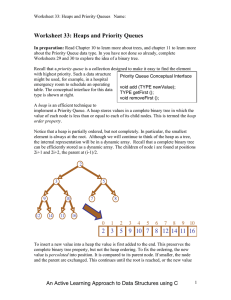
Chapter 11: Priority Queues and Heaps
... The term heap is used for two very different concepts in computer science. The heap data structure is an abstract data type used to implement priority queues. The terms heap, heap memory. heap allocation, and so on are used to describe memory that is allocated directly by the user, using the malloc ...
... The term heap is used for two very different concepts in computer science. The heap data structure is an abstract data type used to implement priority queues. The terms heap, heap memory. heap allocation, and so on are used to describe memory that is allocated directly by the user, using the malloc ...
chap06
... Data for each node in a linked list contains the same data type (i.e. simple data type or structural) as in Figure 6.4. In Figure 6.4, the first node contains a single field, number, and a link. The second is more typical. It contains three data fields, a name, id, and grade points (grdPts), and ...
... Data for each node in a linked list contains the same data type (i.e. simple data type or structural) as in Figure 6.4. In Figure 6.4, the first node contains a single field, number, and a link. The second is more typical. It contains three data fields, a name, id, and grade points (grdPts), and ...
Data Structures and Algorithms for Data
... operations that augment collection libraries in many languages today. Data collection operations like reduction, filtering or mapping can be executed by a single processor or many processors at once. However, there are multiple challenges to overcome when parallelizing collection operations. First, ...
... operations that augment collection libraries in many languages today. Data collection operations like reduction, filtering or mapping can be executed by a single processor or many processors at once. However, there are multiple challenges to overcome when parallelizing collection operations. First, ...
Linked Lists
... Linked lists are the simplest of the fundamental computer science objects known as dynamically linked structures They are dynamic in that their size can vary during execution as individual items are inserted into or removed from the list, like the list of students in CS315, which can and usually ...
... Linked lists are the simplest of the fundamental computer science objects known as dynamically linked structures They are dynamic in that their size can vary during execution as individual items are inserted into or removed from the list, like the list of students in CS315, which can and usually ...
Higher-Order Representation Predicates in Separation Logic
... This specification of peek is sufficient for most practical applications. Its only limitation is that, after a call to peek, the queue cannot be acted upon before the ownership of the head element has been given back to the queue. Indeed, the magic wand form does not match the pre-condition of other ...
... This specification of peek is sufficient for most practical applications. Its only limitation is that, after a call to peek, the queue cannot be acted upon before the ownership of the head element has been given back to the queue. Indeed, the magic wand form does not match the pre-condition of other ...
Data Structure - knowledgebounce
... Discuss the advantages & disadvantages of circular linked list. Circular lists have certain advantages over singly linked list. The first advantage is that in a circular list every node is accessible from a given node. A second advantage is concerned with the deletion operation. In order to delete a ...
... Discuss the advantages & disadvantages of circular linked list. Circular lists have certain advantages over singly linked list. The first advantage is that in a circular list every node is accessible from a given node. A second advantage is concerned with the deletion operation. In order to delete a ...
Efficient, Oblivious Data Structures for MPC
... Other than the works already discussed [11,16,25], Gentry et al. [13] describe how to use homomorphic encryption combined with ORAM for reducing the communication cost of ORAM and also for secure computation in a client-server situation. These works are in a similar vein to ours, but our work is the ...
... Other than the works already discussed [11,16,25], Gentry et al. [13] describe how to use homomorphic encryption combined with ORAM for reducing the communication cost of ORAM and also for secure computation in a client-server situation. These works are in a similar vein to ours, but our work is the ...
View
... Allocated memory can be many types: Contiguous memory allocation: Allocation of adjacent memory locations Non-Contiguous memory allocation: Allocation of non adjacent memory locations Heap: Collection of all free memory locations available for allocation De-allocation: Releasing of allocated ...
... Allocated memory can be many types: Contiguous memory allocation: Allocation of adjacent memory locations Non-Contiguous memory allocation: Allocation of non adjacent memory locations Heap: Collection of all free memory locations available for allocation De-allocation: Releasing of allocated ...
Maintaining External Memory Efficient Hash Tables
... in expected O(n + log log |U |) time such that its encoding requires only almost optimal (1 + o(1))(n · log e + log log |U |) space. Multiple non-oblivious probes into external memory are required for lookups in these space efficient dynamic or static schemes. Dictionary algorithms such as Cuckoo-Ha ...
... in expected O(n + log log |U |) time such that its encoding requires only almost optimal (1 + o(1))(n · log e + log log |U |) space. Multiple non-oblivious probes into external memory are required for lookups in these space efficient dynamic or static schemes. Dictionary algorithms such as Cuckoo-Ha ...
Chapter 7: Relational Database Design
... extra insertion and deletion overhead, space overhead. Advantages of B+-trees outweigh disadvantages B+-trees are used extensively ...
... extra insertion and deletion overhead, space overhead. Advantages of B+-trees outweigh disadvantages B+-trees are used extensively ...