previous-qns-and-answers
... •For instance, students IDs or ISBN codes may contain common subsequences which may increase the likelihood of collision. •Very fast but digits/characters distribution in keys may not bevery even Folding •It involves splitting keys into two or more parts and then combining the parts to form the has ...
... •For instance, students IDs or ISBN codes may contain common subsequences which may increase the likelihood of collision. •Very fast but digits/characters distribution in keys may not bevery even Folding •It involves splitting keys into two or more parts and then combining the parts to form the has ...
Linear-Space Data Structures for Range Minority Query in Arrays⋆
... data structure that supports range mode queries in O( n/ log n) time [5], an O(n log(1/β +1))-space data structure that supports β-majority range queries in O(1/β) time [9], and a O(n log n)-space data structure that supports α-majority range queries in O(1/α) time [11]. Related generalizations incl ...
... data structure that supports range mode queries in O( n/ log n) time [5], an O(n log(1/β +1))-space data structure that supports β-majority range queries in O(1/β) time [9], and a O(n log n)-space data structure that supports α-majority range queries in O(1/α) time [11]. Related generalizations incl ...
Lecture 8 Notes
... Collections Framework. As a working programmer, you may often use these, and most of the rest of the time, you will use various libraries that supply alternatives. You will not often have to implement the data structures yourself. ...
... Collections Framework. As a working programmer, you may often use these, and most of the rest of the time, you will use various libraries that supply alternatives. You will not often have to implement the data structures yourself. ...
Sorting Algorithms
... • If we implement the mergesort using linked lists, we do not need to be concerned with the amount of time needed to move data – Instead, we just need to concentrate on the number of comparisons. – When lists get very long, the number of comparisons is far less with the mergesort than it is with the ...
... • If we implement the mergesort using linked lists, we do not need to be concerned with the amount of time needed to move data – Instead, we just need to concentrate on the number of comparisons. – When lists get very long, the number of comparisons is far less with the mergesort than it is with the ...
Fall 2008 (Midterm 2)
... integers to sort them in ascending order (smallest value on the left). Note: You do not need to write any Java code, however, you need to show each step in the sorting process to receive full credit. ...
... integers to sort them in ascending order (smallest value on the left). Note: You do not need to write any Java code, however, you need to show each step in the sorting process to receive full credit. ...
Indexing and Hashing.key
... hashing wins because h(value) takes us right to the bucket that holds the records For queries where we search based on a range (i.e., select … from r where attr ! max and attr # min), ordered indexing wins because you can find records in sequence from min up to max, but there is no easy way to do th ...
... hashing wins because h(value) takes us right to the bucket that holds the records For queries where we search based on a range (i.e., select … from r where attr ! max and attr # min), ordered indexing wins because you can find records in sequence from min up to max, but there is no easy way to do th ...
word - Courses
... solution would be to avoid collisions altogether. We might try to achieve this goal through our choice of hash function h. One possibility is to make h appear to be random, thus avoiding collisions or at least minimizing their number. The very term “hash”, which evokes images of random mixing and c ...
... solution would be to avoid collisions altogether. We might try to achieve this goal through our choice of hash function h. One possibility is to make h appear to be random, thus avoiding collisions or at least minimizing their number. The very term “hash”, which evokes images of random mixing and c ...
Amortized Analysis Master MOSIG
... to insert a new element is linear in the size of the array. We can improve the time for insertion by keeping several sorted arrays. Speci cally, suppose that we wish to support search and insert on a set of n elements. Let k = dlg(n + 1)e, and let the binary representation of n be nk−1 , . . . , n0 ...
... to insert a new element is linear in the size of the array. We can improve the time for insertion by keeping several sorted arrays. Speci cally, suppose that we wish to support search and insert on a set of n elements. Let k = dlg(n + 1)e, and let the binary representation of n be nk−1 , . . . , n0 ...
COMP 121 Week 9
... Simplest class that implements the List interface Improvement over an array Used when a programmer wants to add new elements to the end of a list but still needs the capability to access the elements stored in the list in arbitrary order The size of an ArrayList automatically increases as new elemen ...
... Simplest class that implements the List interface Improvement over an array Used when a programmer wants to add new elements to the end of a list but still needs the capability to access the elements stored in the list in arbitrary order The size of an ArrayList automatically increases as new elemen ...
Lecture 3 Data Structures (DAT037)
... • For using as a queue, provides add = addFirst, remove = removeLast • For using as a stack, provides push = addFirst, pop = removeFirst • Note: Java also provides a Stack class, but this ...
... • For using as a queue, provides add = addFirst, remove = removeLast • For using as a stack, provides push = addFirst, pop = removeFirst • Note: Java also provides a Stack class, but this ...
Efficient representation of integer sets
... use of these objects, and, in some cases, they are at the very core of the algorithm. This makes it necessary to have a simple and efficient way to represent and manipulate these objects. We present a solution that uses bitmaps and bitwise operators to represent nonnegative integer sets and implemen ...
... use of these objects, and, in some cases, they are at the very core of the algorithm. This makes it necessary to have a simple and efficient way to represent and manipulate these objects. We present a solution that uses bitmaps and bitwise operators to represent nonnegative integer sets and implemen ...
CMSC 425: Lecture 10 Geometric Data Structures for Games: Index
... Fig. 1: Examples of common enclosures: (a) AABB, (b) general BB, (c) sphere, (d) ellipsoid, (e) 8-DOP. General bounding boxes: The principal shortcoming of axis-parallel bounding boxes is that it is not possible to rotate the object without recomputing the entire bounding box. In contrast, general ( ...
... Fig. 1: Examples of common enclosures: (a) AABB, (b) general BB, (c) sphere, (d) ellipsoid, (e) 8-DOP. General bounding boxes: The principal shortcoming of axis-parallel bounding boxes is that it is not possible to rotate the object without recomputing the entire bounding box. In contrast, general ( ...
Efficient data structures for sparse network representation
... high-dimensional or sparse, but large. This is the common case in network science. Such data cannot be laid out in memory in such a way that conceptually adjacent elements — such as connected nodes in a network — would also be adjacent in the main memory. There is thus no spatial locality to be expl ...
... high-dimensional or sparse, but large. This is the common case in network science. Such data cannot be laid out in memory in such a way that conceptually adjacent elements — such as connected nodes in a network — would also be adjacent in the main memory. There is thus no spatial locality to be expl ...
Basic Introduction into Algorithms and Data Structures
... the running time is given as a function of the size of the input (n here). Furthermore, for sequences of equal length, sorting ‘almost sorted’ sequences should be faster than ‘unsorted’ ones. Often, the so-called worst case running time of an algorithm is studied as a function of the size of the inp ...
... the running time is given as a function of the size of the input (n here). Furthermore, for sequences of equal length, sorting ‘almost sorted’ sequences should be faster than ‘unsorted’ ones. Often, the so-called worst case running time of an algorithm is studied as a function of the size of the inp ...
Chapter 19 Java Data Structures
... some people refer a data structure as a container object or a collection object. To define a data structure is essentially to declare a class. The class for a data structure should use data fields to store data and provide methods to support operations such as insertion and deletion. To create a dat ...
... some people refer a data structure as a container object or a collection object. To define a data structure is essentially to declare a class. The class for a data structure should use data fields to store data and provide methods to support operations such as insertion and deletion. To create a dat ...
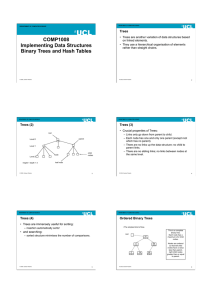
Binary Trees and Hash Tables
... • Hashing is so important that in Java every object has a hash code to enable easy storage in hash tables and other data structures. • See the method hashCode implemented by all objects. ...
... • Hashing is so important that in Java every object has a hash code to enable easy storage in hash tables and other data structures. • See the method hashCode implemented by all objects. ...
UNIT- V: Sorting: Bubble sort, Merge sort, Insertion Sort, Selection
... elements. In insertion sort the element is inserted at an appropriate place similar to card insertion. Here the list is divided into two parts sorted and unsorted sub-lists. In each pass, the first element of unsorted sub list is picked up and moved into the sorted sub list by inserting it in suitab ...
... elements. In insertion sort the element is inserted at an appropriate place similar to card insertion. Here the list is divided into two parts sorted and unsorted sub-lists. In each pass, the first element of unsorted sub list is picked up and moved into the sorted sub list by inserting it in suitab ...