Structures - CS Course Webpages
... • When a pointer to a structure is passed to a function, only the address of the structure is pushed on the stack. This makes for very fast function calls. • Passing a pointer makes it possible for the function to modify the contents of the structure used as the argument via call-byreference. ...
... • When a pointer to a structure is passed to a function, only the address of the structure is pushed on the stack. This makes for very fast function calls. • Passing a pointer makes it possible for the function to modify the contents of the structure used as the argument via call-byreference. ...
Data Structures and Algorithms - Cambridge Computer Laboratory
... this is first to adopt a generic idea of what a computer is, and measure costs in abstract “program steps” rather than in real seconds, and then to agree to ignore constant factors in the cost-estimation formula. As a further simplification we agree that all small problems can be solved pretty rapidly ...
... this is first to adopt a generic idea of what a computer is, and measure costs in abstract “program steps” rather than in real seconds, and then to agree to ignore constant factors in the cost-estimation formula. As a further simplification we agree that all small problems can be solved pretty rapidly ...
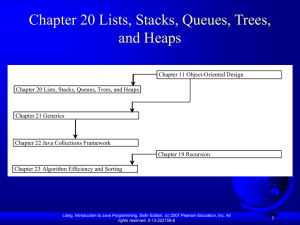
Chapter 19 Java Data Structures
... some people refer a data structure as a container object or a collection object. To define a data structure is essentially to declare a class. The class for a data structure should use data fields to store data and provide methods to support operations such as insertion and deletion. To create a dat ...
... some people refer a data structure as a container object or a collection object. To define a data structure is essentially to declare a class. The class for a data structure should use data fields to store data and provide methods to support operations such as insertion and deletion. To create a dat ...
Document
... merging problem. • Every element inside a matching block has to be ranked inside the other matching block. • Hence, the problem of merging a pair of matching blocks is an independent subproblem which does not affect any other block. Page 16 ...
... merging problem. • Every element inside a matching block has to be ranked inside the other matching block. • Hence, the problem of merging a pair of matching blocks is an independent subproblem which does not affect any other block. Page 16 ...
7. Full-Text Indexes in External Memory
... character occupies a single machine word, and all usual integer operations on characters can be performed in constant time. For internal memory computation, we sometimes assume the constant alphabet model , which differs from the integer alphabet model in that dictionary operations on sets of charact ...
... character occupies a single machine word, and all usual integer operations on characters can be performed in constant time. For internal memory computation, we sometimes assume the constant alphabet model , which differs from the integer alphabet model in that dictionary operations on sets of charact ...
Dictionaries-Hash-Tables-and-Sets
... Implement the data structure "hash table" in a class HashTable. Keep the data in array of lists of keyvalue pairs (LinkedList>[]) with
initial capacity of 16. When the hash table load runs
over 75%, perform resizing to 2 times larger capacity.
Implement the following methods a ...
... Implement the data structure "hash table" in a class HashTable
Succinct Data Structures - the David R. Cheriton School of Computer
... Given: Universe of n elements [0,...n-1] and m arbitrary elements from this universe Create: a static structure to support search in constant time (lg n bit word and usual operations) Using: Essentially minimum possible # bits n )) ... lg((m Operation: Member query in O(1) time (Brodnik & M.) ...
... Given: Universe of n elements [0,...n-1] and m arbitrary elements from this universe Create: a static structure to support search in constant time (lg n bit word and usual operations) Using: Essentially minimum possible # bits n )) ... lg((m Operation: Member query in O(1) time (Brodnik & M.) ...
heap property
... Each of these will run in O(lg n) time, which means that the procedure will also run in O(lg n) time. The heap provides an efficient implementation for a priority queue using the operations outlined, but is not so efficient in other cases For example, an operation which may sometimes be required is ...
... Each of these will run in O(lg n) time, which means that the procedure will also run in O(lg n) time. The heap provides an efficient implementation for a priority queue using the operations outlined, but is not so efficient in other cases For example, an operation which may sometimes be required is ...
The vector class
... An array is a container that stores the n (size) elements in a contiguous block of memory. Once declared, n cannot be changed. Array name is associated with the address of the array. So when an array is passed to a function, the size (or the number of elements that need to be processed) of the array ...
... An array is a container that stores the n (size) elements in a contiguous block of memory. Once declared, n cannot be changed. Array name is associated with the address of the array. So when an array is passed to a function, the size (or the number of elements that need to be processed) of the array ...
Min-Max Heaps and Generalized Priority Queues
... Using the properties of min-max heaps, an orderstatistics tree can be constructed in linear time, any Find operation (on the specified set of ranks) can be performed in constant time, the Insert operation and any Delete operation (on the specified set of ranks) can be performed in logarithmic time, ...
... Using the properties of min-max heaps, an orderstatistics tree can be constructed in linear time, any Find operation (on the specified set of ranks) can be performed in constant time, the Insert operation and any Delete operation (on the specified set of ranks) can be performed in logarithmic time, ...
Soft Kinetic Data Structures
... a sorted sequence of keys. We consider also the same events as in sorting, namely, an even occur when two keys change their relative order• We observe also that it does not seem to be a good idea to measure the quality of the search tree by its edit distance to a correct search tree. This is because ...
... a sorted sequence of keys. We consider also the same events as in sorting, namely, an even occur when two keys change their relative order• We observe also that it does not seem to be a good idea to measure the quality of the search tree by its edit distance to a correct search tree. This is because ...
**** 1 - postech
... • The steps are: Pick an element, called a pivot, from the list. Partitioning: Reorder the list so that all elements with values less than the pivot come before the pivot, while all elements with values greater than the pivot come after it. • Equal values can go either way. • After this partitio ...
... • The steps are: Pick an element, called a pivot, from the list. Partitioning: Reorder the list so that all elements with values less than the pivot come before the pivot, while all elements with values greater than the pivot come after it. • Equal values can go either way. • After this partitio ...
MS Word - School of Computer Science Student WWW Server
... “At 36.7 seconds after H0 (approx. 30 seconds after lift-off) the computer within the back-up inertial reference system, which was working on stand-by for guidance and attitude control, became inoperative. This was caused by an internal variable related to the horizontal velocity of the launcher e ...
... “At 36.7 seconds after H0 (approx. 30 seconds after lift-off) the computer within the back-up inertial reference system, which was working on stand-by for guidance and attitude control, became inoperative. This was caused by an internal variable related to the horizontal velocity of the launcher e ...
Chapter 27 Hashing Why Hashing? Objectives Map
... Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Liang, Introduction to Java Programming, Tenth Edition, (c) 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...