chapter 3: the fertile crescent
... place or people) by use of military force The city-states of Sumer were constantly fighting with each other. This constant fighting led to the creation of empires. Two of the largest city-states, Umma and Lagash often fought for power for Sumer and its city-states. In a battle fought around 2450 B ...
... place or people) by use of military force The city-states of Sumer were constantly fighting with each other. This constant fighting led to the creation of empires. Two of the largest city-states, Umma and Lagash often fought for power for Sumer and its city-states. In a battle fought around 2450 B ...
Mesopotamia *between the rivers
... -Tigris and Euphrates Rivers - Iraq • Why is this area known as the Fertile Crescent? - Rich soil (silt) ...
... -Tigris and Euphrates Rivers - Iraq • Why is this area known as the Fertile Crescent? - Rich soil (silt) ...
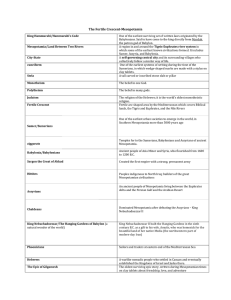
Mesopotamia Vocabulary Terms
... The center of Sumerian life was the ziggurat the courts. The lives of Sumerian women compared with today’s women would be described as having the ability to sell property and own businesses. ...
... The center of Sumerian life was the ziggurat the courts. The lives of Sumerian women compared with today’s women would be described as having the ability to sell property and own businesses. ...
First Cities of Sumer
... mesopotAmiA lies between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers—an area that now covers much of modern Iraq. It was the ancient Greeks who named this region Mesopotamia, meaning “the land between the rivers.” In about 5000 bce, the farming people of Sumer founded small settlements that grew into the wo ...
... mesopotAmiA lies between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers—an area that now covers much of modern Iraq. It was the ancient Greeks who named this region Mesopotamia, meaning “the land between the rivers.” In about 5000 bce, the farming people of Sumer founded small settlements that grew into the wo ...
*The land between two rivers* Sumer*Babylon*Assyrians Ms. Jerome
... Sumerian social structure Sumer became attractive to raiders for its wealth This developed the need for a recognized military By 3,000 b.c.e. all Sumerian cities had kings who ...
... Sumerian social structure Sumer became attractive to raiders for its wealth This developed the need for a recognized military By 3,000 b.c.e. all Sumerian cities had kings who ...
document
... The Kassites tried for many years to take Babylon. The Hittites came from the north and attacked Babylon. They robed with there chariots Babylon and left. Babylon was weekend and the Kassites toke over. ...
... The Kassites tried for many years to take Babylon. The Hittites came from the north and attacked Babylon. They robed with there chariots Babylon and left. Babylon was weekend and the Kassites toke over. ...
CHAPTER 1 – The First Civilizations
... 2. A group of many different lands under one ruler -___________________ 3. Using walls, waterways, and ditches to bring water to crops -________________ 4. One of the boundaries of Mesopotamia - ___________________ 5. The Sumerian form of writing -___________________ ...
... 2. A group of many different lands under one ruler -___________________ 3. Using walls, waterways, and ditches to bring water to crops -________________ 4. One of the boundaries of Mesopotamia - ___________________ 5. The Sumerian form of writing -___________________ ...
Akkadian Empire

The Akkadian Empire /əˈkeɪdiən/ was an ancient Semitic empire centered in the city of Akkad /ˈækæd/ and its surrounding region, also called Akkad in ancient Mesopotamia. The empire united all the indigenous Akkadian-speaking Semites and the Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire controlled Mesopotamia, the Levant, and parts of Iran.During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Semitic Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism. Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language somewhere between the 3rd and the 2nd millennia BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate).The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad (2334–2279 BC). Under Sargon and his successors, Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though there are earlier Sumerian claimants.After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the Akkadian people of Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian speaking nations: Assyria in the north, and, a few centuries later, Babylonia in the south.