Ext2
... Civil war in DRC leads to massive displacement, need for food and many people with guns designed for killing large primates Park rangers and anti-poaching patrols attacked ...
... Civil war in DRC leads to massive displacement, need for food and many people with guns designed for killing large primates Park rangers and anti-poaching patrols attacked ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions – Chapters 1 and 2
... water, and they change the qualities of water such as its temperature, oxygen content, and nutrient content. Channelization destroys habits by removing streamside habitat and changing the rate at which water flows. As water moves more quickly, sediments are flushed further downstream, often carried ...
... water, and they change the qualities of water such as its temperature, oxygen content, and nutrient content. Channelization destroys habits by removing streamside habitat and changing the rate at which water flows. As water moves more quickly, sediments are flushed further downstream, often carried ...
How did life on Earth begin and evolve? The many different species
... The many different species of living things on Earth (and many species that are now extinct) evolved from very simple living things. Life on Earth began about 3500 million years ago. Evidence for evolution is provided by fossils and from analysis of similarities and differences in DNA of organisms. ...
... The many different species of living things on Earth (and many species that are now extinct) evolved from very simple living things. Life on Earth began about 3500 million years ago. Evidence for evolution is provided by fossils and from analysis of similarities and differences in DNA of organisms. ...
word - KScience
... The many different species of living things on Earth (and many species that are now extinct) evolved from very simple living things. Life on Earth began about 3500 million years ago. Evidence for evolution is provided by fossils and from analysis of similarities and differences in DNA of organisms. ...
... The many different species of living things on Earth (and many species that are now extinct) evolved from very simple living things. Life on Earth began about 3500 million years ago. Evidence for evolution is provided by fossils and from analysis of similarities and differences in DNA of organisms. ...
20130402094281
... • Also-carnivores tend to be larger at successive trophic levels-can’t get enough food to meet needs ...
... • Also-carnivores tend to be larger at successive trophic levels-can’t get enough food to meet needs ...
invaders!
... • Are usually tolerant of a wide range of conditions instead of a narrow niche. • Usually have high rates of reproduction. ...
... • Are usually tolerant of a wide range of conditions instead of a narrow niche. • Usually have high rates of reproduction. ...
Threats to Biodiversity
... • “Naïve” species w/ no prior contact w/ humans (dodo bird) • Species closely related to other extinct or near extinct/threatened species (rhinos, oryx, whales) ...
... • “Naïve” species w/ no prior contact w/ humans (dodo bird) • Species closely related to other extinct or near extinct/threatened species (rhinos, oryx, whales) ...
Biodiversity - ScienceWithMrShrout
... • Thermal pollution: is the degradation of water quality by any process that changes ambient water temperature – Power plants and industry using local water supplies to cool during manufacturing. – The temperature of the discharge water is significantly warmer than normal – Warmer water holds less O ...
... • Thermal pollution: is the degradation of water quality by any process that changes ambient water temperature – Power plants and industry using local water supplies to cool during manufacturing. – The temperature of the discharge water is significantly warmer than normal – Warmer water holds less O ...
A Closer Look at Natural Selection…
... Throughout Earth’s Geologic History, the environments have changed greatly. ...
... Throughout Earth’s Geologic History, the environments have changed greatly. ...
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
... information on the number of pairs and single birds and their habitats is collected with the help of volunteers. As shown above, the number of shrikes in the province decreased substantially between 1992 (55 pairs) and 1997 (17 pairs). In 1998 the population rebounded slightly to 30 pairs, which is ...
... information on the number of pairs and single birds and their habitats is collected with the help of volunteers. As shown above, the number of shrikes in the province decreased substantially between 1992 (55 pairs) and 1997 (17 pairs). In 1998 the population rebounded slightly to 30 pairs, which is ...
CH 41 Reading Guide Communities
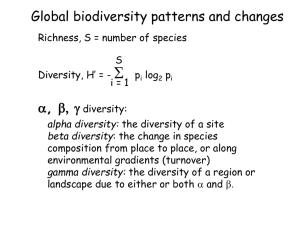
... 26. There are probably two key factors in latitudinal gradients. List and explain both here, and put a star next to the one that is probably the primary cause of the latitudinal difference in biodiversity. ...
... 26. There are probably two key factors in latitudinal gradients. List and explain both here, and put a star next to the one that is probably the primary cause of the latitudinal difference in biodiversity. ...
ESPM 169 Lecture September 12, 2002
... - most basic building-block of BD: blueprint for individual organisms 2. Species (most useful measure) - distinctive groups of similar populations that are isolated reproductively from other such groups 3. Ecosystems 4. All add up to the biosphere - through which BD is distributed - hot-spots; tropi ...
... - most basic building-block of BD: blueprint for individual organisms 2. Species (most useful measure) - distinctive groups of similar populations that are isolated reproductively from other such groups 3. Ecosystems 4. All add up to the biosphere - through which BD is distributed - hot-spots; tropi ...
Biodiversity Notes Main Idea Details Biodiversity What is biodiversity
... There are ________ billion humans living on Earth. ...
... There are ________ billion humans living on Earth. ...
endangered_speices_project Cummings
... Small Whorled Pogonia: The plant is endangered because of habitat destruction. ...
... Small Whorled Pogonia: The plant is endangered because of habitat destruction. ...
Biology
... The Importance of Biodiversity • Why preserve biodiversity? – Direct Economic Value: provides plants and animals that give us food, clothing, medicine, and shelter. • Even those species we don’t use are important to the health of species we do. • May need genes from species we don’t use for those w ...
... The Importance of Biodiversity • Why preserve biodiversity? – Direct Economic Value: provides plants and animals that give us food, clothing, medicine, and shelter. • Even those species we don’t use are important to the health of species we do. • May need genes from species we don’t use for those w ...
Unit 3 Study Guide – The Nature of Ecology
... 4. Distinguish between food chains and food webs and how the laws of thermodynamics influence them. 5. Diagram and label several food webs. 6. Describe the carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and water cycles. 7. Discuss the importance of biodiversity 8. Distinguish between different types of biom ...
... 4. Distinguish between food chains and food webs and how the laws of thermodynamics influence them. 5. Diagram and label several food webs. 6. Describe the carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and water cycles. 7. Discuss the importance of biodiversity 8. Distinguish between different types of biom ...
7th grade Science
... sustainable yield—an amount of a renewable resource that can be harvested regularly without reducing the future supply fishery—an area with a large population of valuable ocean organisms aquaculture—the practice of raising fish and other water-dwelling organisms for food Lesson 5 vocab biodiversity— ...
... sustainable yield—an amount of a renewable resource that can be harvested regularly without reducing the future supply fishery—an area with a large population of valuable ocean organisms aquaculture—the practice of raising fish and other water-dwelling organisms for food Lesson 5 vocab biodiversity— ...
Think like an Ecologist… a scientist who studies the relationships
... Ecotourism: Environmentally, culturally, and scientifically responsible tourism of unusual or interesting ecological sites. It safeguards the nature of the attraction and serves to strengthen conservation and scientific research efforts in the area. Endangered species: Wild species with so few indiv ...
... Ecotourism: Environmentally, culturally, and scientifically responsible tourism of unusual or interesting ecological sites. It safeguards the nature of the attraction and serves to strengthen conservation and scientific research efforts in the area. Endangered species: Wild species with so few indiv ...
poster
... efforts with conservation importance and dominant, widespread, or locally abundant species, such as foundation species, at low risk of extinction receive relatively little attention unless they are invasive. • Foundation species are distinct from these other types of species, because they also have ...
... efforts with conservation importance and dominant, widespread, or locally abundant species, such as foundation species, at low risk of extinction receive relatively little attention unless they are invasive. • Foundation species are distinct from these other types of species, because they also have ...
4-1 What is Biodiversity and Why Important?
... Difference between the 2 is mainly about the starting substrate – know what it is for each ...
... Difference between the 2 is mainly about the starting substrate – know what it is for each ...
Extinction
In biology and ecology, extinction is the end of an organism or of a group of organisms (taxon), normally a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly ""reappears"" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation—where new varieties of organisms arise and thrive when they are able to find and exploit an ecological niche—and species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superior competition. The relationship between animals and their ecological niches has been firmly established. A typical species becomes extinct within 10 million years of its first appearance, although some species, called living fossils, survive with virtually no morphological change for hundreds of millions of years. Mass extinctions are relatively rare events; however, isolated extinctions are quite common. Only recently have extinctions been recorded and scientists have become alarmed at the current high rate of extinctions. Most species that become extinct are never scientifically documented. Some scientists estimate that up to half of presently existing plant and animal species may become extinct by 2100.