CRJU 2001: Study terms and questions for Exam #1
... 8. Compare and contrast the two sets of Ten Commandments contained in Exodus. Be sure to include an explanation of the differences and the reasons for them. 9. Discuss the position of women in early Western culture. Back it up with examples of customs and laws in specific societies (including the Bi ...
... 8. Compare and contrast the two sets of Ten Commandments contained in Exodus. Be sure to include an explanation of the differences and the reasons for them. 9. Discuss the position of women in early Western culture. Back it up with examples of customs and laws in specific societies (including the Bi ...
Early Civilizations Study Guide Ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, India
... 2. Describe how warfare and trade influenced the ancient Middle East. (Civics 1.e) ...
... 2. Describe how warfare and trade influenced the ancient Middle East. (Civics 1.e) ...
fertile crescent notes
... has a crescent-shaped area that is known as The Fertile Crescent. Identifiable civilization records date back to 5000 B.C.E in this area. The society was built around the cooperation necessary to control floodwaters and irrigate fields. With 2 major rivers, Tigris and Euphrates flowing from the Turk ...
... has a crescent-shaped area that is known as The Fertile Crescent. Identifiable civilization records date back to 5000 B.C.E in this area. The society was built around the cooperation necessary to control floodwaters and irrigate fields. With 2 major rivers, Tigris and Euphrates flowing from the Turk ...
No Slide Title
... to read and write. Their school is at the temple. When they mastered this skill, they are given titles as scribes. Scribes had the jobs of recording trades and working at the palace. ...
... to read and write. Their school is at the temple. When they mastered this skill, they are given titles as scribes. Scribes had the jobs of recording trades and working at the palace. ...
Study Guide Answers - Mayfield City Schools
... _class system_______-system in which a society is divided into several social groups, usually by wealth _cuneiform_________-Sumerian’s first system of writing, used wedge-shape symbols on clay tablets _city-state__________-a central city and its surrounding land, all follow same rules _specializatio ...
... _class system_______-system in which a society is divided into several social groups, usually by wealth _cuneiform_________-Sumerian’s first system of writing, used wedge-shape symbols on clay tablets _city-state__________-a central city and its surrounding land, all follow same rules _specializatio ...
Chap 1
... divided into two areas: Upper Egypt, along the southern part of the Nile as far south as the First Cataract, and Lower Egypt, the northern delta area. The climate was good for agriculture, but with little or no rainfall, farmers had to depend on the river for irrigation. ...
... divided into two areas: Upper Egypt, along the southern part of the Nile as far south as the First Cataract, and Lower Egypt, the northern delta area. The climate was good for agriculture, but with little or no rainfall, farmers had to depend on the river for irrigation. ...
I. Mesopotamia A. Settled Agriculture in an Unstable Landscape 1
... something like a citadel that may have been a center of authority, structures that may have been storehouses for grain, and barracks that may have been for artisans. 3. Both urban centers may have controlled the surrounding farmland. Harappa was located on the frontier between agricultural land and ...
... something like a citadel that may have been a center of authority, structures that may have been storehouses for grain, and barracks that may have been for artisans. 3. Both urban centers may have controlled the surrounding farmland. Harappa was located on the frontier between agricultural land and ...
Timeline of Mesopotamian Civilizations: Sumerians: 3500‐1800
... peoples, the Akkadians, who migrated up from the Arabian peninsula. The Akkadians were a Semitic people, that is, they spoke a Semitic language related to languages such as Hebrew and Arabic. When the two peoples clashed, the Sumerians gradually lost control over the city‐ states they had so brilian ...
... peoples, the Akkadians, who migrated up from the Arabian peninsula. The Akkadians were a Semitic people, that is, they spoke a Semitic language related to languages such as Hebrew and Arabic. When the two peoples clashed, the Sumerians gradually lost control over the city‐ states they had so brilian ...
The Akkadians and The Babylonians
... Sargon I • Eventually, Sargon I united the city-states of Mesopotamia. • Sargon I ruled a kingdom north of Sumer called Akkad. • The Akkadians ruled the city-states of Mesopotamia. E. Napp ...
... Sargon I • Eventually, Sargon I united the city-states of Mesopotamia. • Sargon I ruled a kingdom north of Sumer called Akkad. • The Akkadians ruled the city-states of Mesopotamia. E. Napp ...
Cities and Civilizations
... “Between Two Rivers” (Tigris River and Euphrates River) The southern part of Mesopotamia was called Babylonia, originally Sumer. Which country is Mesopotamia today? ...
... “Between Two Rivers” (Tigris River and Euphrates River) The southern part of Mesopotamia was called Babylonia, originally Sumer. Which country is Mesopotamia today? ...
Why did civilizations rise and fall in Mesopotamia? PPT
... The Sumerians developed a civilization in Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia is a Greek word. It means “between the rivers.” Mesopotamia was the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in present-day Iraq. ...
... The Sumerians developed a civilization in Mesopotamia. Mesopotamia is a Greek word. It means “between the rivers.” Mesopotamia was the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in present-day Iraq. ...
Final Global review #1.ppt
... punishments Punishments also based on class Where is Babylon located? ...
... punishments Punishments also based on class Where is Babylon located? ...
Mesopotamia Review and Summary
... 3. While it offered protection to all people, social status did have an impact of the type of punishment someone received 4. U.S. Bill of Rights vs. Hammurabi's Code * Both want to ensure safety of it citizens * Both have discipline for actions * The way they deal with crimes and punishments are ver ...
... 3. While it offered protection to all people, social status did have an impact of the type of punishment someone received 4. U.S. Bill of Rights vs. Hammurabi's Code * Both want to ensure safety of it citizens * Both have discipline for actions * The way they deal with crimes and punishments are ver ...
Ancient Mesopotamia by Stephen Fienstein
... Chapter Four: The Babylonian Empire For more than two hundred years, Mesopotamia remained in constant upheaval. City-states under control of Amorite kings were often in conflict with each other, just as in earlier times these same city-states under Sumerian rule had waged war against one another. Ba ...
... Chapter Four: The Babylonian Empire For more than two hundred years, Mesopotamia remained in constant upheaval. City-states under control of Amorite kings were often in conflict with each other, just as in earlier times these same city-states under Sumerian rule had waged war against one another. Ba ...
Floods in the Fertile Crescent
... Although the floods were important for the soil, they could also be quite devastating. In the spring, when melted snow from nearby mountains flowed into the Tigris and Euphrates and the rivers overflowed their banks, the crops that were ready for harvest could be destroyed. Often, the floods ruined ...
... Although the floods were important for the soil, they could also be quite devastating. In the spring, when melted snow from nearby mountains flowed into the Tigris and Euphrates and the rivers overflowed their banks, the crops that were ready for harvest could be destroyed. Often, the floods ruined ...
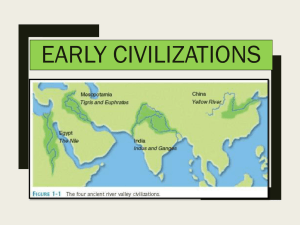
The Four River Valley Civilizations
... – Social stratification became more pronounced– kings, noble class, priests controlled most land ...
... – Social stratification became more pronounced– kings, noble class, priests controlled most land ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.