File - Mr Wold Social Studies
... ARTS: pottery, art as a reflection of culture; art typically seen in religion ...
... ARTS: pottery, art as a reflection of culture; art typically seen in religion ...
Ancient Knowledge
... The Nature of Ancient Knowledge In Babylon, for example, the science of astronomy was thus deeply intertwined with the religious system of astrology. But all sciences began this way: they were at first deeply intertwined with magic, religion and ...
... The Nature of Ancient Knowledge In Babylon, for example, the science of astronomy was thus deeply intertwined with the religious system of astrology. But all sciences began this way: they were at first deeply intertwined with magic, religion and ...
6.2.1_Rivers_Ancient Cities - California History
... a code of laws/decrees to reestablish justice in the land. His compilation of decrees was the largest ever found by archaeologists since it was on a stone monument. However, other clay tablets of laws have been found that date back several centuries before Hammurabi. Artifact: Hammurabi’s Code This ...
... a code of laws/decrees to reestablish justice in the land. His compilation of decrees was the largest ever found by archaeologists since it was on a stone monument. However, other clay tablets of laws have been found that date back several centuries before Hammurabi. Artifact: Hammurabi’s Code This ...
Hammurabi/s Code
... The diorite stele is a large stone shaped like a giant finger. It is about seven feet tall and two feet wide. It contains around 4000 lines of text describing 282 different laws. At the top, or "fingertip", of the stele is a carved picture of King Hammurabi being given the laws from the Babylonian s ...
... The diorite stele is a large stone shaped like a giant finger. It is about seven feet tall and two feet wide. It contains around 4000 lines of text describing 282 different laws. At the top, or "fingertip", of the stele is a carved picture of King Hammurabi being given the laws from the Babylonian s ...
The Ancient Near East
... of cities in Mesopotamia, and their continuing evolution through the Bronze Age. The Ashmolean has an impressive collection of cuneiform tablets and prisms of clay, one of the most representative in Europe. Tablets from Jemdet Nasr and Kish in Iraq are particularly important. Tablets from Mesopotami ...
... of cities in Mesopotamia, and their continuing evolution through the Bronze Age. The Ashmolean has an impressive collection of cuneiform tablets and prisms of clay, one of the most representative in Europe. Tablets from Jemdet Nasr and Kish in Iraq are particularly important. Tablets from Mesopotami ...
River Valley Civs & Neolithic Cities
... Commonalities Amongst the Early Civilizations We Discuss • Use of metal (e.g., bronze, iron) tools and weapons • Increasing agricultural surplus: Better tools, plows, irrigation • Increasing trade along rivers and by sea (Phoenicians) • Social organization was often rigid with caste system of socie ...
... Commonalities Amongst the Early Civilizations We Discuss • Use of metal (e.g., bronze, iron) tools and weapons • Increasing agricultural surplus: Better tools, plows, irrigation • Increasing trade along rivers and by sea (Phoenicians) • Social organization was often rigid with caste system of socie ...
Mesopotamia
... 1. Hammurabi ruled ___________________ in the years around _________________ B.C. 2. Hammurabi had laws carved into a huge black stone called a ______________________. 3. The Code of Hammuabi is the first known complete _____________________________. 4. One goal of the Code of Hammurabi was t ...
... 1. Hammurabi ruled ___________________ in the years around _________________ B.C. 2. Hammurabi had laws carved into a huge black stone called a ______________________. 3. The Code of Hammuabi is the first known complete _____________________________. 4. One goal of the Code of Hammurabi was t ...
File
... I'm not referencing Mark Twain, Me from the Past. I'm referencing Benjamin Franklin, who was probably himself referencing the unfortunately named playwright Christopher Bullock. Listen, you may be smart, kid, but I've been smart longer. By the way, today's illustration points out that "an eye for an ...
... I'm not referencing Mark Twain, Me from the Past. I'm referencing Benjamin Franklin, who was probably himself referencing the unfortunately named playwright Christopher Bullock. Listen, you may be smart, kid, but I've been smart longer. By the way, today's illustration points out that "an eye for an ...
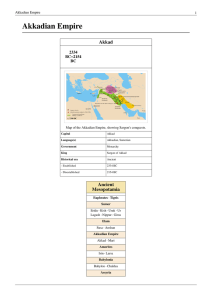
Akkad was the capital of the Akkadian Empire, which was
... Before Akkad was identified in Mesopotamian cuneiform texts, the city was only known from a single reference in Genesis 10:10. However, the city of Akkad is mentioned more than 160 times in cuneiform sources ranging in date from the Akkadian period itself (2350–2170 or 2230–2050 BCE, according to r ...
... Before Akkad was identified in Mesopotamian cuneiform texts, the city was only known from a single reference in Genesis 10:10. However, the city of Akkad is mentioned more than 160 times in cuneiform sources ranging in date from the Akkadian period itself (2350–2170 or 2230–2050 BCE, according to r ...
ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS
... ANCIENT CHINA Great Wall Began 2000 B.C. Mandate of Heaven Dynasties Silk astronomy ...
... ANCIENT CHINA Great Wall Began 2000 B.C. Mandate of Heaven Dynasties Silk astronomy ...
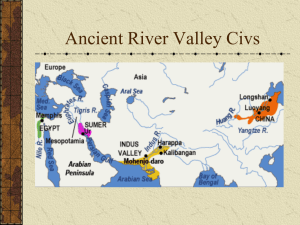
Early River Valley Civilizations0809sep
... » Believed in spirits of family ancestors. » Consulted the gods through the use of oracle bones ...
... » Believed in spirits of family ancestors. » Consulted the gods through the use of oracle bones ...
Egypt & Mesopotamia Notes
... to rule its people. You live in the capital city of Babylon which is located right between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. After decades of bountiful harvests the population of the city has skyrocketed. The people have been hardworking; many have left the farms due to the surplus of crops to start ...
... to rule its people. You live in the capital city of Babylon which is located right between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. After decades of bountiful harvests the population of the city has skyrocketed. The people have been hardworking; many have left the farms due to the surplus of crops to start ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide Questions
... What is the meaning of the Greek word Mesopotamia? To what rivers does the name refer? Explain the structure and organization of Ancient Sumer’s city-states. How did Sumerian city planning reflect the role of the local god in daily life? What is cuneiform? Of what material is the White Temple made? ...
... What is the meaning of the Greek word Mesopotamia? To what rivers does the name refer? Explain the structure and organization of Ancient Sumer’s city-states. How did Sumerian city planning reflect the role of the local god in daily life? What is cuneiform? Of what material is the White Temple made? ...
Paleolithic/Neolithic/River Valley Civilizations Study Guide. Be
... Be identify/ know the importance for each term: Paleolithic – old stone age Neolithic – New stone age Civilization - all components plus writing History – written record Agricultural Revolution – another term for the Neolithic period Fertile Crescent – area of Mesopotamia Mesopotamia – land between ...
... Be identify/ know the importance for each term: Paleolithic – old stone age Neolithic – New stone age Civilization - all components plus writing History – written record Agricultural Revolution – another term for the Neolithic period Fertile Crescent – area of Mesopotamia Mesopotamia – land between ...
Domination and Resilience in Bronze Age Mesopotamia
... survey, which involves the systematic examination and recording of remains that are visible on the surface (e.g., artifacts, architecture, and landscape features; see, e.g., Wilkinson 2000a). Traditional survey is now supplemented by a host of remote-sensing techniques that use innovative technologi ...
... survey, which involves the systematic examination and recording of remains that are visible on the surface (e.g., artifacts, architecture, and landscape features; see, e.g., Wilkinson 2000a). Traditional survey is now supplemented by a host of remote-sensing techniques that use innovative technologi ...
Chapter 12
... practically oriented monumental works: temples, palaces, or mortuary features like pyramids. This kind of monumental construction, today diagnostic of ancient civilizations, was both a cause and effect of the new social dynamic of the world's first civilizations. Large, impressive monuments served a ...
... practically oriented monumental works: temples, palaces, or mortuary features like pyramids. This kind of monumental construction, today diagnostic of ancient civilizations, was both a cause and effect of the new social dynamic of the world's first civilizations. Large, impressive monuments served a ...
Ancient Near East
... With agriculture, a field must be sown, tended, and later harvested all at once. The harvest must be stored. Domestic animals must be maintained as a herd and be held in a contained area. When all goes well, there will be a surplus of food that is not immediately distributed. It is valuable, and mus ...
... With agriculture, a field must be sown, tended, and later harvested all at once. The harvest must be stored. Domestic animals must be maintained as a herd and be held in a contained area. When all goes well, there will be a surplus of food that is not immediately distributed. It is valuable, and mus ...
ancient writings
... Invention of writing • The earliest written documents are records of the first advanced, centralized civilizations, those that emerged in the area we know as the Middle East • These documents contain commercial, administrative, political, and legal information ...
... Invention of writing • The earliest written documents are records of the first advanced, centralized civilizations, those that emerged in the area we know as the Middle East • These documents contain commercial, administrative, political, and legal information ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.