River Valley civilizations (3500 BC to 500 BC)
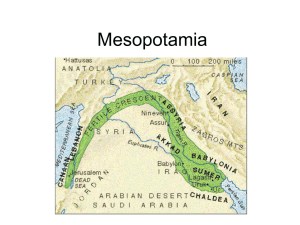
... • Located in Southwest Asia (Middle East) • Nicknames: “Cradle of Civilization” “Fertile Crescent” and “Land between the Rivers”. • Located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers; flows into the Persian Gulf • Modern day Iraq • Open Plains left Mesopotamia open to invasion. ...
... • Located in Southwest Asia (Middle East) • Nicknames: “Cradle of Civilization” “Fertile Crescent” and “Land between the Rivers”. • Located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers; flows into the Persian Gulf • Modern day Iraq • Open Plains left Mesopotamia open to invasion. ...
Lecture outline
... Ancient Mesopotamia: inventors of the decimal, sexagesimal, systems, mathematics, law, the first city, record keeping, the first written language (?), the ziggurat, 1. From hunter-gatherers to farmers: the geography of upper Mesopotamia (8,000-6,000 BC) 2. The formation of an elaborate social struct ...
... Ancient Mesopotamia: inventors of the decimal, sexagesimal, systems, mathematics, law, the first city, record keeping, the first written language (?), the ziggurat, 1. From hunter-gatherers to farmers: the geography of upper Mesopotamia (8,000-6,000 BC) 2. The formation of an elaborate social struct ...
mesopotamia study guide
... 4. What is the difference between canals and rivers? (Hint: How are they made & by whom?) ...
... 4. What is the difference between canals and rivers? (Hint: How are they made & by whom?) ...
Mesopotamia Study Guide
... Part I – Study all vocabulary words and skills sheets. Part II – Fill in the blank 1. Farmers in Sumer used __________ to keep flooding rivers in their banks. 2. A complex _____________ ________ _________ developed in Sumer due to a food surplus. 3. ____________________ compiled a collection of laws ...
... Part I – Study all vocabulary words and skills sheets. Part II – Fill in the blank 1. Farmers in Sumer used __________ to keep flooding rivers in their banks. 2. A complex _____________ ________ _________ developed in Sumer due to a food surplus. 3. ____________________ compiled a collection of laws ...
Early Humans Vocabulary - Hewlett
... Mesopotamia – “land between the rivers” (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) Flat plain which lay in the eastern part of the Fertile Crescent, a curving strip of land that extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf in what is now known as southern Iraq Irrigation - a system of dams, channels, w ...
... Mesopotamia – “land between the rivers” (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) Flat plain which lay in the eastern part of the Fertile Crescent, a curving strip of land that extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf in what is now known as southern Iraq Irrigation - a system of dams, channels, w ...
Ancient Near Eastern Art
... Complete the following sentences: In 1595 B.C.E the ______________________________conquered Babylon. The Hittites established an empire at ___________________________in Anatolia circa 1600 B.C.E. ...
... Complete the following sentences: In 1595 B.C.E the ______________________________conquered Babylon. The Hittites established an empire at ___________________________in Anatolia circa 1600 B.C.E. ...
Agricultural Revolution Mesopotamia Review
... • Mesopotamia is the land between two rivers • The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers gave life to Mesopotamia • When the rivers flooded, they dug canals to irrigate the fields ...
... • Mesopotamia is the land between two rivers • The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers gave life to Mesopotamia • When the rivers flooded, they dug canals to irrigate the fields ...
Mesopotamia
... SSWH1a: Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies: include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code. ...
... SSWH1a: Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies: include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code. ...
Mesopotamia
... SSWH1a: Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies: include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code. ...
... SSWH1a: Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies: include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code. ...
The Cradle of Civilization
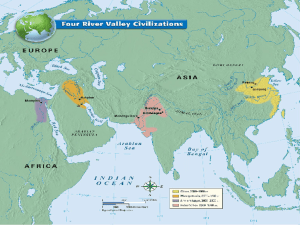
... 1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? Tigris & Euphrates Rivers 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? ...
... 1. What two rivers run through the Fertile Crescent? Tigris & Euphrates Rivers 2. Which two river valley civilizations are shown on this map? ...
First Cities of Sumer
... mesopotAmiA lies between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers—an area that now covers much of modern Iraq. It was the ancient Greeks who named this region Mesopotamia, meaning “the land between the rivers.” In about 5000 bce, the farming people of Sumer founded small settlements that grew into the wo ...
... mesopotAmiA lies between the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers—an area that now covers much of modern Iraq. It was the ancient Greeks who named this region Mesopotamia, meaning “the land between the rivers.” In about 5000 bce, the farming people of Sumer founded small settlements that grew into the wo ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide
... Which group of people grew more powerful because of trade? Pheonicians What was Mesopotamian society based on, even with the growth of cities? farming What technologies did the Hittites and Assyrians use in battle that made them very powerful? iron weapons and chariots Which group of people in Meso ...
... Which group of people grew more powerful because of trade? Pheonicians What was Mesopotamian society based on, even with the growth of cities? farming What technologies did the Hittites and Assyrians use in battle that made them very powerful? iron weapons and chariots Which group of people in Meso ...
A river in southwestern Asia that flows through the eastern part of the
... 1 Fertile Crescent – A fertile region in southwestern Asia that includes the region of Mesopotamia. 2. Tigris River ...
... 1 Fertile Crescent – A fertile region in southwestern Asia that includes the region of Mesopotamia. 2. Tigris River ...
Mesopotamia
... ninth millennium B.C. 4th millennium- realized that drawing tokens was easier than making tokens Result was the development of cuneiform: ...
... ninth millennium B.C. 4th millennium- realized that drawing tokens was easier than making tokens Result was the development of cuneiform: ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.