Electromagnetic Induction
... A loop of area 2.00 cm2 is in a constant magnetic field of 0.100 T. What is the magnetic flux through the loop in each of the following situations: When the loop is perpendicular to the field When the loop is parallel to the field When the normal to the loop and the field have an angle of 60 ...
... A loop of area 2.00 cm2 is in a constant magnetic field of 0.100 T. What is the magnetic flux through the loop in each of the following situations: When the loop is perpendicular to the field When the loop is parallel to the field When the normal to the loop and the field have an angle of 60 ...
17 A Low-Frequency Current Comparator For Precision Resistance
... with a SQUID as the magnetic field null-detector can be considered to be ultimately precise, i.e., the ratio error can be kept negligibly small by appropriate design. However, operation of a CCC is rather complicated and requires low temperature. Different from that, the DCC is a roomtemperature dev ...
... with a SQUID as the magnetic field null-detector can be considered to be ultimately precise, i.e., the ratio error can be kept negligibly small by appropriate design. However, operation of a CCC is rather complicated and requires low temperature. Different from that, the DCC is a roomtemperature dev ...
2010 EMC Modeling of an Industrial Variable Speed Drive Wih an Adapted PEEC Method
... approach, the bars are not meshed in their length, but only in the cross section: 15 elements along the z axis and 4 along the x axis whereas in the FEM approach, air and bars are meshed with a total number of mesh elements around 600 000. So the gap between degrees of freedom number of the two meth ...
... approach, the bars are not meshed in their length, but only in the cross section: 15 elements along the z axis and 4 along the x axis whereas in the FEM approach, air and bars are meshed with a total number of mesh elements around 600 000. So the gap between degrees of freedom number of the two meth ...
Fill in the correct symbol and units for the following: Symbol Units
... c. Three resistors with resistance values of 2 , 4 , and 6 are placed in parallel. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____ resistor. 13. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. Whic ...
... c. Three resistors with resistance values of 2 , 4 , and 6 are placed in parallel. These would provide a resistance that is equivalent to one _____ resistor. 13. Three identical light bulbs are connected to a D-cell as shown below. P, Q, X, Y and Z represent locations along the circuit. Whic ...
induced current
... The purpose of the secondary circuit is to detect current that might be produced by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the ammeter reads a current and then returns to zero When the switch is opened, the ammeter reads a current in the opposite direction and then returns to zero When there ...
... The purpose of the secondary circuit is to detect current that might be produced by the magnetic field When the switch is closed, the ammeter reads a current and then returns to zero When the switch is opened, the ammeter reads a current in the opposite direction and then returns to zero When there ...
Investigating Electrical Circuits with the PhET Animation
... This animation allows you to drag objects onto the working area and move them around. Place objects close to each other to connect them. Control-click on a connection to see the options for that connection, including disconnecting the objects. Clicking on an object and using the delete key on your k ...
... This animation allows you to drag objects onto the working area and move them around. Place objects close to each other to connect them. Control-click on a connection to see the options for that connection, including disconnecting the objects. Clicking on an object and using the delete key on your k ...
2 Principles of dc machines
... rotation but not both. The voltage induced would be very low but the currents of very large amplitudes can be supplied by such machines. Such sources are used in some applications like pulse-current and MHD generators, liquid metal pumps or plasma rockets. The steady field can also be produced using ...
... rotation but not both. The voltage induced would be very low but the currents of very large amplitudes can be supplied by such machines. Such sources are used in some applications like pulse-current and MHD generators, liquid metal pumps or plasma rockets. The steady field can also be produced using ...
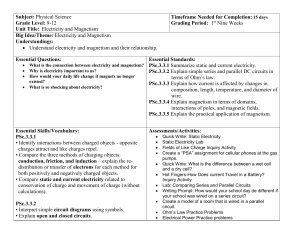
Subject: Physical Science - Currituck County Schools
... • Compare series and parallel circuits. Conceptually explore the flow of electricity in series and parallel circuits. • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and resistance. PSc.3.3.3 • Explain how the wire in a circuit can affect the current ...
... • Compare series and parallel circuits. Conceptually explore the flow of electricity in series and parallel circuits. • Explain how the flow of electricity through series and parallel circuits is affected by voltage and resistance. PSc.3.3.3 • Explain how the wire in a circuit can affect the current ...
Copper Cabling
... • Conductor diameter (size) is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), or just Gauge (sometimes spelled Gage) • Conductor size reduces with an increase in the gauge number. ▫ a 24 AWG conductor is much smaller than a 12 AWG conductor. • Typical sizes ▫ Data communications: 20 to 28 AWG ▫ Electrical 1 ...
... • Conductor diameter (size) is measured in American Wire Gauge (AWG), or just Gauge (sometimes spelled Gage) • Conductor size reduces with an increase in the gauge number. ▫ a 24 AWG conductor is much smaller than a 12 AWG conductor. • Typical sizes ▫ Data communications: 20 to 28 AWG ▫ Electrical 1 ...
EM worksheet
... nickel, cobalt and steel. However, electromagnets are temporary where as bar magnets are considered permanent. Since electricity creates an electromagnet, it can be turned off at the flip of a switch! This makes electromagnets valuable for many everyday devices such as small motors, speakers and jun ...
... nickel, cobalt and steel. However, electromagnets are temporary where as bar magnets are considered permanent. Since electricity creates an electromagnet, it can be turned off at the flip of a switch! This makes electromagnets valuable for many everyday devices such as small motors, speakers and jun ...
Magnetic field of a bar magnet
... Lenz’s law and the law of conservation of energy Lenz’s law is a direct example of the law of conservation of energy. Energy is used when a current flows round a circuit, so energy must be used to induce this current in the first place. As it can be seen above, energy was being used to move the magn ...
... Lenz’s law and the law of conservation of energy Lenz’s law is a direct example of the law of conservation of energy. Energy is used when a current flows round a circuit, so energy must be used to induce this current in the first place. As it can be seen above, energy was being used to move the magn ...
Sample Paper Two partitioned (1)
... a) for a reliable and cost effective design b) because the customer must be provided with the information c) in order that the correct supply rating is used d) as it is an REC requirement 8) When assessing the general characteristics of a circuit that needs a "continuity of service" one of the chara ...
... a) for a reliable and cost effective design b) because the customer must be provided with the information c) in order that the correct supply rating is used d) as it is an REC requirement 8) When assessing the general characteristics of a circuit that needs a "continuity of service" one of the chara ...
fn1_unit_4_topics_mram
... Giant Magneto Resistance Effect (GMR) • The GMR effect is observed when current is passed through a film stack consisting of two magnetic layers separated by a conductive layer. • A small resistance is observed when the magnetic layers are aligned, with the north and south poles of the magnetic lay ...
... Giant Magneto Resistance Effect (GMR) • The GMR effect is observed when current is passed through a film stack consisting of two magnetic layers separated by a conductive layer. • A small resistance is observed when the magnetic layers are aligned, with the north and south poles of the magnetic lay ...
Document
... The switch in the circuit shown in the figure below is closed and the lightbulb glows steadily. The inductor is a simple air-core solenoid. An iron rod is inserted into the interior of the solenoid, which increases the magnitude of the magnetic field in the solenoid. As the rod is inserted into the ...
... The switch in the circuit shown in the figure below is closed and the lightbulb glows steadily. The inductor is a simple air-core solenoid. An iron rod is inserted into the interior of the solenoid, which increases the magnitude of the magnetic field in the solenoid. As the rod is inserted into the ...
Skin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor, and decreases with greater depths in the conductor. The electric current flows mainly at the ""skin"" of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The skin effect causes the effective resistance of the conductor to increase at higher frequencies where the skin depth is smaller, thus reducing the effective cross-section of the conductor. The skin effect is due to opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. At 60 Hz in copper, the skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies the skin depth becomes much smaller. Increased AC resistance due to the skin effect can be mitigated by using specially woven litz wire. Because the interior of a large conductor carries so little of the current, tubular conductors such as pipe can be used to save weight and cost.