Theories In Electronics Vocabulary Teacher`s Guide
... where r is the separation distance and ke is a proportionality constant. A positive force implies it is repulsive, while a negative force implies it is attractive. Horsepower – The equivalent of work-rate of 550 ft-lb per second. One horsepower is also equal to 746 watts. Efficiency – The ratio of p ...
... where r is the separation distance and ke is a proportionality constant. A positive force implies it is repulsive, while a negative force implies it is attractive. Horsepower – The equivalent of work-rate of 550 ft-lb per second. One horsepower is also equal to 746 watts. Efficiency – The ratio of p ...
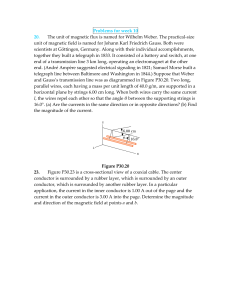
Problems for week 10
... together they built a telegraph in 1833. It consisted of a battery and switch, at one end of a transmission line 3 km long, operating an electromagnet at the other end. (André Ampère suggested electrical signaling in 1821; Samuel Morse built a telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington in 1844. ...
... together they built a telegraph in 1833. It consisted of a battery and switch, at one end of a transmission line 3 km long, operating an electromagnet at the other end. (André Ampère suggested electrical signaling in 1821; Samuel Morse built a telegraph line between Baltimore and Washington in 1844. ...
Chap 20
... 33. What is the inductance of a coil that has an emf of 0.82 V induced in it while the current through it is changing at 2.0 A/s? A. 3.3 H B. 33 mH C. 1.6 H D. 41 mH E. 0.41 H 35. If the magnetic energy stored by a 0.50 H inductor is 3.6 J, what is the current through it? A. 0.13 A B. 0.90 A C. 1.8 ...
... 33. What is the inductance of a coil that has an emf of 0.82 V induced in it while the current through it is changing at 2.0 A/s? A. 3.3 H B. 33 mH C. 1.6 H D. 41 mH E. 0.41 H 35. If the magnetic energy stored by a 0.50 H inductor is 3.6 J, what is the current through it? A. 0.13 A B. 0.90 A C. 1.8 ...
Physics 2102 Spring 2002 Lecture 8
... a current i. The loop is placed in a magnetic field so that the normal nˆ to the loop forms an angle with B. The magnitude of the magnetic force on sides 1 and 3 is F1 F3 iaB sin 90 iaB. The magnetic force on sides 2 and 4 is F2 F4 ibB sin(90 - ) ibB cos . These forces cancel in p ...
... a current i. The loop is placed in a magnetic field so that the normal nˆ to the loop forms an angle with B. The magnitude of the magnetic force on sides 1 and 3 is F1 F3 iaB sin 90 iaB. The magnetic force on sides 2 and 4 is F2 F4 ibB sin(90 - ) ibB cos . These forces cancel in p ...
Electricity notes - Lesmahagow High School
... Electric current WILL pass through a conductor and will NOT pass though an insulator. ...
... Electric current WILL pass through a conductor and will NOT pass though an insulator. ...
Electromagnetic surveying
... • Gives apparent resistivity of the ground and phase shift by measuring H and E • Various local radio waves can be used to chose a depth of investigation (frequency can be chosen) ...
... • Gives apparent resistivity of the ground and phase shift by measuring H and E • Various local radio waves can be used to chose a depth of investigation (frequency can be chosen) ...
to investigate the induced EFM and current in a moving wire
... Put on the table strong magnet and digital multimeter. Connect the wire to the multimeter to measure the voltage. Switch on the multimeter. Move the wire fast across a magnetic filed. What can you observe? Explanation: When a wire is moved across a magnetic field, a small EMF (voltage) in generated ...
... Put on the table strong magnet and digital multimeter. Connect the wire to the multimeter to measure the voltage. Switch on the multimeter. Move the wire fast across a magnetic filed. What can you observe? Explanation: When a wire is moved across a magnetic field, a small EMF (voltage) in generated ...
intro electromagnetism
... Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields are all going in the same direction These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...
... Groups of atoms join so that their magnetic fields are all going in the same direction These areas of atoms are called “domains” ...
Right Hand Rule Study Sheet
... A solenoid creates a magnetic field down its center. If a piece of iron is slipped into the solenoid it becomes a stronger electromagnet. This Right Hand Rule can be used to determine the polarity of an electromagnet. Right Hand Rule #3 A current-carrying wire experiences forces when placed in a mag ...
... A solenoid creates a magnetic field down its center. If a piece of iron is slipped into the solenoid it becomes a stronger electromagnet. This Right Hand Rule can be used to determine the polarity of an electromagnet. Right Hand Rule #3 A current-carrying wire experiences forces when placed in a mag ...
Producing Electric Current - District 273 Technology Services
... Contrast: Batteries have DC. Generators have AC. ...
... Contrast: Batteries have DC. Generators have AC. ...
Mechanical Design of Transmission Lines
... • Tower of smaller height can be used • A reduction in the number of supports also include reduction in insulators and the risk of lines outage due to flash over or faults is reduced. • losses are reduced due to larger diameter of conductor. • High current carrying capacity. ...
... • Tower of smaller height can be used • A reduction in the number of supports also include reduction in insulators and the risk of lines outage due to flash over or faults is reduced. • losses are reduced due to larger diameter of conductor. • High current carrying capacity. ...
ELECTROMAGNETISM
... At this stage, you understand roughly as much about the classification of interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially ...
... At this stage, you understand roughly as much about the classification of interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially ...
Skin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor, and decreases with greater depths in the conductor. The electric current flows mainly at the ""skin"" of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The skin effect causes the effective resistance of the conductor to increase at higher frequencies where the skin depth is smaller, thus reducing the effective cross-section of the conductor. The skin effect is due to opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. At 60 Hz in copper, the skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies the skin depth becomes much smaller. Increased AC resistance due to the skin effect can be mitigated by using specially woven litz wire. Because the interior of a large conductor carries so little of the current, tubular conductors such as pipe can be used to save weight and cost.