Coaxial Cable Protection
... The right arrow indicates area when the center conductor elevates referenced to the decreasing potential on the shield. Current can flow from coax cable center conductor through unprotected equipment inputs back to the shield. This phenomenon is common to unbalanced cable (coax cable). Coaxial cable ...
... The right arrow indicates area when the center conductor elevates referenced to the decreasing potential on the shield. Current can flow from coax cable center conductor through unprotected equipment inputs back to the shield. This phenomenon is common to unbalanced cable (coax cable). Coaxial cable ...
CHAPTER 18 - QUESTIONS 1-3
... field. A current carrying wire causes a magnet to move. 11. Compare solenoids and electromagnets. Solenoids: a coil of wire with an electric current running through it. Electromagnet: a magnet that has an electric current attached that can be switched on and off. A solenoid is part of an electromagn ...
... field. A current carrying wire causes a magnet to move. 11. Compare solenoids and electromagnets. Solenoids: a coil of wire with an electric current running through it. Electromagnet: a magnet that has an electric current attached that can be switched on and off. A solenoid is part of an electromagn ...
hazard of medical instrument
... Touching H & N simultaneously with two limbs can direct currents through vital organs of circulation & respiration Because N are internally grounded, touching H & G can produced macroshock Example : Inexpensive AC / DC radio ...
... Touching H & N simultaneously with two limbs can direct currents through vital organs of circulation & respiration Because N are internally grounded, touching H & G can produced macroshock Example : Inexpensive AC / DC radio ...
Network Hardware
... Method for sending device to indicate that it has finished sending a message. ...
... Method for sending device to indicate that it has finished sending a message. ...
Gary`s Physics Problem In college physics we learned that the
... significantly higher voltage when the coil is located near either the hot or neutral leads than when furthest away from both. But in this case I saw only a very small voltage (pretty much zero due to the phase cancellation) regardless of where I positioned the coil around the toroid. So what gives? ...
... significantly higher voltage when the coil is located near either the hot or neutral leads than when furthest away from both. But in this case I saw only a very small voltage (pretty much zero due to the phase cancellation) regardless of where I positioned the coil around the toroid. So what gives? ...
Magnetism
... What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that go undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 x 103 V/m and 3.5 x 10-3 T, respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off? me = 9.1 x 10-31kg qe = 1.6 x 10-19 ...
... What is the velocity of a beam of electrons that go undeflected when passing through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields of magnitude 8.8 x 103 V/m and 3.5 x 10-3 T, respectively? What is the radius of the electron orbit if the electric field is turned off? me = 9.1 x 10-31kg qe = 1.6 x 10-19 ...
transformer - Madison County Schools
... through wires at high voltages. Your home, though, uses electrical energy at low voltages. Transformers are used to change the voltage of an electric current. ...
... through wires at high voltages. Your home, though, uses electrical energy at low voltages. Transformers are used to change the voltage of an electric current. ...
File
... Lights for this experiment Battery pack - the pack can lack the aligator clips. If you donot have them, wrap the foil around the bare wire. you can find the parts to make this at Radio Shack - You moight have to let them know in advance to have enought battery packs to do this with a class. Do not u ...
... Lights for this experiment Battery pack - the pack can lack the aligator clips. If you donot have them, wrap the foil around the bare wire. you can find the parts to make this at Radio Shack - You moight have to let them know in advance to have enought battery packs to do this with a class. Do not u ...
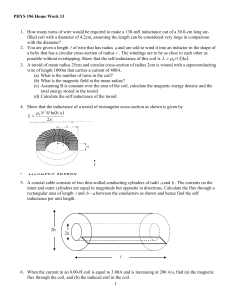
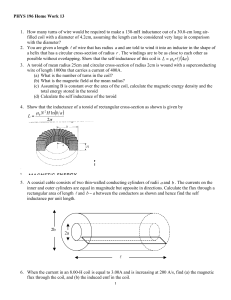
PHYS 196 Class Problem 1
... 9. A coil that has self-inductance of 2.00-H and a resistance of 12.0-Ω is connected to an ideal 24.0-V battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0c ...
... 9. A coil that has self-inductance of 2.00-H and a resistance of 12.0-Ω is connected to an ideal 24.0-V battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0c ...
HW13
... 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0cm2 and a length equal to 30 cm. The solenoid carries a current of 4.0A. (a) Calculate the magnetic energy stored in the solenoid using U = LI 2 2 where L = µ 0 n 2 A . (b) Divide your answer in (a) by the volume of the region inside th ...
... 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0cm2 and a length equal to 30 cm. The solenoid carries a current of 4.0A. (a) Calculate the magnetic energy stored in the solenoid using U = LI 2 2 where L = µ 0 n 2 A . (b) Divide your answer in (a) by the volume of the region inside th ...
Skin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor, and decreases with greater depths in the conductor. The electric current flows mainly at the ""skin"" of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The skin effect causes the effective resistance of the conductor to increase at higher frequencies where the skin depth is smaller, thus reducing the effective cross-section of the conductor. The skin effect is due to opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. At 60 Hz in copper, the skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies the skin depth becomes much smaller. Increased AC resistance due to the skin effect can be mitigated by using specially woven litz wire. Because the interior of a large conductor carries so little of the current, tubular conductors such as pipe can be used to save weight and cost.