Student Handout #2 Extract - AS 440-221, Safe Laboratory
... passing through the skin could be calculated as 120 divided by 200,000 = 0.001 ampere (1 milliampere), which would not be particularly harmful. If, however, the resistance of the skin were reduced to 1,000 ohms because of perspiration, and if the person were standing on a wet or damp ground, the cur ...
... passing through the skin could be calculated as 120 divided by 200,000 = 0.001 ampere (1 milliampere), which would not be particularly harmful. If, however, the resistance of the skin were reduced to 1,000 ohms because of perspiration, and if the person were standing on a wet or damp ground, the cur ...
Electromagnetic Induction Study Guide
... 1. Pushing a door open shoves a magnet attached to the door toward a solenoid of 20 coils with a cross-sectional area of .0004 m2 as shown. The magnetic field inside the coils changes from 0.05 T to 0.18 T in 1.9 s. (Assume that the magnetic field is perpendicular to the coils and has the same stren ...
... 1. Pushing a door open shoves a magnet attached to the door toward a solenoid of 20 coils with a cross-sectional area of .0004 m2 as shown. The magnetic field inside the coils changes from 0.05 T to 0.18 T in 1.9 s. (Assume that the magnetic field is perpendicular to the coils and has the same stren ...
Design of Inductors and High Frequency Transformers Calculation
... A high frequency transformers transfer electric power. Its mechanical size depends on the power to be transfered and on the operating frequency. The higher the frequency the smaller the mechanical size. Usually frequencies are from 20 to 100kHz. The material of the core is ferrite. Databooks for app ...
... A high frequency transformers transfer electric power. Its mechanical size depends on the power to be transfered and on the operating frequency. The higher the frequency the smaller the mechanical size. Usually frequencies are from 20 to 100kHz. The material of the core is ferrite. Databooks for app ...
Chapter 30 Inductors and Self Inductance
... Chapter 30 – Inductors and self Inductance Inductance is to Capacitance what current is to a stationary charge. They are both defined relative to the voltage produced. ...
... Chapter 30 – Inductors and self Inductance Inductance is to Capacitance what current is to a stationary charge. They are both defined relative to the voltage produced. ...
346N_No19_Elect_Design2
... Objectives • Review conductor and conduit selection • Learn about protection systems (basic rules) • Learn to design Residential Electrical Systems ...
... Objectives • Review conductor and conduit selection • Learn about protection systems (basic rules) • Learn to design Residential Electrical Systems ...
THE sEcRET INsIDE RENEwAbLE ENERGY - Hi
... Inside every dynamo is a coil of wire and strong magnets. Michael Faraday, in 1831, discovered that if you spin a coil of copper wire between magnets you could get a flow of electricity. The more loops of wire you have, the more electricity is generated. By turning the handle on the dynamo, you turn ...
... Inside every dynamo is a coil of wire and strong magnets. Michael Faraday, in 1831, discovered that if you spin a coil of copper wire between magnets you could get a flow of electricity. The more loops of wire you have, the more electricity is generated. By turning the handle on the dynamo, you turn ...
What is an effective or a root mean square value of an alternating
... An effective value of an alternating current is root mean square of its instantaneous value over one cycle. This is 1/1.4142 of the peak current value for a normal (= sinusoidal) alternating current. An effective value of an alternating voltage is defined in the same manner. It is 1/1.4142 of the pe ...
... An effective value of an alternating current is root mean square of its instantaneous value over one cycle. This is 1/1.4142 of the peak current value for a normal (= sinusoidal) alternating current. An effective value of an alternating voltage is defined in the same manner. It is 1/1.4142 of the pe ...
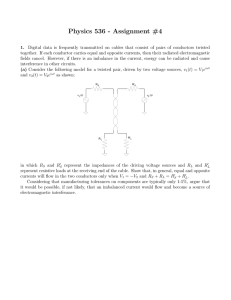
Physics 536 - Assignment #4
... together. If each conductor carries equal and opposite currents, then their radiated electromagnetic fields cancel. However, if there is an imbalance in the current, energy can be radiated and cause interference in other circuits. (a) Consider the following model for a twisted pair, driven by two vo ...
... together. If each conductor carries equal and opposite currents, then their radiated electromagnetic fields cancel. However, if there is an imbalance in the current, energy can be radiated and cause interference in other circuits. (a) Consider the following model for a twisted pair, driven by two vo ...
Motor Effect A magnet exerts a force on current
... The deflecting force that a magnet exerts on a current-carrying wire is the mechanism behind the operation of most electric motors. Curiously (and happily for our sense of symmetry!), the reverse effect is also true: Move a loop of wire across the pole of a magnet, and a current will begin to flow i ...
... The deflecting force that a magnet exerts on a current-carrying wire is the mechanism behind the operation of most electric motors. Curiously (and happily for our sense of symmetry!), the reverse effect is also true: Move a loop of wire across the pole of a magnet, and a current will begin to flow i ...
Sections 2 - Columbia Physics
... (b) Check that you recover the same idealized capacitor result in the L → ∞ limit. ...
... (b) Check that you recover the same idealized capacitor result in the L → ∞ limit. ...
Article 200 Use and Identification of Grounded Neutral Conductors
... (b) posted inside each junction box where both system neutrals are present (c) done using a listed labeling technique (d) all of these ...
... (b) posted inside each junction box where both system neutrals are present (c) done using a listed labeling technique (d) all of these ...
Magnetism
... Electricity and magnetism are related. This is called electromagnetism An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporar ...
... Electricity and magnetism are related. This is called electromagnetism An electric current flowing through a wire gives rise to a magnetic field whose direction depends upon the direction of the current. Coiling a conductor around a piece of soft iron will produce a powerful magnet. This is temporar ...
Physics 100 Name: Electricity Notes, Part IV: Odds, Ends, and Lenz
... 6. In the diagrams on the right, current is flowing through a simple motor coil. Directly above or beneath the motor coil, there is a permanent magnet with labeled polarity. The top segment of the coil is labeled with an X. For each diagram, tell whether that coil segment (the X segment) will rotate ...
... 6. In the diagrams on the right, current is flowing through a simple motor coil. Directly above or beneath the motor coil, there is a permanent magnet with labeled polarity. The top segment of the coil is labeled with an X. For each diagram, tell whether that coil segment (the X segment) will rotate ...
Skin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor, and decreases with greater depths in the conductor. The electric current flows mainly at the ""skin"" of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The skin effect causes the effective resistance of the conductor to increase at higher frequencies where the skin depth is smaller, thus reducing the effective cross-section of the conductor. The skin effect is due to opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. At 60 Hz in copper, the skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies the skin depth becomes much smaller. Increased AC resistance due to the skin effect can be mitigated by using specially woven litz wire. Because the interior of a large conductor carries so little of the current, tubular conductors such as pipe can be used to save weight and cost.