Should You Become an Entrepreneur?
... • As the Price INCREASES, Suppliers/Producers are willing to Provide MORE. ...
... • As the Price INCREASES, Suppliers/Producers are willing to Provide MORE. ...
The Market Mechanism - PowerPoint Presentation
... Demand and Supply How do we end up with a price for a good or service? • it is set by the level of demand and supply in the market • depends on how much of the product consumers want to and are able to buy • and how much firms are willing or able to sell ...
... Demand and Supply How do we end up with a price for a good or service? • it is set by the level of demand and supply in the market • depends on how much of the product consumers want to and are able to buy • and how much firms are willing or able to sell ...
Key - KSU Web Home
... Consider the costs of complying with bureaucratic regulations to economic decision makers in Singapore, South Africa, and Venezuela. According to the results of the “Ease of Doing Business” study, of these three countries, such costs are: B. lowest in Singapore and highest in Venezuela. ...
... Consider the costs of complying with bureaucratic regulations to economic decision makers in Singapore, South Africa, and Venezuela. According to the results of the “Ease of Doing Business” study, of these three countries, such costs are: B. lowest in Singapore and highest in Venezuela. ...
Supply-Demand Assig
... Supply & Demand Charts Phase I: You are going to create a table and chart displaying the prices, supply and demand of TWO separate products at various levels. You may work with 1 partner if you wish to help complete all aspects of this project. Apply the information from the handouts in class to aid ...
... Supply & Demand Charts Phase I: You are going to create a table and chart displaying the prices, supply and demand of TWO separate products at various levels. You may work with 1 partner if you wish to help complete all aspects of this project. Apply the information from the handouts in class to aid ...
PowerPoint
... in supply or demand? • Changes in supply or demand refer to overall changes in the products and services provided and the demand for them – Change in supply may be a decrease in milk supply due to widespread mastitis infections. ...
... in supply or demand? • Changes in supply or demand refer to overall changes in the products and services provided and the demand for them – Change in supply may be a decrease in milk supply due to widespread mastitis infections. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 10. Give the similarities and dissimilarities between the quantity theory of money and Cambridge cash balance theory. 11. Examine Patinkin’s contribution to the analysis of the relationship between money supply, interest rate and price level. 12. Explain the effects of lags in the monetary policy. 1 ...
... 10. Give the similarities and dissimilarities between the quantity theory of money and Cambridge cash balance theory. 11. Examine Patinkin’s contribution to the analysis of the relationship between money supply, interest rate and price level. 12. Explain the effects of lags in the monetary policy. 1 ...
Opportunity cost (기회비용)
... 6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity. (시장의 효율성) ...
... 6. Markets are usually a good way to organize economic activity. (시장의 효율성) ...
Homework C due 8th May51.5 KB
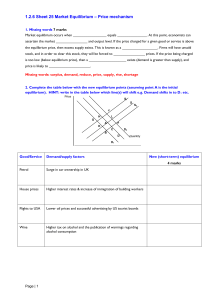
... 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is ...
... 1. Missing words 7 marks Market equilibrium occurs when _________________ equals _______________. At this point, economists can ascertain the market ________________ and output level. If the price charged for a given good or service is above the equilibrium price, then excess supply exists. This is ...
Shifts of the demand curve
... T—consumer tastes I—consumer income R—price of related goods/services ...
... T—consumer tastes I—consumer income R—price of related goods/services ...
Problem Areas in AP Economics Real Interest rate
... Real Interest rate – cost of borrowing the money to buy the capital goods (machinery) If rate of return is greater than the cost of the interest, the investment will be profitable Ex: 10% rate of return is greater than 7% interest = ...
... Real Interest rate – cost of borrowing the money to buy the capital goods (machinery) If rate of return is greater than the cost of the interest, the investment will be profitable Ex: 10% rate of return is greater than 7% interest = ...
Economics PowerPoint
... Labor Force – over 16, willing and able to work Underemployment - Job requires less skills than you have; working part-time instead of full-time ...
... Labor Force – over 16, willing and able to work Underemployment - Job requires less skills than you have; working part-time instead of full-time ...
Globalization
... demand for products bought with currency (goods and financial investments) Strong Dollar: Increased demand US goods (or decreased demand foreign goods) appreciation US exports fall (more expensive for foreigners to purchase US goods), imports rise (cheaper to buy foreign goods) Weak Dollar: Decrea ...
... demand for products bought with currency (goods and financial investments) Strong Dollar: Increased demand US goods (or decreased demand foreign goods) appreciation US exports fall (more expensive for foreigners to purchase US goods), imports rise (cheaper to buy foreign goods) Weak Dollar: Decrea ...
5.01 Objective 5.01 Key Terms
... One price compared to another; the ratio between two prices. A condition resulting from the gap between unlimited wants for goods and services and limited resources. The best time for producers to sell; characterized by large demand, small supply, and high prices. Intangible activities that are perf ...
... One price compared to another; the ratio between two prices. A condition resulting from the gap between unlimited wants for goods and services and limited resources. The best time for producers to sell; characterized by large demand, small supply, and high prices. Intangible activities that are perf ...
Key Terms
... Factors of production that are used in the production of goods and services, including human, natural, capital and ...
... Factors of production that are used in the production of goods and services, including human, natural, capital and ...
Document
... Demand • Demand- the desire and ability of consumers to buy a certain quantity of goods or services at a specified price within a specified period of time. ...
... Demand • Demand- the desire and ability of consumers to buy a certain quantity of goods or services at a specified price within a specified period of time. ...
Types of economies
... The willingness and ability of producers to offer a good or service for sale Law of Supply: Producers will supply (offer) more of a product for sale as its price rises and less as its price drops But what makes the price rise???? ...
... The willingness and ability of producers to offer a good or service for sale Law of Supply: Producers will supply (offer) more of a product for sale as its price rises and less as its price drops But what makes the price rise???? ...
Economic Crises - University of Texas at Austin
... flight further deflation due to link of domestic money level to gold and further reduction in economic activity Such deflation SHOULD result in lower prices and increasingly competitive exports whose growth would spur recovery. So crisis should be corrected via shift from trade deficit to trade su ...
... flight further deflation due to link of domestic money level to gold and further reduction in economic activity Such deflation SHOULD result in lower prices and increasingly competitive exports whose growth would spur recovery. So crisis should be corrected via shift from trade deficit to trade su ...
File
... differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: France, Germany, Great Britain. ...
... differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: France, Germany, Great Britain. ...
Quick_Econ_Overview
... Economic Goals: The goals of a balanced and healthy economy are as follows: economic growth, full employment, economic efficiency, price-level stability, economic freedom (and free will), equitable distribution of income, economic security, and balance of trade (with the rest of the world). The assu ...
... Economic Goals: The goals of a balanced and healthy economy are as follows: economic growth, full employment, economic efficiency, price-level stability, economic freedom (and free will), equitable distribution of income, economic security, and balance of trade (with the rest of the world). The assu ...
Changes in Price due to Change in Supply and Demand
... Changes in Demand Fad- sudden and dramatic increase in demand ...
... Changes in Demand Fad- sudden and dramatic increase in demand ...
Economic Foundations
... Increased government involvement Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: France, Germany, Great Britain. ...
... Increased government involvement Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: France, Germany, Great Britain. ...
CA_3_Market Economy PowerPoint
... Students will be able to answer the three economic questions in regards to a market economy. Student will be able to explain supply and demand. Students will be able to identify the difference between an equilibrium, shortage, and surplus. Students will be able to explain the difference between elas ...
... Students will be able to answer the three economic questions in regards to a market economy. Student will be able to explain supply and demand. Students will be able to identify the difference between an equilibrium, shortage, and surplus. Students will be able to explain the difference between elas ...
SEM_I-301
... Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: ___________________ ...
... Government tries to reduce the differences between the rich and poor. Based on the welfare of people. Examples: ___________________ ...
The Price System (Markets)
... With supply and demand both on graph, we now have a market. Market equilibrium – where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal ©2012, TESCCC ...
... With supply and demand both on graph, we now have a market. Market equilibrium – where quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal ©2012, TESCCC ...