Science Fair Paper Template
... [in this section, explain to me why you thought this was a good project. Explain why or how the information in the results can be used in the real world. Here is where you must convince me that it was not a waste of time to read your paper and that what you had to say was interesting and useful. In ...
... [in this section, explain to me why you thought this was a good project. Explain why or how the information in the results can be used in the real world. Here is where you must convince me that it was not a waste of time to read your paper and that what you had to say was interesting and useful. In ...
Chapter 10 Heat and Heat Technology (PS 7)
... Energy is always transferred from the object with the ____higher______temperature to the object with the ___lower_______ temperature until both objects reach the ___same___ temperature. This will continue until both objects reach the same temperature and is called _____thermal equilibrium___. One o ...
... Energy is always transferred from the object with the ____higher______temperature to the object with the ___lower_______ temperature until both objects reach the ___same___ temperature. This will continue until both objects reach the same temperature and is called _____thermal equilibrium___. One o ...
Selff sustaining greenhouse
... liquid to a colder location. Heat transfer by convection includes not only the movement of air but also the movement of water vapor. • Radiation • Radiation heat transfer occurs between two bodies without direct contact or the need for a medium such as air. Like light, heat radiation follows a strai ...
... liquid to a colder location. Heat transfer by convection includes not only the movement of air but also the movement of water vapor. • Radiation • Radiation heat transfer occurs between two bodies without direct contact or the need for a medium such as air. Like light, heat radiation follows a strai ...
10 PRE-LABORATORY ASSIGNMENT EXPERIMENT 7 1. Is t
... Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes. Thermochemistry has many practical applications. For example, using thermochemistry: (1) mining engineers can calculate how much fuel will be needed to prepare metals from their ores, (2) structural ...
... Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes. Thermochemistry has many practical applications. For example, using thermochemistry: (1) mining engineers can calculate how much fuel will be needed to prepare metals from their ores, (2) structural ...
RESEARCH ARTICLE Survival and arm abscission are linked to
... 1983), with significant implications for predator avoidance (Srygley and Chai, 1990). Some organisms have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to generate regional heterothermy. For example, in large ectotherms such as some reptiles, blood flow to appendages can be modified to control for warming or coo ...
... 1983), with significant implications for predator avoidance (Srygley and Chai, 1990). Some organisms have evolved sophisticated mechanisms to generate regional heterothermy. For example, in large ectotherms such as some reptiles, blood flow to appendages can be modified to control for warming or coo ...
The Laws of Thermodynamics
... of a quantity of mercury or alcohol (glycol) in a thin glass tube. As the temperature varies, the fluid expands and contracts, and its height in the tube changes. A scale is supplied to read off the height of the fluid directly in terms of temperature. The simple thermometers described above have ce ...
... of a quantity of mercury or alcohol (glycol) in a thin glass tube. As the temperature varies, the fluid expands and contracts, and its height in the tube changes. A scale is supplied to read off the height of the fluid directly in terms of temperature. The simple thermometers described above have ce ...
Document
... 2.1 kJ to raise the temperature of the ice to 0 0C. At that stage, if we add another 2.1 kJ, the temperature of the ice remains at 0 0C and nothing seems to have happened. But as we continue to add more energy to the ice block, something is happening to the molecules inside. The kinetic energy we a ...
... 2.1 kJ to raise the temperature of the ice to 0 0C. At that stage, if we add another 2.1 kJ, the temperature of the ice remains at 0 0C and nothing seems to have happened. But as we continue to add more energy to the ice block, something is happening to the molecules inside. The kinetic energy we a ...
15-7 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... for the warmer water is also 41860 J, but negative because it is removed. Thus: ...
... for the warmer water is also 41860 J, but negative because it is removed. Thus: ...
heat engine
... Water near the surface of a tropical ocean has a temperature of 298.2 K, whereas the water 700 meters beneath the surface has a temperature of 280.2 K. It has been proposed that the warm water be used as the hot reservoir and the cool water as the cold reservoir of a heat engine. Find the maximum po ...
... Water near the surface of a tropical ocean has a temperature of 298.2 K, whereas the water 700 meters beneath the surface has a temperature of 280.2 K. It has been proposed that the warm water be used as the hot reservoir and the cool water as the cold reservoir of a heat engine. Find the maximum po ...
Theory
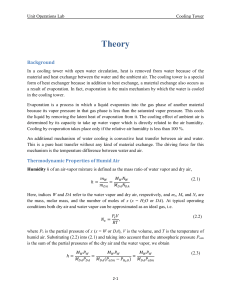
... saturated air that would be obtained by an adiabatic evaporation of water initially at the same temperature T as the air. If the water to be evaporated is already at the same temperature as the air, all it needs for evaporation is the supply of latent heat, which is taken from the air by reduction o ...
... saturated air that would be obtained by an adiabatic evaporation of water initially at the same temperature T as the air. If the water to be evaporated is already at the same temperature as the air, all it needs for evaporation is the supply of latent heat, which is taken from the air by reduction o ...