2 nd Law of Thermodynamics
... General Features of the Entropy S • It is a state function, so that ΔS between given macrostates is independent of the path. • It is a quantitative measure of the disorder in a system. • It gives a criterion for the direction of a process, since an isolated system will reach a state of maximum entr ...
... General Features of the Entropy S • It is a state function, so that ΔS between given macrostates is independent of the path. • It is a quantitative measure of the disorder in a system. • It gives a criterion for the direction of a process, since an isolated system will reach a state of maximum entr ...
TECHNIQUES FOR PRECISION AIR TEMPERATURE CONTROL
... heating and and/or In the the case case of of the the heating /or cooling cooling devices devices it it is is desirable, desirable, whenever whenever possible possible to to consider static heat heat transfer transfer characteristics, characteristics, but consider not not only only their their stati ...
... heating and and/or In the the case case of of the the heating /or cooling cooling devices devices it it is is desirable, desirable, whenever whenever possible possible to to consider static heat heat transfer transfer characteristics, characteristics, but consider not not only only their their stati ...
At a material level, a satellite is a collection of components
... thermal model of DINO, is the rate at which heat can conduct from node to node. If the nodes are of the same material, then equation 2 can be applied directly with the temperature gradient determined by the temperature difference and the distance between the centers of each node. If the nodes are di ...
... thermal model of DINO, is the rate at which heat can conduct from node to node. If the nodes are of the same material, then equation 2 can be applied directly with the temperature gradient determined by the temperature difference and the distance between the centers of each node. If the nodes are di ...
Annexure-I
... (iv) The connecting wires used inside the luminaire, shall be low smoke halogen free, fire retardant e-beam cable and fuse protection shall be provided in input side. (v) Care shall be taken in the design that there is no water stagnation anywhere. The entire housing shall be dust and water proof ha ...
... (iv) The connecting wires used inside the luminaire, shall be low smoke halogen free, fire retardant e-beam cable and fuse protection shall be provided in input side. (v) Care shall be taken in the design that there is no water stagnation anywhere. The entire housing shall be dust and water proof ha ...
Topic 6 CONTROLLING HEAT TRANSFER In this chapter you will
... Visualize the size of one and a half millimetres. If you have a crack this wide around the outside of one window, your furnace may burn an extra litre of fuel per day. Windows in modern houses have double or triple glazing. They are constructed with two or three panes of glass spaced a few millimetr ...
... Visualize the size of one and a half millimetres. If you have a crack this wide around the outside of one window, your furnace may burn an extra litre of fuel per day. Windows in modern houses have double or triple glazing. They are constructed with two or three panes of glass spaced a few millimetr ...
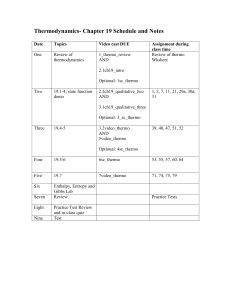
Schedule and sample problems
... (b) ∆G˚ = ∆H˚ – T∆S˚. Both ∆S˚ and ∆H˚ are (+). As temperature increases, at some point the sign of ∆G˚ will change from (+) to (–), when the system will become spontaneous. (c) There will be no change in the partial pressure of the chlorine. Without a volume or temperature change, the pressure is i ...
... (b) ∆G˚ = ∆H˚ – T∆S˚. Both ∆S˚ and ∆H˚ are (+). As temperature increases, at some point the sign of ∆G˚ will change from (+) to (–), when the system will become spontaneous. (c) There will be no change in the partial pressure of the chlorine. Without a volume or temperature change, the pressure is i ...
HYPOTHERMIA
... •Cardiac arrests from VF or VT have the most favorable results with hypothermia. Asystole and PEA are much less positive. •Most of the literature suggests cooling to a temperature of 33°C and to remain at that temperature for 24 hours. •Many animal studies have shown that starting cooling as soon as ...
... •Cardiac arrests from VF or VT have the most favorable results with hypothermia. Asystole and PEA are much less positive. •Most of the literature suggests cooling to a temperature of 33°C and to remain at that temperature for 24 hours. •Many animal studies have shown that starting cooling as soon as ...
HEAT TRANSFER AND THE SECOND LAW
... This requires either a perfect thermal insulator (Q̇ = 0) or a zero temperature gradient (T1 = T2). These two constraints on the heat transfer process —non-negative entropy production —zero entropy production iff zero heat flow are consequences of the second law of thermodynamics. ...
... This requires either a perfect thermal insulator (Q̇ = 0) or a zero temperature gradient (T1 = T2). These two constraints on the heat transfer process —non-negative entropy production —zero entropy production iff zero heat flow are consequences of the second law of thermodynamics. ...
energy changes in physical and chemical processes
... has melted. The heat supplied during melting is absorbed by the water molecules and transformed into kinetic energy. The molecules now have a higher freedom of movement in the liquid state because of the absence of fixed three dimensional bonds. The amount of heat needed to convert a given amount of ...
... has melted. The heat supplied during melting is absorbed by the water molecules and transformed into kinetic energy. The molecules now have a higher freedom of movement in the liquid state because of the absence of fixed three dimensional bonds. The amount of heat needed to convert a given amount of ...
1 CHAPTER 8 HEAT CAPACITY, AND THE EXPANSION OF GASES
... the internal energy. Each vibrational mode adds two such terms – a kinetic energy term and a potential energy term. This means that the predicted molar heat capacity for a nonrigid diatomic molecular gas would be 72 R. Polyatomic gases have many vibrational modes and consequently a higher molar heat ...
... the internal energy. Each vibrational mode adds two such terms – a kinetic energy term and a potential energy term. This means that the predicted molar heat capacity for a nonrigid diatomic molecular gas would be 72 R. Polyatomic gases have many vibrational modes and consequently a higher molar heat ...
EGU2016-10322 - CO Meeting Organizer
... with Ae a pre-exponential constant related to the viscosity at infinite temperature, Be (J mol−1 ) a constant proportional to the potential energy barrier opposed to the cooperative rearrangement of the liquid structure and S conf (T ) (J mol−1 K−1 ) the melt configurational entropy. With expressing ...
... with Ae a pre-exponential constant related to the viscosity at infinite temperature, Be (J mol−1 ) a constant proportional to the potential energy barrier opposed to the cooperative rearrangement of the liquid structure and S conf (T ) (J mol−1 K−1 ) the melt configurational entropy. With expressing ...
ert254-chapter 4
... Most existing heat pumps use the cold outside air as the heat source in winter (air-source HP). In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such h ...
... Most existing heat pumps use the cold outside air as the heat source in winter (air-source HP). In cold climates their efficiency drops considerably when temperatures are below the freezing point. In such cases, geothermal (ground-source) HP that use the ground as the heat source can be used. Such h ...