Chemistry – Chapter 11 Thermochemistry
... Energy is the capacity to do work or to transfer heat energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion ex. heat energy - the energy of the moving particles of a substance) and potential energy is energy that is stored (ex. chemical energy - the energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance). Heat ...
... Energy is the capacity to do work or to transfer heat energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion ex. heat energy - the energy of the moving particles of a substance) and potential energy is energy that is stored (ex. chemical energy - the energy stored in the chemical bonds of a substance). Heat ...
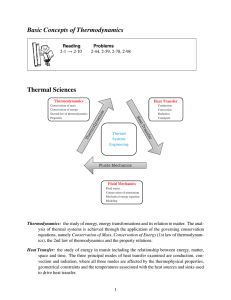
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Thermal Sciences
... M̃ = molecular wieght (or molar mass) of the gas (see Table A-1)) • When is the ideal gas assumption viable? – for a low density gas where: ∗ the gas particles take up negligible volume ∗ the intermolecular potential energy between particles is small ∗ particles act independent of one another – Unde ...
... M̃ = molecular wieght (or molar mass) of the gas (see Table A-1)) • When is the ideal gas assumption viable? – for a low density gas where: ∗ the gas particles take up negligible volume ∗ the intermolecular potential energy between particles is small ∗ particles act independent of one another – Unde ...
Example 1: A single effect evaporator is to be used to concentrate a
... of 0.07 bar is maintained in the evaporator. Assuming that the properties of the solution are the same as those of water, and taking the overall heat transfer coefficient to be 2300 W m−2K−1, calculate the rate of steam consumption and the necessary heat transfer surface area. Working in units of kg ...
... of 0.07 bar is maintained in the evaporator. Assuming that the properties of the solution are the same as those of water, and taking the overall heat transfer coefficient to be 2300 W m−2K−1, calculate the rate of steam consumption and the necessary heat transfer surface area. Working in units of kg ...
Heat Transfer: A Practical Approach
... Two parallel disks whose back sides are insulated are black, and are maintained at a uniform temperature. The net rate of radiation heat transfer from the disks to the environment is to be determined. Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist 2 The surfaces are opaque, diffuse, and gray. 3 Con ...
... Two parallel disks whose back sides are insulated are black, and are maintained at a uniform temperature. The net rate of radiation heat transfer from the disks to the environment is to be determined. Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist 2 The surfaces are opaque, diffuse, and gray. 3 Con ...
An analysis of a packed bed latent heat thermal energy storage
... paraffin and MgCl2$6H2O respectively. Most of the aforementioned investigations do not consider the non-isothermal behavior of the phase change process. The major objective of the present study is to investigate the effect of phase change temperature range on the performance of the packed bed latent ...
... paraffin and MgCl2$6H2O respectively. Most of the aforementioned investigations do not consider the non-isothermal behavior of the phase change process. The major objective of the present study is to investigate the effect of phase change temperature range on the performance of the packed bed latent ...
About the Guide - American Chemical Society
... process an isentropic process. Isentropic means constant entropy. The second law states that if the physical process is irreversible, the combined entropy of the system and the environment must increase. The final entropy must be greater than the initial entropy for an irreversible process: Sf > Si ...
... process an isentropic process. Isentropic means constant entropy. The second law states that if the physical process is irreversible, the combined entropy of the system and the environment must increase. The final entropy must be greater than the initial entropy for an irreversible process: Sf > Si ...
Chemical Thermodynamics John Murrell Introduction
... stabilization energies of about 0.1eV (10kJ/mol), or more for polar molecules due to electrostatic energies. These intermolecular forces therefore lower the enthalpies of liquids and solids relative to gasses. As there is not a great deal of difference between the binding energies in liquids and sol ...
... stabilization energies of about 0.1eV (10kJ/mol), or more for polar molecules due to electrostatic energies. These intermolecular forces therefore lower the enthalpies of liquids and solids relative to gasses. As there is not a great deal of difference between the binding energies in liquids and sol ...
Simulation of Heat Gain through Building Envelope for Buildings in
... guideline to design the appropriate shape of building for energy conservation. In addition, the investigation also considers the method to reduce heat gain by using internal shading devices and thermal insulating materials. At first an investigation of all factors to be used for calculating heat gai ...
... guideline to design the appropriate shape of building for energy conservation. In addition, the investigation also considers the method to reduce heat gain by using internal shading devices and thermal insulating materials. At first an investigation of all factors to be used for calculating heat gai ...
Numerical Simulation of Magneto-hydrodynamics mixed convection
... governing physical parameters in the considered problem are the Rayleigh numbers, and Hartmann numbers. In this investigation, our attention is taken into account to investigate the effects of controlling parameters namely Hartmann number (Ha), and Rayleigh numbers (Ra). Here, the effect of Hartman ...
... governing physical parameters in the considered problem are the Rayleigh numbers, and Hartmann numbers. In this investigation, our attention is taken into account to investigate the effects of controlling parameters namely Hartmann number (Ha), and Rayleigh numbers (Ra). Here, the effect of Hartman ...
Effect of Temperature and Humidity on Evaporative Water Loss in
... Richards 1976; Edwards and Haines 1978; Welch 1980; Webster and King 1987). These studies show that when eva is high, EWL is low in both mammals and birds at all temperatures. In pigeons ( Columba livia), for example, EWL at high humidity (l?va=25 g · m- 3 ) is less than 50% of that at low humidity ...
... Richards 1976; Edwards and Haines 1978; Welch 1980; Webster and King 1987). These studies show that when eva is high, EWL is low in both mammals and birds at all temperatures. In pigeons ( Columba livia), for example, EWL at high humidity (l?va=25 g · m- 3 ) is less than 50% of that at low humidity ...
12. THE LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS Key Words
... disorder. The entropy of a system can be considered a measure for the disorder of the system. Now we can formulate the second law of thermodynamics as natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder (because they have greater probability). The separate hot and cold objects could se ...
... disorder. The entropy of a system can be considered a measure for the disorder of the system. Now we can formulate the second law of thermodynamics as natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder (because they have greater probability). The separate hot and cold objects could se ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment
... Diabetes is a disease affecting the insulin producing glands of the pancreas. If there is not enough insulin being produced by these cells, the amount of glucose in the blood will remain high. A blood glucose level above 140 for an extended period of time is not considered normal. This disease, if n ...
... Diabetes is a disease affecting the insulin producing glands of the pancreas. If there is not enough insulin being produced by these cells, the amount of glucose in the blood will remain high. A blood glucose level above 140 for an extended period of time is not considered normal. This disease, if n ...
Thermal Engineering - Nilachal Polytechnic
... When a body ‘A’ is in thermal equilibrium with a body ‘B’and also separately with a body ‘C’ then B & C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other. 14. Define path. Ans. The succession of states passed through during a change of state is called the path of change of state. ...
... When a body ‘A’ is in thermal equilibrium with a body ‘B’and also separately with a body ‘C’ then B & C will be in thermal equilibrium with each other. 14. Define path. Ans. The succession of states passed through during a change of state is called the path of change of state. ...
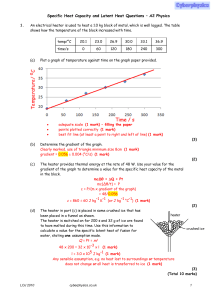
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions
... (b) State and explain one reason why the actual time taken to heat the room is longer than the value calculated in part (a)(ii). Heat is lost to surroundings or other objects in room or to heater itself(1 mark) therefore more ...
... (b) State and explain one reason why the actual time taken to heat the room is longer than the value calculated in part (a)(ii). Heat is lost to surroundings or other objects in room or to heater itself(1 mark) therefore more ...