District heating engineering - DH distribution DH
... • Installation of single and dual bonded pipes – Pipes must lay at least 40 cm below surface – Not fastened – soil friction keeps pipes on place – To reduce heat loss, dual pipes are installed so that supply pipe is below the return pipe ...
... • Installation of single and dual bonded pipes – Pipes must lay at least 40 cm below surface – Not fastened – soil friction keeps pipes on place – To reduce heat loss, dual pipes are installed so that supply pipe is below the return pipe ...
Heat - FER
... Energy Balance for Steady-Flow Systems A large number of engineering devices such as water heaters and car radiators involve mass flow in and out of a system, and are modeled as control volumes. Most control volumes are analyzed under steady operating conditions. The term steady means no change wit ...
... Energy Balance for Steady-Flow Systems A large number of engineering devices such as water heaters and car radiators involve mass flow in and out of a system, and are modeled as control volumes. Most control volumes are analyzed under steady operating conditions. The term steady means no change wit ...
Heat Conduction
... The laws governing the transfer of heat and the type of apparatus that have for their main object the control of heat flow are therefore of great importance. ...
... The laws governing the transfer of heat and the type of apparatus that have for their main object the control of heat flow are therefore of great importance. ...
Elementary Notes on Classical Thermodynamics
... motion; this is, really, the realm of Mechanics. We can rather talk of an internal energy that the system has as a result of the numerous micro-processes happening inside it. We do not need to be concerned with the exact nature of these processes, as this would require a deepening of the molecular n ...
... motion; this is, really, the realm of Mechanics. We can rather talk of an internal energy that the system has as a result of the numerous micro-processes happening inside it. We do not need to be concerned with the exact nature of these processes, as this would require a deepening of the molecular n ...
253 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics GOALS When you have mastered
... 2000 kcal (ΔQ = 2000 kcal) from the food when burned in the body. The body does work amounting to 3000 kcal (ΔW = + 3000 kcal). This work takes many forms, mechanical work in terms of body motion, chemical changes in the muscles, and electrical energy in nerve activity. From the first law it follows ...
... 2000 kcal (ΔQ = 2000 kcal) from the food when burned in the body. The body does work amounting to 3000 kcal (ΔW = + 3000 kcal). This work takes many forms, mechanical work in terms of body motion, chemical changes in the muscles, and electrical energy in nerve activity. From the first law it follows ...
HANDBOOK OF FOOD SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY - FEA
... device, such as a fan (14). Convection from the heating medium to the product surface, and conduction from the product surface to the inner part of the food occur at the same time, for example, meat batters, stuffed in water permeable casing, or cuts such as ham, ribs or loins in stockings cooked in ...
... device, such as a fan (14). Convection from the heating medium to the product surface, and conduction from the product surface to the inner part of the food occur at the same time, for example, meat batters, stuffed in water permeable casing, or cuts such as ham, ribs or loins in stockings cooked in ...
Coupled cellular automata for frozen soil processes
... so far, z is the cell elevation and k represents the average hydraulic conductivity of the region between the ith and the ζ th cells. In this study, phase change and associated temperature change is brought about by integrating along a soil freezing curve (SFC). SFCs can be defined because the liqui ...
... so far, z is the cell elevation and k represents the average hydraulic conductivity of the region between the ith and the ζ th cells. In this study, phase change and associated temperature change is brought about by integrating along a soil freezing curve (SFC). SFCs can be defined because the liqui ...
This is a heat engine
... The giant star Betelgeuse emits radiant energy at a rate 104 times greater than our Sun, whereas its surface temperature is only half (2900 K) that of our Sun. Estimate the radius of Betelgeuse, assuming ε = 1 for both. The Sun’s radius is rS = 0.7 Mkm. Answer: ...
... The giant star Betelgeuse emits radiant energy at a rate 104 times greater than our Sun, whereas its surface temperature is only half (2900 K) that of our Sun. Estimate the radius of Betelgeuse, assuming ε = 1 for both. The Sun’s radius is rS = 0.7 Mkm. Answer: ...
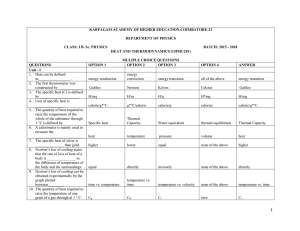
Heat and Thermodynamics 300 MCQ
... Petit's law, the atomic heat of an element of constant volume 24. The degeneracy parameter ea satisfies this condition, the gas is said to be 25. RMS speed of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its 26. The RMS speed of gas at 400 K is 27. Which of the following variables co ...
... Petit's law, the atomic heat of an element of constant volume 24. The degeneracy parameter ea satisfies this condition, the gas is said to be 25. RMS speed of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its 26. The RMS speed of gas at 400 K is 27. Which of the following variables co ...