Paper
... ribbon production. It is well known that the cooling rate of the ribbon on the drum must be high enough to achieve the amorphous solidification. The previous estimations showed that the average cooling rate must range 105 K/s to 106 K/s [3]. Theoretical analysis of heat transfer in this case is comp ...
... ribbon production. It is well known that the cooling rate of the ribbon on the drum must be high enough to achieve the amorphous solidification. The previous estimations showed that the average cooling rate must range 105 K/s to 106 K/s [3]. Theoretical analysis of heat transfer in this case is comp ...
Chapter 15 THERMODYNAMICS
... are four laws of thermodynamics, of which two appear on the AP Physics B exam by name (1st and 2nd). However, the concepts involved in the other two (0th and 3rd) are important to the understanding of thermodynamics as well. The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two systems are in equilibr ...
... are four laws of thermodynamics, of which two appear on the AP Physics B exam by name (1st and 2nd). However, the concepts involved in the other two (0th and 3rd) are important to the understanding of thermodynamics as well. The zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two systems are in equilibr ...
Application of POD-RBF technique for retrieving thermal diffusivity of
... collected experimental data. Analytical model assumes that the carbon block due to its large size in contrary to laser emission spot and duration of the experiment (less than 3s) can be treated as semiinfinity space which considerable simplified the model formulation. In [2,3] the simple analytical ...
... collected experimental data. Analytical model assumes that the carbon block due to its large size in contrary to laser emission spot and duration of the experiment (less than 3s) can be treated as semiinfinity space which considerable simplified the model formulation. In [2,3] the simple analytical ...
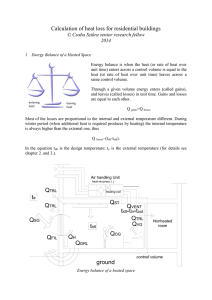
Calculation of heat loss for buildings
... Definition of air changes (ACH): Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air e ...
... Definition of air changes (ACH): Air changes per hour is a measure of how many times the air within a defined space (normally a room or house) is replaced. Air changes in a confined space are important for a variety of reasons, mainly though, we need fresh air to live. Without sufficient fresh air e ...
Processing of temperature field in chemical microreactors with
... investigating the chemical reactions in fluid flow situations in micro channel. The small size is suitable to master the mixing of the reactants with very low Reynolds laminar flows. It is also very convenient to use a few amount of products and to be able to easily and quickly test a great number o ...
... investigating the chemical reactions in fluid flow situations in micro channel. The small size is suitable to master the mixing of the reactants with very low Reynolds laminar flows. It is also very convenient to use a few amount of products and to be able to easily and quickly test a great number o ...
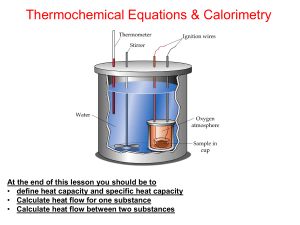
Thermochemistry Lesson 2
... • A piece of iron (Fe) weighing 40 g is heated to 800C and dropped into 100 g of water at 250C. (Specific heat of Fe is 0.446 J /g0C and Specific heat of H2O is 4.182 J /g0C) What is the temperature when thermal equilibrium has been reached ? (Ans = 27.50C) • Heat lost by iron is equal to heat gaine ...
... • A piece of iron (Fe) weighing 40 g is heated to 800C and dropped into 100 g of water at 250C. (Specific heat of Fe is 0.446 J /g0C and Specific heat of H2O is 4.182 J /g0C) What is the temperature when thermal equilibrium has been reached ? (Ans = 27.50C) • Heat lost by iron is equal to heat gaine ...
• Conservation of energy principle • Total energy • Energy transfer
... CONVE CTION: Is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent liquid or gas which in motion and it involves the combined effects of “conduction and fluid motion”. The faster the fluid motion, the greater the convection heat transfer. In the absence of any bulk fluid motion, he ...
... CONVE CTION: Is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent liquid or gas which in motion and it involves the combined effects of “conduction and fluid motion”. The faster the fluid motion, the greater the convection heat transfer. In the absence of any bulk fluid motion, he ...
Review of fundamental principles ? Thermodynamics : Part II
... Also, from Eq. (5.1b), T ds=dh - vdP , hence for a constant pressure process (dP = 0), therefore, for a constant pressure process Tds = dh, which means that for an isobaric process the area under the curve is equal to change in enthalpy on T-s diagram. Properties at Saturation The properties of refr ...
... Also, from Eq. (5.1b), T ds=dh - vdP , hence for a constant pressure process (dP = 0), therefore, for a constant pressure process Tds = dh, which means that for an isobaric process the area under the curve is equal to change in enthalpy on T-s diagram. Properties at Saturation The properties of refr ...
Heat Transfer: A Practical Approach
... A 3-m diameter spherical tank filled with liquid nitrogen at 1 atm and -196°C is exposed to convection and radiation with the surrounding air and surfaces. The rate of evaporation of liquid nitrogen in the tank as a result of the heat gain from the surroundings for the cases of no insulation, 5-cm t ...
... A 3-m diameter spherical tank filled with liquid nitrogen at 1 atm and -196°C is exposed to convection and radiation with the surrounding air and surfaces. The rate of evaporation of liquid nitrogen in the tank as a result of the heat gain from the surroundings for the cases of no insulation, 5-cm t ...
effects of temperature on the size of aquatic ectotherms
... rearing temperatures is easily explicable if temperatures are stressfully high or resources are either in short supply or of poor quality so that individual growth rates are reduced (Brett, 1971; Cossins and Bowler, 1987; Moore and Folt, 1993). A more difficult problem is to explain why an organism’ ...
... rearing temperatures is easily explicable if temperatures are stressfully high or resources are either in short supply or of poor quality so that individual growth rates are reduced (Brett, 1971; Cossins and Bowler, 1987; Moore and Folt, 1993). A more difficult problem is to explain why an organism’ ...
Analysis of selected gaseous organic micro
... In an SPME based methodology, the sample analyte concentration is derived from the analyte amount absorbed in the fiber stationary phase. The most often used and reliable approach is based on the fiber exposition until equilibrium is reached. Partition coefficients determining the amount of an analy ...
... In an SPME based methodology, the sample analyte concentration is derived from the analyte amount absorbed in the fiber stationary phase. The most often used and reliable approach is based on the fiber exposition until equilibrium is reached. Partition coefficients determining the amount of an analy ...
Modelling the hot rolling process using a finite volume
... that, in turn, depends upon the accumulated effective strains and strain-rates, the temperature and some internal variables defining the material microstructure. Thus, the material behaviour in bulk metal forming can be considered as rigidviscoplastic likewise an incompressible non-Newtonian fluid. ...
... that, in turn, depends upon the accumulated effective strains and strain-rates, the temperature and some internal variables defining the material microstructure. Thus, the material behaviour in bulk metal forming can be considered as rigidviscoplastic likewise an incompressible non-Newtonian fluid. ...
Heat Transfer Enhancement in Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage
... E-mail address: [email protected] a ...
... E-mail address: [email protected] a ...
Optimal heating and cooling strategies for heat exchanger design
... tied, whereas the amount of entropy produced depends on the way in which the process is carried out (primarily the temperature gradient). Since the entropy produced is equivalent to availability lost, this means that an improved heat exchanger design which reduces the entropy production can in princ ...
... tied, whereas the amount of entropy produced depends on the way in which the process is carried out (primarily the temperature gradient). Since the entropy produced is equivalent to availability lost, this means that an improved heat exchanger design which reduces the entropy production can in princ ...