Total view of the AFM
... maintained at ~10-8 Torr vacuum. • Microscopes are usually operated in the voltage range of 20 – 30 keV, but for insulating samples 1 kV or less can be used. For insulating samples a thin metal coating can also be used. • The standard electron detector is an EverhartThornley design that is capable o ...
... maintained at ~10-8 Torr vacuum. • Microscopes are usually operated in the voltage range of 20 – 30 keV, but for insulating samples 1 kV or less can be used. For insulating samples a thin metal coating can also be used. • The standard electron detector is an EverhartThornley design that is capable o ...
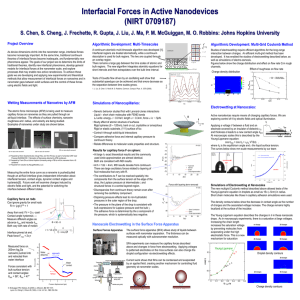
Interfacial Forces in Active Nanodevices
... of charges and the associated voltage increase. The charge remains highly localized at the surface of the insulator. The Young-Lippmann equation describes the changes in q in these nanoscale drops. As in macroscopic experiments, there is a saturation at large voltages. Increasing the chain length in ...
... of charges and the associated voltage increase. The charge remains highly localized at the surface of the insulator. The Young-Lippmann equation describes the changes in q in these nanoscale drops. As in macroscopic experiments, there is a saturation at large voltages. Increasing the chain length in ...
Surface Characterization by Spectroscopy and Microscopy
... The first three methods listed in the above table are based upon the analysis of emitted electrons produced by various incident beams. In electron spectroscopy, the spectroscopic measurement consists of the determination of the power of the electron beam as a function of the energy (or frequency hv) ...
... The first three methods listed in the above table are based upon the analysis of emitted electrons produced by various incident beams. In electron spectroscopy, the spectroscopic measurement consists of the determination of the power of the electron beam as a function of the energy (or frequency hv) ...
Supplementary information
... Substrate preparation. Polycrystalline Au films are prepared by thermally depositing 2nm thick Ti layer followed by 8nm Au layer on SiO2 substrates under a high vacuum condition (pressure ~ 2 x 10 -7 torr). We can routinely obtain lattice resolved AFM images on Au films prepared by this method. Surf ...
... Substrate preparation. Polycrystalline Au films are prepared by thermally depositing 2nm thick Ti layer followed by 8nm Au layer on SiO2 substrates under a high vacuum condition (pressure ~ 2 x 10 -7 torr). We can routinely obtain lattice resolved AFM images on Au films prepared by this method. Surf ...
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)
... the surface (and by the time the data has been processed it may even look like a real picture of the surface ! ). ...
... the surface (and by the time the data has been processed it may even look like a real picture of the surface ! ). ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... There were two IR lasers used to provide the illuminated IR light necessary in s-SNOM. The first is a CO2 gas laser which emits light with a wavelength of around 10.6 µm. The second is called a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) and uses a series of semiconductors stacked on one another to tunnel electron ...
... There were two IR lasers used to provide the illuminated IR light necessary in s-SNOM. The first is a CO2 gas laser which emits light with a wavelength of around 10.6 µm. The second is called a Quantum Cascade Laser (QCL) and uses a series of semiconductors stacked on one another to tunnel electron ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
... Each plane represents a different value of the tip-sample V, and the lateral position on the plane gives the x,y position of the tip. Filled states are given in red. The plane at the Fermi energy (V=0) is shown in blue. ...
... Each plane represents a different value of the tip-sample V, and the lateral position on the plane gives the x,y position of the tip. Filled states are given in red. The plane at the Fermi energy (V=0) is shown in blue. ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
... Each plane represents a different value of the tip-sample V, and the lateral position on the plane gives the x,y position of the tip. Filled states are given in red. The plane at the Fermi energy (V=0) is shown in blue. ...
... Each plane represents a different value of the tip-sample V, and the lateral position on the plane gives the x,y position of the tip. Filled states are given in red. The plane at the Fermi energy (V=0) is shown in blue. ...
University of Groningen Designing molecular nano
... diffusion that make TF-AFM a very difficult technique to operate. A very high level of instrument stability and user skills are needed with respect to standard STM and AFM imaging, and the acquisition time can be extremely long (about 5 hours for 1 image, about 1 day to get the system in stable operati ...
... diffusion that make TF-AFM a very difficult technique to operate. A very high level of instrument stability and user skills are needed with respect to standard STM and AFM imaging, and the acquisition time can be extremely long (about 5 hours for 1 image, about 1 day to get the system in stable operati ...
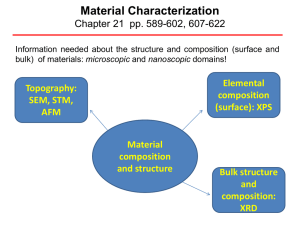
Material Characterization
... A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a powerful instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer (at IBM Zürich), the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral r ...
... A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a powerful instrument for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer (at IBM Zürich), the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. For an STM, good resolution is considered to be 0.1 nm lateral r ...
Document
... Nanoscope I, in 1987. In a recent Nanoscope IV STM for operation in ambient air, the sample is held in position while a piezoelectric crystal in the form of a cylindrical tube (referred to as PZT tube scanner) scans the sharp metallic probe over the surface in a raster pattern while sensing and outp ...
... Nanoscope I, in 1987. In a recent Nanoscope IV STM for operation in ambient air, the sample is held in position while a piezoelectric crystal in the form of a cylindrical tube (referred to as PZT tube scanner) scans the sharp metallic probe over the surface in a raster pattern while sensing and outp ...
Scanning Probe MicroScopy History of Scanning Probe Microscopy
... Figure 10: The de ection of the tip is measured by bouncing a laser o the cantilever arm which gives us the contour of the surface at atomic resolution (since inter-atomic forces are related to the distance between the atoms). One possible complication is formation of bonds between the tip and the ...
... Figure 10: The de ection of the tip is measured by bouncing a laser o the cantilever arm which gives us the contour of the surface at atomic resolution (since inter-atomic forces are related to the distance between the atoms). One possible complication is formation of bonds between the tip and the ...
ieee-icra-2005
... higher precision of alignment and narrower width of lithography than those obtained by the use of photon, electron and scanning probe lithography. In contact mode, the probe is in contact with the surface and the AFM uses various forces that occur when two objects are brought within nanometers of ea ...
... higher precision of alignment and narrower width of lithography than those obtained by the use of photon, electron and scanning probe lithography. In contact mode, the probe is in contact with the surface and the AFM uses various forces that occur when two objects are brought within nanometers of ea ...
- National Physical Laboratory
... materials is understanding the correlation between surface morphology and catalytic activity on different length scales. In particular spatially resolved characterization of catalysts under reaction conditions remains a fundamental challenge. Scanning electrochemical microscopy offers a unique means ...
... materials is understanding the correlation between surface morphology and catalytic activity on different length scales. In particular spatially resolved characterization of catalysts under reaction conditions remains a fundamental challenge. Scanning electrochemical microscopy offers a unique means ...
Lec 2014 09 23
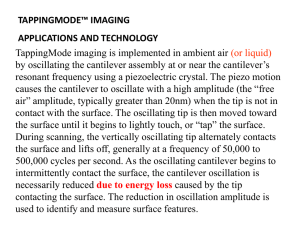
... TappingMode imaging is implemented in ambient air (or liquid) by oscillating the cantilever assembly at or near the cantilever’s resonant frequency using a piezoelectric crystal. The piezo motion causes the cantilever to oscillate with a high amplitude (the “free air” amplitude, typically greater th ...
... TappingMode imaging is implemented in ambient air (or liquid) by oscillating the cantilever assembly at or near the cantilever’s resonant frequency using a piezoelectric crystal. The piezo motion causes the cantilever to oscillate with a high amplitude (the “free air” amplitude, typically greater th ...
unit - i principles of dynamics (9)
... take measurements over a small area. To acquire an image the microscope raster-scans the probe over the sample while measuring the local property in question. The resulting image resembles an image on a television screen in that both consist of many rows or lines of information placed one above the ...
... take measurements over a small area. To acquire an image the microscope raster-scans the probe over the sample while measuring the local property in question. The resulting image resembles an image on a television screen in that both consist of many rows or lines of information placed one above the ...
Principles of Nanometrology
... http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/physics/microscopes/tem/index.html ...
... http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/physics/microscopes/tem/index.html ...
Atomic force microscopy

Atomic-force microscopy (AFM) or scanning-force microscopy (SFM) is a very high-resolution type of Scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit.