AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 12 - A
... With reference to the structure shown above give one reason why ice is less dense than ...
... With reference to the structure shown above give one reason why ice is less dense than ...
heat vs temp student sheet
... Specific Heat (C) is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. The symbol for specific heat is C. It has units of joules / g oC or calories / g oC. Every substance has its own unique specific heat that can be found in reference books. The formula used to ...
... Specific Heat (C) is the amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1oC. The symbol for specific heat is C. It has units of joules / g oC or calories / g oC. Every substance has its own unique specific heat that can be found in reference books. The formula used to ...
Dr. McCord Calorimetry
... OK, I’ve got qcal. Now what? OK, so you’ve done the work and solved for qcal, what now? Are you done? Not quite. Most heat transfer processes that are measured are recorded as an intensive property and not extensively. So even though you have a value for ∆U or ∆H, those values happen to be for the a ...
... OK, I’ve got qcal. Now what? OK, so you’ve done the work and solved for qcal, what now? Are you done? Not quite. Most heat transfer processes that are measured are recorded as an intensive property and not extensively. So even though you have a value for ∆U or ∆H, those values happen to be for the a ...
our provided Word-Template - sCO2-Seminar-2016
... dehydration in one thermochemical storage station increases the complexity of the system. This is shown by a simplified flowsheet of a district heating station in Figure 4. This design has the advantage that it is not necessary to transport the TCM, but also the disadvantage of higher heat loss thro ...
... dehydration in one thermochemical storage station increases the complexity of the system. This is shown by a simplified flowsheet of a district heating station in Figure 4. This design has the advantage that it is not necessary to transport the TCM, but also the disadvantage of higher heat loss thro ...
Measuring and Using Energy Changes
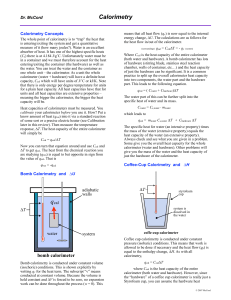
... - A bomb calorimeter has many more parts than a polystyrene calorimeter. - All of these parts can absorb or release small quantities of energy. Therefore, you cannot assume that the heat lost to the calorimeter is small enough to be negligible. - To obtain precise heat measurements, you must know o ...
... - A bomb calorimeter has many more parts than a polystyrene calorimeter. - All of these parts can absorb or release small quantities of energy. Therefore, you cannot assume that the heat lost to the calorimeter is small enough to be negligible. - To obtain precise heat measurements, you must know o ...
Document
... The first term is positive and the second is negative. After a complete cycle, the system is back to its original state, which means it is back to its original pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, and entropy. Thus, S for a complete cycle must be zero. ...
... The first term is positive and the second is negative. After a complete cycle, the system is back to its original state, which means it is back to its original pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, and entropy. Thus, S for a complete cycle must be zero. ...
FSK Shield - Fi-Foil
... temperatures upward to 150 degrees or higher. These higher temperatures will increase the heat gain in your air con-ditioning ducts and reduce the performance of mass insulation (the R-values of mass insulation are determined at 75oF - higher temperatures lowers the R-value). In addition, the extrem ...
... temperatures upward to 150 degrees or higher. These higher temperatures will increase the heat gain in your air con-ditioning ducts and reduce the performance of mass insulation (the R-values of mass insulation are determined at 75oF - higher temperatures lowers the R-value). In addition, the extrem ...
An Empirical Formula of Mean Specific Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases
... basic for thermodynamic calculation for real gases. For gases at normal pressure or a little higher pressure, real gases can be treated as ideal gases. Eq.11 and Eq.12 are widely applied in thermal engineering for both ideal gases and real gases [3, 4, 5]. For ideal gases, specific heat capacity eit ...
... basic for thermodynamic calculation for real gases. For gases at normal pressure or a little higher pressure, real gases can be treated as ideal gases. Eq.11 and Eq.12 are widely applied in thermal engineering for both ideal gases and real gases [3, 4, 5]. For ideal gases, specific heat capacity eit ...
Paper
... metallic alloy ribbon as a function of the thermophysical properties of the melt and cooling drum. The calculations were carry out for different vitrification temperatures and for different values of the melt cooling ratio 2. In all calculations, the drum material was copper, the melt temperature w ...
... metallic alloy ribbon as a function of the thermophysical properties of the melt and cooling drum. The calculations were carry out for different vitrification temperatures and for different values of the melt cooling ratio 2. In all calculations, the drum material was copper, the melt temperature w ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.