Shield Volcano
... • Shield volcanoes are broad, gently sloping volcanic mountains (What does it look like?) • Shield volcanoes are slowly formed by layer over layer of solidified lava, and formed by effusive eruptions of fluid lava. (How is it formed?) • Shield Volcanoes have effusive eruptions that are low in silica ...
... • Shield volcanoes are broad, gently sloping volcanic mountains (What does it look like?) • Shield volcanoes are slowly formed by layer over layer of solidified lava, and formed by effusive eruptions of fluid lava. (How is it formed?) • Shield Volcanoes have effusive eruptions that are low in silica ...
volcanoes - boykinhonors
... crater - depression found at the top of a volcano; formed by the explosion of the upper portion of the cone ...
... crater - depression found at the top of a volcano; formed by the explosion of the upper portion of the cone ...
Chapter 9 - Volcanoes
... underneath (subducted) under another. Oceanic crust will subduct under continental crust because it is denser than continental crust. This process generates tremendous heat and pressure that helps in the formation of magma and new volcanoes. ...
... underneath (subducted) under another. Oceanic crust will subduct under continental crust because it is denser than continental crust. This process generates tremendous heat and pressure that helps in the formation of magma and new volcanoes. ...
national geographic readings on volcanoes - Whitlock-Science
... What is the name of the tiny southernmost part of the Juan de Fuca plate subducting under northern California? 5. Whey is Glass Mountain in Lava Beds National Monument named as such? ...
... What is the name of the tiny southernmost part of the Juan de Fuca plate subducting under northern California? 5. Whey is Glass Mountain in Lava Beds National Monument named as such? ...
6VolcanicT2 - Arizona State University
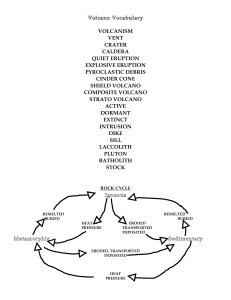
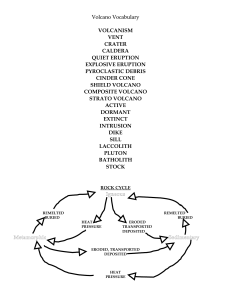
... Plutons (individual magma chambers) Large Batholiths (merged magma chambers) Laccolith (bubble up strata) ...
... Plutons (individual magma chambers) Large Batholiths (merged magma chambers) Laccolith (bubble up strata) ...
Document
... 2. Lahars – mudflow formed from volcanic ash and water (melted snow or rain) 3. Eruptions – you’re there one minute and gone the next… ...
... 2. Lahars – mudflow formed from volcanic ash and water (melted snow or rain) 3. Eruptions – you’re there one minute and gone the next… ...
2_2013_papervolcanoactivity
... (“fire-broken”) material, that have been explosively erupted from the vent of the volcano. As the material falls back to the ground, it generally piles up to form a symmetrical, steep-sided cone around the vent. Sunset Crater in Arizona and Paricutin in Mexico are well-known examples of cinder cones ...
... (“fire-broken”) material, that have been explosively erupted from the vent of the volcano. As the material falls back to the ground, it generally piles up to form a symmetrical, steep-sided cone around the vent. Sunset Crater in Arizona and Paricutin in Mexico are well-known examples of cinder cones ...
Volcanoes
... 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
... 4. Lava flow – the area cover by lava as it pours out of a volcano’s vent 5. Crater – a bowl-shaped area that forms around a volcano’s central opening ...
Volcanoes - Helena High School
... • An active volcano is one that is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms). • A dormant volcano is one that has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. ...
... • An active volcano is one that is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms). • A dormant volcano is one that has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. ...
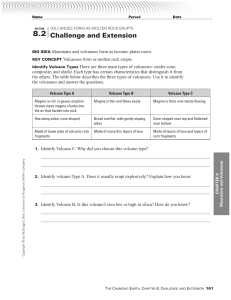
Challenge and Extension - Effingham County Schools
... BIG IDEA Mountains and volcanoes form as tectonic plates move. KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table be ...
... BIG IDEA Mountains and volcanoes form as tectonic plates move. KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it from the others. The table be ...
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
VOLCANO’S ACTIVITY
... As you can see in this picture, magma begins in the lava chamber and comes to the surface through the throat of the volcano. The volcano is constructed layer by layer, as ash and lava solidify, one upon the other. ...
... As you can see in this picture, magma begins in the lava chamber and comes to the surface through the throat of the volcano. The volcano is constructed layer by layer, as ash and lava solidify, one upon the other. ...
Lecture 12
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop as the Pacific Plate moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop as the Pacific Plate moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
... the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crater Lake) and Paricutin (1943, Mexico). 2. Shield Volcano- is usually wider than it is tall, much like a shield. It ...
Volcanoes
... - interbedded pyroclastics and lavas. - typically andesitic to rhyolitic lava > intermediate to felsic magma composition ...
... - interbedded pyroclastics and lavas. - typically andesitic to rhyolitic lava > intermediate to felsic magma composition ...
Volcanoes
... Dormant- are not currently erupting but are considered likely to do so. Mt. St Helens was dormant for 123 years before it erupted in 1980. ...
... Dormant- are not currently erupting but are considered likely to do so. Mt. St Helens was dormant for 123 years before it erupted in 1980. ...
Section
... 9. How may volcanic eruptions influence global climate? Explosive eruptions, particularly, may put large volumes of dust and sulfuric acid aerosols into the atmosphere. These block sunlight and thus contribute to global cooling, although they precipitate out of the atmosphere in a matter of years. ...
... 9. How may volcanic eruptions influence global climate? Explosive eruptions, particularly, may put large volumes of dust and sulfuric acid aerosols into the atmosphere. These block sunlight and thus contribute to global cooling, although they precipitate out of the atmosphere in a matter of years. ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/teacherspackets/volcanoes/poster/poster.html ...
... http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/teacherspackets/volcanoes/poster/poster.html ...
Notes Igneous Activity
... b. Frequently occurs in groups surrounding a large stratovolcano c. Sunset Crater, Flagstaff, AZ Sunset Crater Paracutin in Mexico ...
... b. Frequently occurs in groups surrounding a large stratovolcano c. Sunset Crater, Flagstaff, AZ Sunset Crater Paracutin in Mexico ...
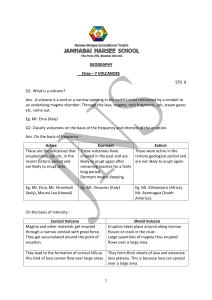
GEOGRAPHY Chap – 7 VOLCANOES STD. 8 Q1. What is a volcano
... Typical extrusive landform found is the cone shaped hill called volcanic cone. Most volcanoes start as cinder cones and grow into large volcanic hills with alternating layers of lava and ash. They are called composite cones. Q4. How is a crater formed? ...
... Typical extrusive landform found is the cone shaped hill called volcanic cone. Most volcanoes start as cinder cones and grow into large volcanic hills with alternating layers of lava and ash. They are called composite cones. Q4. How is a crater formed? ...
Volcanoes SHOW
... Half of the 1,000 geysers in the world are in Yellowstone National Park, WY (United States) ...
... Half of the 1,000 geysers in the world are in Yellowstone National Park, WY (United States) ...
Mauna Loa

Mauna Loa (/ˌmɔːnə ˈloʊ.ə/ or /ˌmaʊnə ˈloʊ.ə/; Hawaiian: [ˈmɔunə ˈlowə]; English: Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaiʻi in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano in both mass and volume, Mauna Loa has historically been considered the largest volcano on Earth. It is an active shield volcano with relatively shallow slopes, with a volume estimated at approximately 18,000 cubic miles (75,000 km3), although its peak is about 120 feet (37 m) lower than that of its neighbor, Mauna Kea. Lava eruptions from Mauna Loa are silica-poor and very fluid, and they tend to be non-explosive.Mauna Loa has probably been erupting for at least 700,000 years, and may have emerged above sea level about 400,000 years ago. The oldest-known dated rocks are not older than 200,000 years. The volcano's magma comes from the Hawaii hotspot, which has been responsible for the creation of the Hawaiian island chain over tens of millions of years. The slow drift of the Pacific Plate will eventually carry Mauna Loa away from the hotspot within 500,000 to one million years from now, at which point it will become extinct.Mauna Loa's most recent eruption occurred from March 24 to April 15, 1984. No recent eruptions of the volcano have caused fatalities, but eruptions in 1926 and 1950 destroyed villages, and the city of Hilo is partly built on lava flows from the late 19th century. Because of the potential hazards it poses to population centers, Mauna Loa is part of the Decade Volcanoes program, which encourages studies of the world's most dangerous volcanoes. Mauna Loa has been monitored intensively by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory since 1912. Observations of the atmosphere are undertaken at the Mauna Loa Observatory, and of the Sun at the Mauna Loa Solar Observatory, both located near the mountain's summit. Hawaii Volcanoes National Park covers the summit and the southeastern flank of the volcano, and also incorporates Kīlauea, a separate volcano.