Volcanoes - PrinceBwis
... • Energy from water and steam that has been heated by magma • Geothermal energy is produced by drilling a well into the ground where thermal activity is occuring. • Once a well has been identified and a well head attached, the steam is separated from the water, the water is diverted through a turbin ...
... • Energy from water and steam that has been heated by magma • Geothermal energy is produced by drilling a well into the ground where thermal activity is occuring. • Once a well has been identified and a well head attached, the steam is separated from the water, the water is diverted through a turbin ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Lava flows that are characterized by rough, broken rock fragments on the surface and top of the flow, and a molten center. As the flow is moving slowly the bottom stays in place and the front moves forward, while breaking up and then flowing over its own debris. Gas from the molten lava interior mig ...
... Lava flows that are characterized by rough, broken rock fragments on the surface and top of the flow, and a molten center. As the flow is moving slowly the bottom stays in place and the front moves forward, while breaking up and then flowing over its own debris. Gas from the molten lava interior mig ...
volcano eruption styles
... The next least explosive kind of eruption Fluid magmas with small amounts of gas Eruptions relatively gentle Periodically have a violent eruption but very rare - Drive in volcanoes ...
... The next least explosive kind of eruption Fluid magmas with small amounts of gas Eruptions relatively gentle Periodically have a violent eruption but very rare - Drive in volcanoes ...
Volcanoes - Pacific Disaster Net
... Lava flows can reach far distances and are capable of destroying all in their path, although they are usually fairly slow moving and thus not really life threatening. Volcanic gases such as poisonous sulphur and carbon monoxide are emitted during eruptions. Acid rain damages crops and vegetation and ...
... Lava flows can reach far distances and are capable of destroying all in their path, although they are usually fairly slow moving and thus not really life threatening. Volcanic gases such as poisonous sulphur and carbon monoxide are emitted during eruptions. Acid rain damages crops and vegetation and ...
Why Do Volcanoes Erupt? A Step by Step Guide
... volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It couldn’t flow out so enormous pressure built up. The geologists knew Mt. St. Helens was ready in the firs ...
... volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It couldn’t flow out so enormous pressure built up. The geologists knew Mt. St. Helens was ready in the firs ...
Volcanoes
... earth’s surface slowly begins to rise to the surface As the magma rises it melts gaps in the surrounding rock As more magma rises a large reservoir forms as close as 2 miles below the surface (magma chamber) ...
... earth’s surface slowly begins to rise to the surface As the magma rises it melts gaps in the surrounding rock As more magma rises a large reservoir forms as close as 2 miles below the surface (magma chamber) ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... How It All Starts • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...
... How It All Starts • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...
Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mid-ocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic ...
... Students know evidence of plate tectonics is derived from the fit of the continents; the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mid-ocean ridges; and the distribution of fossils, rock types, and ancient climatic ...
Fukutoku-Okanoba, Japan
... 6-3 Volcanic Landforms • Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus. Rock and other materials formed from lava create a variety of landforms including: – Shield Volcano: layers of lava that eventually build up into a sloping mountain. – Cinder Cone: Materials ...
... 6-3 Volcanic Landforms • Some volcanic landforms are formed when lava flows build up mountains and plateaus. Rock and other materials formed from lava create a variety of landforms including: – Shield Volcano: layers of lava that eventually build up into a sloping mountain. – Cinder Cone: Materials ...
Volcanoes - geographylyndon
... boundaries. • Cone volcanoes are tall and steep-sided. • Cone volcanoes are formed by eruptions of thick, viscous (sticky) lava. • The thick lava moves relatively slowly and hardens quickly to form new rock - this explains the formation of a cone shape. • Eruptions tend to be violent ...
... boundaries. • Cone volcanoes are tall and steep-sided. • Cone volcanoes are formed by eruptions of thick, viscous (sticky) lava. • The thick lava moves relatively slowly and hardens quickly to form new rock - this explains the formation of a cone shape. • Eruptions tend to be violent ...
Document
... Lahars are fast-moving mud flows. Two things together make a lahar: Thick, loose deposits of volcanic ash and water. The water can come in several ways: - A major rainstorm dumps water on the volcano. - An eruption melts large amounts of snow and ice on the flanks of the volcano. Lahars are more da ...
... Lahars are fast-moving mud flows. Two things together make a lahar: Thick, loose deposits of volcanic ash and water. The water can come in several ways: - A major rainstorm dumps water on the volcano. - An eruption melts large amounts of snow and ice on the flanks of the volcano. Lahars are more da ...
Word
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
Geol 101: Physical Geology PAST EXAM QUESTIONS LECTURE 8
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
... 8. The three main classes of rocks are classified by how they formed. (1) _________ rocks form from molten rock. (2) _________ rocks form by surface processes. (3) _________ rocks form from existing rocks that are changed by pressure and temperature. A. (1) igneous (2) sedimentary (3) metamorphic B. ...
Week 10
... viscous than felsic (high silica content) magmas. Thus it is relatively easy for gases in such magmas to escape. Thus are large pressures likely to develop? ...
... viscous than felsic (high silica content) magmas. Thus it is relatively easy for gases in such magmas to escape. Thus are large pressures likely to develop? ...
Warm-up #49 Apr. 3
... • Why do volcanoes like this erupt so explosively, while others like Kilauea in Hawaii are relatively quiet? ...
... • Why do volcanoes like this erupt so explosively, while others like Kilauea in Hawaii are relatively quiet? ...
File
... plenty of warning signs way before the eruption. Some but not many did escape in time. Most were overcome by the gasses before the actual eruption. Because ash covered the sky, the visibility was so poor that people were disoriented and stopped in their tracks. The weight from the ash and debris col ...
... plenty of warning signs way before the eruption. Some but not many did escape in time. Most were overcome by the gasses before the actual eruption. Because ash covered the sky, the visibility was so poor that people were disoriented and stopped in their tracks. The weight from the ash and debris col ...
Unit 3 Section 2 Volcanoes Answer Key - WAHS
... A composite cone forms by many eruptions of material with medium or high-silica content. They erupt violently when pressure builds up in the magma. After the initial explosion, lots of gooey (viscous) lava oozes out of the top. The volcano becomes quiet for a while, but pressure builds and repeats t ...
... A composite cone forms by many eruptions of material with medium or high-silica content. They erupt violently when pressure builds up in the magma. After the initial explosion, lots of gooey (viscous) lava oozes out of the top. The volcano becomes quiet for a while, but pressure builds and repeats t ...
S05_4359_L24
... Geothermal Resources (Relatively Clean & Nearly Renewable) Direct heat & Electric energy production Modern usage started at Larderello Italy 1904, electrical power generated by natural steam discharge. Clear Lake, CA (Geysers) is the world’s largest productive geothermal system (~1 GW, enough to pow ...
... Geothermal Resources (Relatively Clean & Nearly Renewable) Direct heat & Electric energy production Modern usage started at Larderello Italy 1904, electrical power generated by natural steam discharge. Clear Lake, CA (Geysers) is the world’s largest productive geothermal system (~1 GW, enough to pow ...
Chapter 2, Section 8
... a flow, the lava can drain out. A hollow tube remains behind. Basalt flows can move at speeds of up to 10 km/h (kilometers per hour) on steep slopes. On a shallow slope, basalt flows move less than 1 km/h. Basalt flows within channels or lava tubes can travel very fast. They can reach speeds of 45 k ...
... a flow, the lava can drain out. A hollow tube remains behind. Basalt flows can move at speeds of up to 10 km/h (kilometers per hour) on steep slopes. On a shallow slope, basalt flows move less than 1 km/h. Basalt flows within channels or lava tubes can travel very fast. They can reach speeds of 45 k ...
1 - Daniel O`Brien
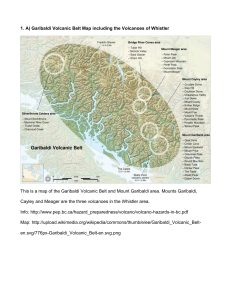
... Belt was caused by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Explorer plates under the North American Plate along the Cascadia subduction zone. It is a 1,094 km-long fault, which extends 80 km off the west-coast of the Pacific Northwest from northern California to Vancouver Island, British Co ...
... Belt was caused by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate and the Explorer plates under the North American Plate along the Cascadia subduction zone. It is a 1,094 km-long fault, which extends 80 km off the west-coast of the Pacific Northwest from northern California to Vancouver Island, British Co ...
volcanoes stations
... The grain size of crystalline igneous rocks can be separated into three broad categories. Coarse-grained igneous rocks have individual grains (crystals) that are visible to the naked eye. Grains can range from millimeters to centimeters in diameter. The grains form an interlocking network. Fine-grai ...
... The grain size of crystalline igneous rocks can be separated into three broad categories. Coarse-grained igneous rocks have individual grains (crystals) that are visible to the naked eye. Grains can range from millimeters to centimeters in diameter. The grains form an interlocking network. Fine-grai ...
Earthquakes originate at a point
... Rapidly moving volcanic material. Speeds up to 200km/h May contain hot, poisonous gases 3. List and describe the three types of volcanoes. What are they made out of? Shield Volcano • Broad Gentle Sloping Sides • Non-Explosive ...
... Rapidly moving volcanic material. Speeds up to 200km/h May contain hot, poisonous gases 3. List and describe the three types of volcanoes. What are they made out of? Shield Volcano • Broad Gentle Sloping Sides • Non-Explosive ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... How to recognize a volcanic rock formed from a gas-rich lava? ...
... How to recognize a volcanic rock formed from a gas-rich lava? ...
Level Mountain

Level Mountain is a massive shield volcano in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just southeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about 50 km (31 mi) north of Mount Edziza. It lies on the Nahlin Plateau, comprising a series of buttes and ridges. The shield is lightly glaciated, as compared to the Coast Mountains just to the west. The only named summit of Level Mountain is Meszah Peak on the north side of the shield with an elevation of 2,190 m (7,185 ft), making it the highest point of Level Mountain. Immediately to the west, however, are the Heart Peaks, a related volcanic range just east of the Sheslay River, which is the edge of the Nahlin Plateau.Level Mountain rises above adjacent forested lowlands and undulating alpine areas surround the steeper central peaks. Streams that originate from these peaks drain across the Nahlin Plateau.