AP Physics Ch 12-15 – Thermal Physics
... If three identical samples of an ideal gas are taken from initial state I to final state F along the paths IAF, IF, and IBF as shown in the pV-diagram above. Which of the following statements must be true? (A) Point F is at a higher temperature than point B. (B) No work is done by the gas along pat ...
... If three identical samples of an ideal gas are taken from initial state I to final state F along the paths IAF, IF, and IBF as shown in the pV-diagram above. Which of the following statements must be true? (A) Point F is at a higher temperature than point B. (B) No work is done by the gas along pat ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-ISSN: 2278-1684
... results for bottom heated fin arrays have been presented for different fin spacings, fin heights, and modified Rayleigh numbers, and the effects on heat transfer have been investigated. It has been determined that the mixed convection heat transfer depends on the fin height and spacing. The effects ...
... results for bottom heated fin arrays have been presented for different fin spacings, fin heights, and modified Rayleigh numbers, and the effects on heat transfer have been investigated. It has been determined that the mixed convection heat transfer depends on the fin height and spacing. The effects ...
Physics, Chapter 18: Transfer of Heat
... water moves down to replace it. The colder water, in turn, is heated; once hot, it rises because of its smaller density, thus setting up a circulation of the liquid. During this circulation the warmer parts of the liquid mix with the cooler parts, and in a short time a fairly uniform temperature is ...
... water moves down to replace it. The colder water, in turn, is heated; once hot, it rises because of its smaller density, thus setting up a circulation of the liquid. During this circulation the warmer parts of the liquid mix with the cooler parts, and in a short time a fairly uniform temperature is ...
UNIT I PART B 1). (i). A spherical balloon of diameter
... the system, they will get neutralized to attain the condition of equilibrium. Two systems are said to be in mechanical equilibrium with each other when their pressures are same. 2) Chemical equilibrium: The system is said to be in chemical equilibrium when there are no chemical reactions going on w ...
... the system, they will get neutralized to attain the condition of equilibrium. Two systems are said to be in mechanical equilibrium with each other when their pressures are same. 2) Chemical equilibrium: The system is said to be in chemical equilibrium when there are no chemical reactions going on w ...
3.1 Thermal concepts (PPT)
... • Cocoa butter is unique among the fats in that it is very regular in composition; whereas most other fats are actually mixtures. This gives it a very definite point; unlike butter, which softens gradually. As it melts in your mouth, it absorbs latent heat. This makes chocolate bars taste "cool". Co ...
... • Cocoa butter is unique among the fats in that it is very regular in composition; whereas most other fats are actually mixtures. This gives it a very definite point; unlike butter, which softens gradually. As it melts in your mouth, it absorbs latent heat. This makes chocolate bars taste "cool". Co ...
ME(HT)-0708 - Andhra University
... Discuss different methods of boundary layer control. Explain the significance of boundary layer suction in delying the transition from laminar to turbulent flow. Distinguish a steady flow from an unsteady flow with examples. Water at 30ºC and atmospheric pressure flows through a smooth pipe of 5 cm ...
... Discuss different methods of boundary layer control. Explain the significance of boundary layer suction in delying the transition from laminar to turbulent flow. Distinguish a steady flow from an unsteady flow with examples. Water at 30ºC and atmospheric pressure flows through a smooth pipe of 5 cm ...
16.2 Heat and Thermodynamics
... • Air at the bottom of an oven heats up, expands, and becomes less dense. The hot air rises ____________. • Rising hot air cools as it moves away _________ from the heat source. • The cool air contracts, become sinks more dense, and _________ ...
... • Air at the bottom of an oven heats up, expands, and becomes less dense. The hot air rises ____________. • Rising hot air cools as it moves away _________ from the heat source. • The cool air contracts, become sinks more dense, and _________ ...
Heat - Quia
... Theuse units for Q, t must in joules, calories, consistent and andm with mmust must those be bein based ingrams. kilograms. on the value of the constant c. ...
... Theuse units for Q, t must in joules, calories, consistent and andm with mmust must those be bein based ingrams. kilograms. on the value of the constant c. ...
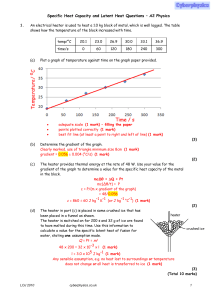
Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat Questions
... Ep = mgh = 0.025 × 9.81 × 1.2 = 0.29(4) J (1 mark) the total change in potential energy after 50 inversions, total change of energy (= 50 × 0.294) = 15 J (1 mark) (14.7 J) (use of 0.29 gives 14.(5) J) the specific heat capacity of the lead. ΔQ = mcΔθ 14.7 = 0.025 × c × 4.5 (1 mark) c = 131 J kg−1 K ...
... Ep = mgh = 0.025 × 9.81 × 1.2 = 0.29(4) J (1 mark) the total change in potential energy after 50 inversions, total change of energy (= 50 × 0.294) = 15 J (1 mark) (14.7 J) (use of 0.29 gives 14.(5) J) the specific heat capacity of the lead. ΔQ = mcΔθ 14.7 = 0.025 × c × 4.5 (1 mark) c = 131 J kg−1 K ...
q 2 - q 1
... ▪ It is interesting to note that the first steam engine ( which is a devices that transfer heat into work using steam as medium ) was built in 1769 and was operational for considerable number of years before introducing the principles of reversible and irreversible ...
... ▪ It is interesting to note that the first steam engine ( which is a devices that transfer heat into work using steam as medium ) was built in 1769 and was operational for considerable number of years before introducing the principles of reversible and irreversible ...
Heat Exchangers Lecture
... 5- plate and frame (or just plate) heat exchanger • The plate and frame (or just plate) heat exchanger is an innovative type of heat exchanger that has found widespread use. It consists of a series of plates with corrugated flat flow passages (Fig. 6). The hot and cold fluids flow in alternate passa ...
... 5- plate and frame (or just plate) heat exchanger • The plate and frame (or just plate) heat exchanger is an innovative type of heat exchanger that has found widespread use. It consists of a series of plates with corrugated flat flow passages (Fig. 6). The hot and cold fluids flow in alternate passa ...
(Chapter 9 - Temperature)
... Banana ice cream freezes at -2ºC and has a heat of fusion of 290 kJ/kg. When frozen its specific heat capacity is 1.9 kJ/kgºC and when melted its specific heat capacity is 3.3 kJ/kgºC. a) A batch of ice cream is mixed at an initial temperature of 18ºC. How much heat is required to make 500-kg of ban ...
... Banana ice cream freezes at -2ºC and has a heat of fusion of 290 kJ/kg. When frozen its specific heat capacity is 1.9 kJ/kgºC and when melted its specific heat capacity is 3.3 kJ/kgºC. a) A batch of ice cream is mixed at an initial temperature of 18ºC. How much heat is required to make 500-kg of ban ...
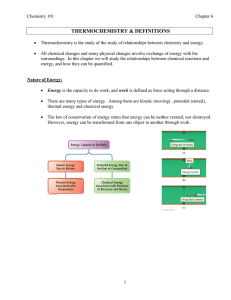
THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS
... When a chemical reaction occurs at constant pressure–for example in an open beaker–the energy evolved can be in the form of both heat and work. The energy change (E) for the reaction is the sum of the heat and work exchanged during the reaction. ...
... When a chemical reaction occurs at constant pressure–for example in an open beaker–the energy evolved can be in the form of both heat and work. The energy change (E) for the reaction is the sum of the heat and work exchanged during the reaction. ...
The First Law of Thermodynamics
... expansion at constant pressure until the volume is 2.5 L, after which is cooled at constant volume until its pressure is 1 atm. It is then compressed at constant pressure until the volume is again 1L, after which it is heated at constant volume until it is back in its original state. Find (a) the wo ...
... expansion at constant pressure until the volume is 2.5 L, after which is cooled at constant volume until its pressure is 1 atm. It is then compressed at constant pressure until the volume is again 1L, after which it is heated at constant volume until it is back in its original state. Find (a) the wo ...
Work Done by an Expanding Gas
... work, the work in thermodynamics is defined as the work done by the system on the exterior world, and not vice versa as is done in the rest of classical mechanics. In classical mechanics, one always considers the work done on a system by the outside world. Rarely does one think about the work done b ...
... work, the work in thermodynamics is defined as the work done by the system on the exterior world, and not vice versa as is done in the rest of classical mechanics. In classical mechanics, one always considers the work done on a system by the outside world. Rarely does one think about the work done b ...
Heat wave

A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is measured relative to the usual weather in the area and relative to normal temperatures for the season. Temperatures that people from a hotter climate consider normal can be termed a heat wave in a cooler area if they are outside the normal climate pattern for that area.The term is applied both to routine weather variations and to extraordinary spells of heat which may occur only once a century. Severe heat waves have caused catastrophic crop failures, thousands of deaths from hyperthermia, and widespread power outages due to increased use of air conditioning. A heat wave is considered extreme weather, and a danger because heat and sunlight may overheat the human body.