Heat Transfer
... aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temperature of the system is 30.5°C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. ...
... aluminum calorimeter cup. (We do not need to know the mass of the insulating jacket since we assume the air space between it and the cup insulates it well, so that its temperature does not change significantly.) The final temperature of the system is 30.5°C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. ...
Example
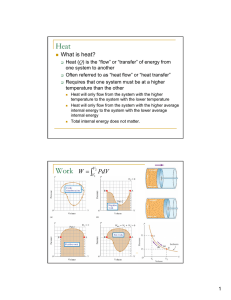
... 18.7 Temperature, Heat and Thermal Energy: Internal energy: all of the energy belonging to a system (while stationary) including nuclear energy, chemical energy, elastic energy as well as thermal energy. Thermal energy: is that portion of internal energy that consists of kinetic and potential energ ...
... 18.7 Temperature, Heat and Thermal Energy: Internal energy: all of the energy belonging to a system (while stationary) including nuclear energy, chemical energy, elastic energy as well as thermal energy. Thermal energy: is that portion of internal energy that consists of kinetic and potential energ ...
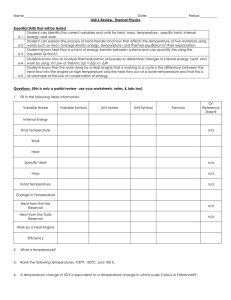
Thermal Energy FlowData set table 1
... Such a roof is typically composed of growing grass and plants atop the main roof which is adequately protected with a membrane to allow for irrigation. TPO is manufactured using ethylene propylene rubber, a material that has excellent flexibility as well as durability regardless of the weather type. ...
... Such a roof is typically composed of growing grass and plants atop the main roof which is adequately protected with a membrane to allow for irrigation. TPO is manufactured using ethylene propylene rubber, a material that has excellent flexibility as well as durability regardless of the weather type. ...
Numerical investigation on thermal non
... condensation in present of NCG, a simulation model, based on the stagnant film model and gas-liquid two-phase conservation equations coupled with flow regime-dependent correlations, is developed to represent the heat, mass and momentum transfer at the gas-liquid inter-phase. A good agreement between ...
... condensation in present of NCG, a simulation model, based on the stagnant film model and gas-liquid two-phase conservation equations coupled with flow regime-dependent correlations, is developed to represent the heat, mass and momentum transfer at the gas-liquid inter-phase. A good agreement between ...
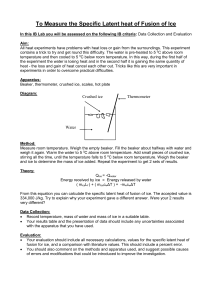
To Measure the Specific Latent heat of Fusion of Ice
... From this equation you can calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. The accepted value is 334,000 J/kg. Try to explain why your experiment gave a different answer. Were your 2 results very different? Data Collection: Record temperature, mass of water and mass of ice in a suitable table ...
... From this equation you can calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. The accepted value is 334,000 J/kg. Try to explain why your experiment gave a different answer. Were your 2 results very different? Data Collection: Record temperature, mass of water and mass of ice in a suitable table ...
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Review
... 6. Explain what happens at the surface of a liquid according to the kinetic theory as thermal energy is added to the liquid. ...
... 6. Explain what happens at the surface of a liquid according to the kinetic theory as thermal energy is added to the liquid. ...
Flat Plate Boundary Layer
... A radiator is a type of heat exchanger. It is designed to transfer heat from the hot coolant that flows through it to the air blown through it by the fan. Most modern cars use aluminum radiators. These radiators are made by brazing thin aluminum fins to flattened aluminum tubes. The coolant flows fr ...
... A radiator is a type of heat exchanger. It is designed to transfer heat from the hot coolant that flows through it to the air blown through it by the fan. Most modern cars use aluminum radiators. These radiators are made by brazing thin aluminum fins to flattened aluminum tubes. The coolant flows fr ...
Thermochemistry
... • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
... • calorie(c)-amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one Celsius degree. (Food you eat is measured in Kilocalories which is abbreviated C). • Joule (J)-the SI unit of energy • 1 c=4.184J ...
Abrasive: A hard material used to grind, cut or
... Grain: Individual crystal in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundary: The boundary between grains (or crystals) which are misoriented with respect to one another. Green ceramic body: Ceramic object which is dried but not fired. Ground state: Lowest electron energy state. Hardness: Resistance to d ...
... Grain: Individual crystal in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundary: The boundary between grains (or crystals) which are misoriented with respect to one another. Green ceramic body: Ceramic object which is dried but not fired. Ground state: Lowest electron energy state. Hardness: Resistance to d ...
What is the DSC used for
... The cell sensor consists of a constantan body with separate raised platforms or vessel to hold the sample and reference (Fig. 1). The platforms are connected to the heating block (base) by thin-walled tubes that create thermal resistances between the platforms and the base. Area detectors (thermocou ...
... The cell sensor consists of a constantan body with separate raised platforms or vessel to hold the sample and reference (Fig. 1). The platforms are connected to the heating block (base) by thin-walled tubes that create thermal resistances between the platforms and the base. Area detectors (thermocou ...
thermodynamics, heat and mass transfer
... FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (CM) 1. During the working stroke of an engine the heat transferred out of the system was 150 kJ/kg of working substance. The internal energy also decreased by 400 kJ/kg of working substance. Determine the work done and state whether it is work done on or by the engine. 2 ...
... FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (CM) 1. During the working stroke of an engine the heat transferred out of the system was 150 kJ/kg of working substance. The internal energy also decreased by 400 kJ/kg of working substance. Determine the work done and state whether it is work done on or by the engine. 2 ...
exhaustion - City of Burnsville
... BEAT THE HEAT (EXHAUSTION) As the mercury rises, not only do we need to be aware of the temperature, but also the heat index in order to keep our bodies from suffering heat exhaustion. The heat index combines temperature and humidity and measures the combined temperature felt by the body. The coolin ...
... BEAT THE HEAT (EXHAUSTION) As the mercury rises, not only do we need to be aware of the temperature, but also the heat index in order to keep our bodies from suffering heat exhaustion. The heat index combines temperature and humidity and measures the combined temperature felt by the body. The coolin ...
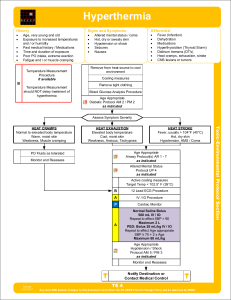
Hyperthermia
... The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (athletes, hard labor), the patient may have sweated profusely and be wet on exam. Rapid cooling takes precedence over transport as early cooling decreases morbidity and mortality. If a ...
... The young and elderly are more prone to be dry with no sweating. Exertional Heat Stroke: In exertional heat stroke (athletes, hard labor), the patient may have sweated profusely and be wet on exam. Rapid cooling takes precedence over transport as early cooling decreases morbidity and mortality. If a ...
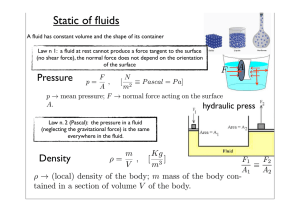
Static of fluids
... or give a quantity Q of heat where m is the mass and cL is the latent heat. ...
... or give a quantity Q of heat where m is the mass and cL is the latent heat. ...
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY OF WATER
... Where E is the electrical energy, I is the current through the resistor, V is the voltage across it and t is the time interval during which the energy is transferred. If this energy is used to heat a cretin mass of water, m, the heat which is absorbed by water is given by, ...
... Where E is the electrical energy, I is the current through the resistor, V is the voltage across it and t is the time interval during which the energy is transferred. If this energy is used to heat a cretin mass of water, m, the heat which is absorbed by water is given by, ...
Tutorial 3
... 1. A 3-mm-diameter and 5-m-long electric wire is tightly wrapped with a 2-mm thick plastic cover whose thermal conductivity is k = 0.15 W/m · °C. Electrical measurements indicate that a current of 10 A passes through the wire and there is a voltage drop of 8 V along the wire. If the insulated wire i ...
... 1. A 3-mm-diameter and 5-m-long electric wire is tightly wrapped with a 2-mm thick plastic cover whose thermal conductivity is k = 0.15 W/m · °C. Electrical measurements indicate that a current of 10 A passes through the wire and there is a voltage drop of 8 V along the wire. If the insulated wire i ...