Le Châtelier`s Principle
... Increase in the concentration of sulfur dioxide: The equilibrium shifts right to use up the extra SO2, producing more sulfur trioxide and using up some oxygen. Decreasing the partial pressure of sulfur trioxide: This is equivalent to decreasing the concentration of sulfur trioxide. The equilibrium w ...
... Increase in the concentration of sulfur dioxide: The equilibrium shifts right to use up the extra SO2, producing more sulfur trioxide and using up some oxygen. Decreasing the partial pressure of sulfur trioxide: This is equivalent to decreasing the concentration of sulfur trioxide. The equilibrium w ...
system
... •Given two out of three of any of the following quantities, be able to calculate the third: change in heat for the system, change in work for the system, overall change in energy for the system •Given initial heat and final heat, be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a system •Be able to d ...
... •Given two out of three of any of the following quantities, be able to calculate the third: change in heat for the system, change in work for the system, overall change in energy for the system •Given initial heat and final heat, be able to calculate the change in enthalpy for a system •Be able to d ...
Energy Notes
... (continue on this slide P2,4) • Heat – Energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference between ...
... (continue on this slide P2,4) • Heat – Energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference between ...
Heat Transfer Equipment Wort kettle – External calandria
... How would the rate of heat transfer change if a 2.5 cm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.05 W/m.K) were added to the “low” temperature side of the ...
... How would the rate of heat transfer change if a 2.5 cm thick layer of insulation (k = 0.05 W/m.K) were added to the “low” temperature side of the ...
Chapter 13: The Atmosphere Learning Target Vocabulary Word
... I can identify the four main layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics . . . Scientists divide Earth’s atmosphere into ________________ main layers according to changes in ______________________. I can explain the characteristics of the atmosphere's layers . . . Earth’s weather occurs in th ...
... I can identify the four main layers of the atmosphere and their characteristics . . . Scientists divide Earth’s atmosphere into ________________ main layers according to changes in ______________________. I can explain the characteristics of the atmosphere's layers . . . Earth’s weather occurs in th ...
Thermo Chemistry
... In addition to the sources of errors and precautions given in experiment 1, the following are the additional ones: 1. Allow the temperature of water in calorimeter to attain a steady valve while the test tube containing salt is kept in it. Otherwise record the temperature every 30 seconds and obtain ...
... In addition to the sources of errors and precautions given in experiment 1, the following are the additional ones: 1. Allow the temperature of water in calorimeter to attain a steady valve while the test tube containing salt is kept in it. Otherwise record the temperature every 30 seconds and obtain ...
module 7
... Second Law considerations but, for the undergraduate student, it is generally more satisfying to arbitrarily choose a set of temperatures and check the results from the two equations. The only restrictions that we place on the case is that it be physically possible for parallel flow, i.e. 1 and 2 ...
... Second Law considerations but, for the undergraduate student, it is generally more satisfying to arbitrarily choose a set of temperatures and check the results from the two equations. The only restrictions that we place on the case is that it be physically possible for parallel flow, i.e. 1 and 2 ...
Thermo chemistry Dealing with
... Energy is the driving force for changes. A change often is associated with a certain amount of energy and amounts of energy can be measured according to the quantities changed. Like other quantities, energy is an extensive property, unlike temperature. Heat is energy in transfer or energy transferre ...
... Energy is the driving force for changes. A change often is associated with a certain amount of energy and amounts of energy can be measured according to the quantities changed. Like other quantities, energy is an extensive property, unlike temperature. Heat is energy in transfer or energy transferre ...
Physics 231 Lab 7 Thermal Energy and Air Resistance
... any macroscopically-scaled model. First there’s the thermal exchange of energy that occurs when objects of different temperatures interact. Second there’s energy dissipation, or more specifically, drag. (Equipment: metal slugs, Styrofoam calorimeter cups, pitcher of room-temp water, beakers of boili ...
... any macroscopically-scaled model. First there’s the thermal exchange of energy that occurs when objects of different temperatures interact. Second there’s energy dissipation, or more specifically, drag. (Equipment: metal slugs, Styrofoam calorimeter cups, pitcher of room-temp water, beakers of boili ...
Air and Conduction Cooling for 3U COTS Cards
... large amounts of heat are being moved across large planes or long distances a composite can be a good solution. But trying to move heat through the thickness is more difficult. There are several research groups working on developing materials ...
... large amounts of heat are being moved across large planes or long distances a composite can be a good solution. But trying to move heat through the thickness is more difficult. There are several research groups working on developing materials ...
Heat of Reaction
... change. It will be either Endo- or Exothermic. To understand this concept, consider the ...
... change. It will be either Endo- or Exothermic. To understand this concept, consider the ...
Take Control of Your Thermostat – During the
... normal, our temperature should remain within the range of 98–102◦F (36.5-37.5 ). Temperature is lowest between 2 and 4 am and typically increases slightly as the day goes on. Peak temperature is reached between 6 and 10 p.m. We expend energy – or calories – preserving our internal core temperature w ...
... normal, our temperature should remain within the range of 98–102◦F (36.5-37.5 ). Temperature is lowest between 2 and 4 am and typically increases slightly as the day goes on. Peak temperature is reached between 6 and 10 p.m. We expend energy – or calories – preserving our internal core temperature w ...
EQ: How can heat be transferred from one place to another?
... temperature if not eaten quickly. BUT!!! Did the food cool or did the surrounding air warm? Why? In science, there is no such thing as coldness. Instead, the matter grows colder as thermal energy flows from it and transfers to another object/form of matter. Heat transfer occurs only in one direction ...
... temperature if not eaten quickly. BUT!!! Did the food cool or did the surrounding air warm? Why? In science, there is no such thing as coldness. Instead, the matter grows colder as thermal energy flows from it and transfers to another object/form of matter. Heat transfer occurs only in one direction ...
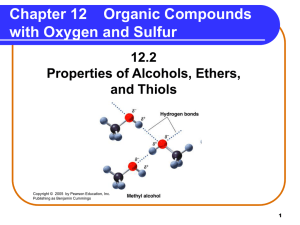
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... groups. • form hydrogen bonds with other alcohol molecules. • have higher boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass. ...
... groups. • form hydrogen bonds with other alcohol molecules. • have higher boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass. ...
Convection Currents and the Mantle
... As you already know, the earth's mantle contains two layers; the stratosphere (tough liquid part of the outer mantle) and the lithosphere (the stiffer outer mantle and the crust). Because of the intense pressure and temperature in the mantle convection currents occur. To learn about what influence t ...
... As you already know, the earth's mantle contains two layers; the stratosphere (tough liquid part of the outer mantle) and the lithosphere (the stiffer outer mantle and the crust). Because of the intense pressure and temperature in the mantle convection currents occur. To learn about what influence t ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... 1. Determine the pressure of dry hydrogen gas collected in each of the following eudiometers. Assume an atmospheric pressure of 756.0 torr and a temperature of 22.0C. Water vapor pressure at 22.0C is 19.8 torr. ...
... 1. Determine the pressure of dry hydrogen gas collected in each of the following eudiometers. Assume an atmospheric pressure of 756.0 torr and a temperature of 22.0C. Water vapor pressure at 22.0C is 19.8 torr. ...
Energy efficiency in architecture
... sources and sinks e.g. solar radiation, outside air, sky, wet surfaces, vegetation, internal gains etc. Energy flows in these systems are by natural means such as by radiation, conduction, convection with minimal or no use of mechanical means. The solar passive systems thus, vary from one climate to ...
... sources and sinks e.g. solar radiation, outside air, sky, wet surfaces, vegetation, internal gains etc. Energy flows in these systems are by natural means such as by radiation, conduction, convection with minimal or no use of mechanical means. The solar passive systems thus, vary from one climate to ...
MECHANICAL AND ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENTS
... handling systems moving less air reduces the energy used by fans. One result can be low distribution efficiency, which causes poorly mixed air within the occupied spaces. With local (individual space) air filtering equipment, both a high circulation rate and proper air mixing are achievable. Each un ...
... handling systems moving less air reduces the energy used by fans. One result can be low distribution efficiency, which causes poorly mixed air within the occupied spaces. With local (individual space) air filtering equipment, both a high circulation rate and proper air mixing are achievable. Each un ...
7. Heat capacity
... When C is large > a given amount of heating results in only a small temperature rise (the system has a large capacity for heat) The heat capacity depends on conditions: - system constrained to have constant volume > Cv (heat capacity at constant volume, or isochoric heat capacity) - system subject t ...
... When C is large > a given amount of heating results in only a small temperature rise (the system has a large capacity for heat) The heat capacity depends on conditions: - system constrained to have constant volume > Cv (heat capacity at constant volume, or isochoric heat capacity) - system subject t ...
THE GASEOUS STATE
... molecules. • These forces are much weaker than chemical bonds that hold atoms together. • And they are nearly nonexistent between gas molecules at room temp. and pressure. • However, they are important in liquids and solids. ...
... molecules. • These forces are much weaker than chemical bonds that hold atoms together. • And they are nearly nonexistent between gas molecules at room temp. and pressure. • However, they are important in liquids and solids. ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... a material, with any bulk motion of the material playing no role in the transfer. ...
... a material, with any bulk motion of the material playing no role in the transfer. ...