How Ebola and Marburg Viruses Battle the Immune System [open
... Figure 1 | System overview of filoviral pathogenesis. Initially, productive infection (that is, that which results in more viral progeny) occurs primarily in dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes and macrophages. All infected cells can be at least partially impaired in interferon (IFN) production, but so ...
... Figure 1 | System overview of filoviral pathogenesis. Initially, productive infection (that is, that which results in more viral progeny) occurs primarily in dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes and macrophages. All infected cells can be at least partially impaired in interferon (IFN) production, but so ...
A role for antigen in the maintenance of immunological memory
... 75 years after an attack of yellow fever, were found to have circulating antibodies to the yellow fever virus18. This virus is thought to be completely eliminated by the immune response, although the longevity of the response leads me to doubt this. The detection of serum antibody for 25 or 30 years ...
... 75 years after an attack of yellow fever, were found to have circulating antibodies to the yellow fever virus18. This virus is thought to be completely eliminated by the immune response, although the longevity of the response leads me to doubt this. The detection of serum antibody for 25 or 30 years ...
Antibody responses of variable lymphocyte receptors in the lamprey
... combinatorial assembly of diverse antigen receptor genes encoding variable lymphocyte receptors of two types: VLRA and VLRB. We describe here the VLRB-bearing lineage of lymphocytes in sea lamprey. These cells responded to repetitive carbohydrate or protein determinants on bacteria or mammalian cell ...
... combinatorial assembly of diverse antigen receptor genes encoding variable lymphocyte receptors of two types: VLRA and VLRB. We describe here the VLRB-bearing lineage of lymphocytes in sea lamprey. These cells responded to repetitive carbohydrate or protein determinants on bacteria or mammalian cell ...
PD-L1 checkpoint blockade prevents immune dysfunction and
... P 5 .0315) of aPD-L1–treated mice compared with isotype controls (Figure 1D and supplemental Figure 1), indicating effective tumor control. Lymph nodes, the primary site of disease in humans, are barely affected in the Em-TCL1 AT mouse model when the transplantation regimen routinely applied by our ...
... P 5 .0315) of aPD-L1–treated mice compared with isotype controls (Figure 1D and supplemental Figure 1), indicating effective tumor control. Lymph nodes, the primary site of disease in humans, are barely affected in the Em-TCL1 AT mouse model when the transplantation regimen routinely applied by our ...
Dendritic Cell Biology - Wiley-VCH
... are there distinct dendritic cells that are devoted to the control of these different key outcomes of antigen presentation? Second, how must dendritic cells differentiate to become potent stimulators of Th1 type CD4 responses and CD8 killer responses? It has been believed for some time that this req ...
... are there distinct dendritic cells that are devoted to the control of these different key outcomes of antigen presentation? Second, how must dendritic cells differentiate to become potent stimulators of Th1 type CD4 responses and CD8 killer responses? It has been believed for some time that this req ...
An Innate Immune System for the Protection of
... capability of the acquired immune system is not perfect – some antigens will go unrecognized, – while that of the innate immune system is perfect. Every artificial immune system is based on some partition of a given set of possible actions into two subsets: the set of self and the set of non-self ac ...
... capability of the acquired immune system is not perfect – some antigens will go unrecognized, – while that of the innate immune system is perfect. Every artificial immune system is based on some partition of a given set of possible actions into two subsets: the set of self and the set of non-self ac ...
王青青_Tumor Immunology
... Immune mechanisms of tumor rejection • Cell-mediated immunity plays a key role in tumor rejection. • Humoral immunity (antibodies) and innate immunity also play a role in the defense against tumors. ...
... Immune mechanisms of tumor rejection • Cell-mediated immunity plays a key role in tumor rejection. • Humoral immunity (antibodies) and innate immunity also play a role in the defense against tumors. ...
Allergy
... Providing antigenic homogeneity and identity of the body is the main objective of the NBI system. Upon detection of foreign antigenic information carrier (virus, bacteria, parasites, tumor cells and other abnormal protein.) Immune system usually provides its neutralization, destruction and removal f ...
... Providing antigenic homogeneity and identity of the body is the main objective of the NBI system. Upon detection of foreign antigenic information carrier (virus, bacteria, parasites, tumor cells and other abnormal protein.) Immune system usually provides its neutralization, destruction and removal f ...
Review: The microstructure of secondary lymphoid organs that
... and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues. Because the immune response is associated with dynamic cellular movements, a study of immune cell trafficking in the secondary lymphoid organs should provide crucial information for understanding the host defense system and the pathogenesis of inflammatory dise ...
... and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues. Because the immune response is associated with dynamic cellular movements, a study of immune cell trafficking in the secondary lymphoid organs should provide crucial information for understanding the host defense system and the pathogenesis of inflammatory dise ...
Outline/ Active Learning Objectives - Rose
... Figure 10.1 illustrates the cells of the immune system. Table 10.2 identifies neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells as the main cells capable of phagocytosis, an ongoing process of the innate immunity. Phagocytes are activated by T cell cytokines, and can directly sense the pathogens through ...
... Figure 10.1 illustrates the cells of the immune system. Table 10.2 identifies neutrophils, macrophages and dendritic cells as the main cells capable of phagocytosis, an ongoing process of the innate immunity. Phagocytes are activated by T cell cytokines, and can directly sense the pathogens through ...
The Immune System
... • The thymus produces hormones that promote the proliferation and maturation of T cells. • Peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs – Lymphoid structures scattered in the respiratory, gastrointestinal, genitourinary tracts, tonsils, lymph nodes, and spleen ...
... • The thymus produces hormones that promote the proliferation and maturation of T cells. • Peripheral (secondary) lymphoid organs – Lymphoid structures scattered in the respiratory, gastrointestinal, genitourinary tracts, tonsils, lymph nodes, and spleen ...
Blood vessels: the endothelium
... transport albumin conjugated to lipids into tissues. To accomplish this, endothelial cells express a receptor that binds more tightly to albumin-lipid than unbound albumin. Unlike endocytosis in other cells that utilize clathrin, endothelial cells employ a membrane proteins called caveolin. Caveolin ...
... transport albumin conjugated to lipids into tissues. To accomplish this, endothelial cells express a receptor that binds more tightly to albumin-lipid than unbound albumin. Unlike endocytosis in other cells that utilize clathrin, endothelial cells employ a membrane proteins called caveolin. Caveolin ...
Syllabus
... current topics in infections, immunological diseases and public health. We will learn how the immune system works to prevent, resolve, or exacerbate disease. A general overview of the immune system (including cell types and functions) will be covered in the beginning in order to demonstrate how immu ...
... current topics in infections, immunological diseases and public health. We will learn how the immune system works to prevent, resolve, or exacerbate disease. A general overview of the immune system (including cell types and functions) will be covered in the beginning in order to demonstrate how immu ...
The immune system and new therapies for
... and blood and have the potential to consume passing antigens and immune complexes by cleaning up debris throughout the body’s immune system. This ability is one of phagocytosis and other cells in the immune system can also undertake this role. When the macrophage works as an APC it uses enzymes to p ...
... and blood and have the potential to consume passing antigens and immune complexes by cleaning up debris throughout the body’s immune system. This ability is one of phagocytosis and other cells in the immune system can also undertake this role. When the macrophage works as an APC it uses enzymes to p ...
Global Dendritic Cell Cancer Vaccine Market Outlook 2020 Brochure
... ex-vivo clinical trials in murine models have now gone on to rephrasing the molecular mechanism of the immune system, enriching our immunological knowledge and empowering our ability to counteract the tumor growth. Dendritic cells have also been successful in generating therapeutic and prophylactic ...
... ex-vivo clinical trials in murine models have now gone on to rephrasing the molecular mechanism of the immune system, enriching our immunological knowledge and empowering our ability to counteract the tumor growth. Dendritic cells have also been successful in generating therapeutic and prophylactic ...
Immunology of Transplantation & Malignancy
... cells or by removal of a primary tumor. Also, immunity can be transferred from an animal, in which a tumor has regressed, to a naive animal by injection of lymphocytes (T cells). All components of the immune system (nonspecific and specific; humoral and cellular) can affect the growth and progressio ...
... cells or by removal of a primary tumor. Also, immunity can be transferred from an animal, in which a tumor has regressed, to a naive animal by injection of lymphocytes (T cells). All components of the immune system (nonspecific and specific; humoral and cellular) can affect the growth and progressio ...
CONQUERING ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
... Certain statements included herein express Faron’s expectaAons or esAmates of future performance and consAtute “Forward-‐looking Statements”. Forward-‐ looking Statements are necessarily based upon a number of esAmates a ...
... Certain statements included herein express Faron’s expectaAons or esAmates of future performance and consAtute “Forward-‐looking Statements”. Forward-‐ looking Statements are necessarily based upon a number of esAmates a ...
Document
... transferred to the infant via breast milk. The main immunoglobulin class transferred is IgA, the transferred IgA works at mucosal surfaces, where it is able to prevent pathogen entry. However other important factors are transferred, including complement and commensal bacteria – which may provide pro ...
... transferred to the infant via breast milk. The main immunoglobulin class transferred is IgA, the transferred IgA works at mucosal surfaces, where it is able to prevent pathogen entry. However other important factors are transferred, including complement and commensal bacteria – which may provide pro ...
Neonatal Immunology
... transferred to the infant via breast milk. The main immunoglobulin class transferred is IgA, the transferred IgA works at mucosal surfaces, where it is able to prevent pathogen entry. However other important factors are transferred, including complement and commensal bacteria – which may provide pro ...
... transferred to the infant via breast milk. The main immunoglobulin class transferred is IgA, the transferred IgA works at mucosal surfaces, where it is able to prevent pathogen entry. However other important factors are transferred, including complement and commensal bacteria – which may provide pro ...
Innate Immune Response to the Dimorphic Fungal Pathogen
... estimated that 100 000 new cases occur in the US each year [7]. Human infection occurs after inhalation of fungal spores (arthroconidia). The majority of Coccidioides infections in people either produce no symptoms or a self-limited pneumonia. Although this mycosis is rarely life-threatening, most p ...
... estimated that 100 000 new cases occur in the US each year [7]. Human infection occurs after inhalation of fungal spores (arthroconidia). The majority of Coccidioides infections in people either produce no symptoms or a self-limited pneumonia. Although this mycosis is rarely life-threatening, most p ...
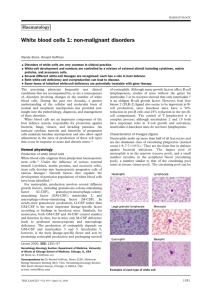
White blood cells 1: non-malignant disorders
... agranular cytoplasm. Two thirds are T cells, which participate in cell-mediated immune responses. The remainder are B cells, which are programmed to produce antibodies. B and T lymphocytes cannot be distinguished morphologically. Some 10% of lymphocytes are large granular lymphocytes, characterised ...
... agranular cytoplasm. Two thirds are T cells, which participate in cell-mediated immune responses. The remainder are B cells, which are programmed to produce antibodies. B and T lymphocytes cannot be distinguished morphologically. Some 10% of lymphocytes are large granular lymphocytes, characterised ...
Phagocyte

Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting (phagocytosing) harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, ""to eat"" or ""devour"", and ""-cyte"", the suffix in biology denoting ""cell"", from the Greek kutos, ""hollow vessel"". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were first discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.Phagocytes of humans and other animals are called ""professional"" or ""non-professional"" depending on how effective they are at phagocytosis. The professional phagocytes include many types of white blood cells (such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and dendritic cells). The main difference between professional and non-professional phagocytes is that the professional phagocytes have molecules called receptors on their surfaces that can detect harmful objects, such as bacteria, that are not normally found in the body. Phagocytes are crucial in fighting infections, as well as in maintaining healthy tissues by removing dead and dying cells that have reached the end of their lifespan.During an infection, chemical signals attract phagocytes to places where the pathogen has invaded the body. These chemicals may come from bacteria or from other phagocytes already present. The phagocytes move by a method called chemotaxis. When phagocytes come into contact with bacteria, the receptors on the phagocyte's surface will bind to them. This binding will lead to the engulfing of the bacteria by the phagocyte. Some phagocytes kill the ingested pathogen with oxidants and nitric oxide. After phagocytosis, macrophages and dendritic cells can also participate in antigen presentation, a process in which a phagocyte moves parts of the ingested material back to its surface. This material is then displayed to other cells of the immune system. Some phagocytes then travel to the body's lymph nodes and display the material to white blood cells called lymphocytes. This process is important in building immunity, and many pathogens have evolved methods to evade attacks by phagocytes.