Brucellosis - Queensland Horse Council
... Brucellosis This disease was eradicated from Australia in 1992. Bovine brucellosis is a chronic infectious disease of cattle that causes abortions, the birth of weak or dead calves, infertility and, as a consequence, reduced milk production. All ages of cattle are susceptible and infection can last ...
... Brucellosis This disease was eradicated from Australia in 1992. Bovine brucellosis is a chronic infectious disease of cattle that causes abortions, the birth of weak or dead calves, infertility and, as a consequence, reduced milk production. All ages of cattle are susceptible and infection can last ...
bacterial Pathogenesis
... iv. antigenic variety -numerous serological types among strains in the world (each strain is antigenically stable) ►M protein of Streptococcus pyogenes ...
... iv. antigenic variety -numerous serological types among strains in the world (each strain is antigenically stable) ►M protein of Streptococcus pyogenes ...
Huntington's Disease - Bridgewater College
... Causes Caused by a single abnormal gene Autosomal dominant disorder because only one copy of the defective gene, inherited from either parent, is necessary to produce the disease 50 % chance of obtaining if one parent has the gene ...
... Causes Caused by a single abnormal gene Autosomal dominant disorder because only one copy of the defective gene, inherited from either parent, is necessary to produce the disease 50 % chance of obtaining if one parent has the gene ...
PEABODY FELLOWS STUDENT PRE-TEST
... c. the patient has an active virus and too many white blood cells. d. the patient has developed antibodies which react to an antigen for the disease. 18. How have people learned to control harmful bacteria without antibiotics? a. By growing vegetables near a stream b. By using garlic and other spice ...
... c. the patient has an active virus and too many white blood cells. d. the patient has developed antibodies which react to an antigen for the disease. 18. How have people learned to control harmful bacteria without antibiotics? a. By growing vegetables near a stream b. By using garlic and other spice ...
Staph - IS MU - Masaryk University
... Pathogenicity = the ability to cause a disease It depends on both microbial and host species Particular microbial species is pathogenic for a specific host species only, for another species it may be non-pathogenic This host species is susceptible to the relevant microbial species, to a different mi ...
... Pathogenicity = the ability to cause a disease It depends on both microbial and host species Particular microbial species is pathogenic for a specific host species only, for another species it may be non-pathogenic This host species is susceptible to the relevant microbial species, to a different mi ...
Mutations and Genetic Diseases
... approximately 37 years, a dramatic increase over the last three decades. ...
... approximately 37 years, a dramatic increase over the last three decades. ...
What is Population Genetics?
... Very important question: if we decide we want to wipe out an infectious disease we need to wipe out at least the areas corresponding to the population size, otherwise we will achieve no result. ...
... Very important question: if we decide we want to wipe out an infectious disease we need to wipe out at least the areas corresponding to the population size, otherwise we will achieve no result. ...
Immunity to infectious diseases
... 1.In tuberculoid leprosy the patient mount an effective cell-mediated response.Macrophages destroy the bacilli and contain the infection . 2. In lepromatous leprosy : the patient is unable to produce a cell-mediated response and organisms multiply and spread in the tissues > ...
... 1.In tuberculoid leprosy the patient mount an effective cell-mediated response.Macrophages destroy the bacilli and contain the infection . 2. In lepromatous leprosy : the patient is unable to produce a cell-mediated response and organisms multiply and spread in the tissues > ...
Immunity
... found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tissues where they are needed. Macrophages are versatile cells; they act as scavengers, they secrete a wide variety of powerful chemicals, and ...
... found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tissues where they are needed. Macrophages are versatile cells; they act as scavengers, they secrete a wide variety of powerful chemicals, and ...
Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infections
... “arms race” against them are primarily responsible. Staphylococcus aureus, the “All Time Champion” of pathogens is just as prominent and just as confounding a cause of disease today as when Sir Alexander Ogston observed it in the wounds of his surgical patients in the 1880s. This chapter will lay ou ...
... “arms race” against them are primarily responsible. Staphylococcus aureus, the “All Time Champion” of pathogens is just as prominent and just as confounding a cause of disease today as when Sir Alexander Ogston observed it in the wounds of his surgical patients in the 1880s. This chapter will lay ou ...
A25 Winn - InfectiousDiseaseEcology
... Latent Infection designates individuals who are infected but do not have active disease and so are not (yet) infectious ...
... Latent Infection designates individuals who are infected but do not have active disease and so are not (yet) infectious ...
The Tale of two Herpes Viruses: CMV and EBV
... – No prospective studies showing efficacy in treatment of PTLD disease, but routinely used – High peripheral viral loads associated with disease or PTLD are present despite antiviral therapy and recent studies show that the majority of these cells are immortalized B cells without lytic EBV activity ...
... – No prospective studies showing efficacy in treatment of PTLD disease, but routinely used – High peripheral viral loads associated with disease or PTLD are present despite antiviral therapy and recent studies show that the majority of these cells are immortalized B cells without lytic EBV activity ...
Evaluation and Monitoring During Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) (PDF)
... Evaluation and Monitoring During Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) All patients should have the following: • An initial pre-treatment clinical evaluation to rule out active TB disease and to assess for the likelihood of adverse effects of therapy • Rule out pregnancy prior to startin ...
... Evaluation and Monitoring During Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) All patients should have the following: • An initial pre-treatment clinical evaluation to rule out active TB disease and to assess for the likelihood of adverse effects of therapy • Rule out pregnancy prior to startin ...
Van Der Werf et al., 2003
... hydronephrosis, were predicted at 18 and 10 million, respectively. Infection with S. mansoni was estimated to cause diarrhoea in 0.78 million individuals, blood in stool in 4.4 million and hepatomegaly in 8.5 million. As the associations between prevalence of S. mansoni infection and prevalence of d ...
... hydronephrosis, were predicted at 18 and 10 million, respectively. Infection with S. mansoni was estimated to cause diarrhoea in 0.78 million individuals, blood in stool in 4.4 million and hepatomegaly in 8.5 million. As the associations between prevalence of S. mansoni infection and prevalence of d ...
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
... die, but over 50% remain with no clinical signs of disease In • late stages of disease (wasting and frequent or severe opportunistic infections), life expectancy is less than 1 year • Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and mouth (stomatitis)—may not respond to treatment or may be difficult to tre ...
... die, but over 50% remain with no clinical signs of disease In • late stages of disease (wasting and frequent or severe opportunistic infections), life expectancy is less than 1 year • Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and mouth (stomatitis)—may not respond to treatment or may be difficult to tre ...
feline_immunodeficiency_virus_infection
... die, but over 50% remain with no clinical signs of disease • In late stages of disease (wasting and frequent or severe opportunistic infections), life expectancy is less than 1 year • Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and mouth (stomatitis)—may not respond to treatment or may be difficult to tre ...
... die, but over 50% remain with no clinical signs of disease • In late stages of disease (wasting and frequent or severe opportunistic infections), life expectancy is less than 1 year • Inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and mouth (stomatitis)—may not respond to treatment or may be difficult to tre ...
ARE YOU A BABY BOOMER? Individuals born between 1945 and
... Individuals born between 1945 and 1965 are sometimes known as baby boomers. A silent disease, HCV infection affects close to 5 million people in the United States, the majority of who were born between 1945 and 1965. It is estimated that between 50-75% of these individuals do not know they are infec ...
... Individuals born between 1945 and 1965 are sometimes known as baby boomers. A silent disease, HCV infection affects close to 5 million people in the United States, the majority of who were born between 1945 and 1965. It is estimated that between 50-75% of these individuals do not know they are infec ...
For Immediate Release: October 31, 2014 Contact: Kristy Weinshel
... www.facebook.com/APICInfectionPreventionandYou. For information on what patients and families can do, visit APIC’s Infection Prevention and You website at www.apic.org/infectionpreventionandyou. PIDS is the world's largest organization of professionals dedicated to the treatment, control and eradica ...
... www.facebook.com/APICInfectionPreventionandYou. For information on what patients and families can do, visit APIC’s Infection Prevention and You website at www.apic.org/infectionpreventionandyou. PIDS is the world's largest organization of professionals dedicated to the treatment, control and eradica ...
Kabatereine et al., 2004
... London, UK Summary Intestinal schistosomiasis caused by infection with Schistosoma mansoni is a widespread public health problem in Uganda. Although long known to be endemic, its current distribution within the country requires updating of parasitological data to help guide planned control. We repor ...
... London, UK Summary Intestinal schistosomiasis caused by infection with Schistosoma mansoni is a widespread public health problem in Uganda. Although long known to be endemic, its current distribution within the country requires updating of parasitological data to help guide planned control. We repor ...
this PDF file
... The introduction during the past 5 years of the first expanded-spectrum triazole, voriconazole, and a new class of cell-wall active agents, the echinocandins, quickly changed the approach to treatment of invasive fungal infections. These agents are safer than and equally effective as the prior refer ...
... The introduction during the past 5 years of the first expanded-spectrum triazole, voriconazole, and a new class of cell-wall active agents, the echinocandins, quickly changed the approach to treatment of invasive fungal infections. These agents are safer than and equally effective as the prior refer ...
Infectious Disease in Space - Risks, Realities and
... Infectious Disease in Space - Risks, Realities and Remedies ...
... Infectious Disease in Space - Risks, Realities and Remedies ...
Document
... • These drugs must be taken exactly as directed. • If the person stops taking the medication without the physicians approval, they may become sick and/or develop TB. ...
... • These drugs must be taken exactly as directed. • If the person stops taking the medication without the physicians approval, they may become sick and/or develop TB. ...
Understanding Influenza
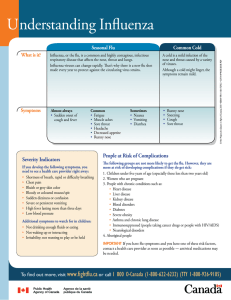
... People at Risk of Complications The following groups are not more likely to get the flu. However, they are more at risk of developing complications if they do get sick: 1. Children under five years of age (especially those less than two years old) 2. Women who are pregnant 3. People with chronic con ...
... People at Risk of Complications The following groups are not more likely to get the flu. However, they are more at risk of developing complications if they do get sick: 1. Children under five years of age (especially those less than two years old) 2. Women who are pregnant 3. People with chronic con ...
Microbes and Diseases ppt
... athletes or those taking part in sports regularly. http://toenailbuddy.com ...
... athletes or those taking part in sports regularly. http://toenailbuddy.com ...
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance
... a) through skin – usually via cut or lesion or bite b) through mucus membranes that line the GI, respiratory, genitourinary tract, and conjunctiva (1) via microbial proteins that (a) degrade cell to cell junctions (b) disrupt the cells (2) via passive mechanisms such as lesions or ulcers, tissue dam ...
... a) through skin – usually via cut or lesion or bite b) through mucus membranes that line the GI, respiratory, genitourinary tract, and conjunctiva (1) via microbial proteins that (a) degrade cell to cell junctions (b) disrupt the cells (2) via passive mechanisms such as lesions or ulcers, tissue dam ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.