feline infectious peritonitis (fip)
... Restrict to prevent exposure of other cats, although greatest degree of virus shed occurs before the patient shows signs DIET ...
... Restrict to prevent exposure of other cats, although greatest degree of virus shed occurs before the patient shows signs DIET ...
How to combat the dangerous rise of antibiotic resistance
... trends out to 2050, the 700,000 deaths could reach 10m. Cynics might be forgiven for thinking that they have heard this argument before. People have fretted about resistance since antibiotics began being used in large quantities during the late 1940s. Their conclusion that bacterial diseases might a ...
... trends out to 2050, the 700,000 deaths could reach 10m. Cynics might be forgiven for thinking that they have heard this argument before. People have fretted about resistance since antibiotics began being used in large quantities during the late 1940s. Their conclusion that bacterial diseases might a ...
Sore Ear (Otitis Media)
... Children may feel sick or vomit, and can be generally unwell. Young babies cannot point to their pain. One of the causes of a hot, irritable, crying baby is an ear infection. Sometimes the eardrum perforates (bursts). This lets out infected mucus and the ear becomes runny for a few days. A bur ...
... Children may feel sick or vomit, and can be generally unwell. Young babies cannot point to their pain. One of the causes of a hot, irritable, crying baby is an ear infection. Sometimes the eardrum perforates (bursts). This lets out infected mucus and the ear becomes runny for a few days. A bur ...
Microbes and Human Disease
... 4) Ability to invade host cells • Invasion allows bacteria to enter safe and nutrient rich environment • Most penetrate via phagocytosis • Many kill/destroy host cell • Other effects: ...
... 4) Ability to invade host cells • Invasion allows bacteria to enter safe and nutrient rich environment • Most penetrate via phagocytosis • Many kill/destroy host cell • Other effects: ...
Vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (whooping cough
... Tetanus is caused by a bacteria present in soil. The bacteria produce toxins that attack the nervous system causing muscle stiffness and painful cramps. Infection can occur when the bacteria enter open wounds and it is not contagious. The disease has a high death rate.. Tetanus is less common in Sca ...
... Tetanus is caused by a bacteria present in soil. The bacteria produce toxins that attack the nervous system causing muscle stiffness and painful cramps. Infection can occur when the bacteria enter open wounds and it is not contagious. The disease has a high death rate.. Tetanus is less common in Sca ...
Unit 4 Immunology Summary
... cells and T lymphocytes produce a clone of B lymphocytes that secrete antibodies into the lymph and blood where they make their way to the infected area. ...
... cells and T lymphocytes produce a clone of B lymphocytes that secrete antibodies into the lymph and blood where they make their way to the infected area. ...
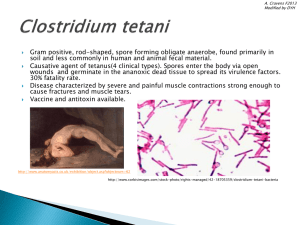
Clostridium tetani
... Gram positive, rod-shaped, spore forming obligate anaerobe, found primarily in soil and less commonly in human and animal fecal material. Causative agent of tetanus(4 clinical types). Spores enter the body via open wounds and germinate in the ananoxic dead tissue to spread its virulence factors. 30% ...
... Gram positive, rod-shaped, spore forming obligate anaerobe, found primarily in soil and less commonly in human and animal fecal material. Causative agent of tetanus(4 clinical types). Spores enter the body via open wounds and germinate in the ananoxic dead tissue to spread its virulence factors. 30% ...
University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point Hepatitis B Virus Vaccination Declination
... I understand that due to my exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. I have been given the opportunity to be vaccinated with hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to me. However, I decline the hepatitis B vaccination at ...
... I understand that due to my exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials I may be at risk of acquiring hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. I have been given the opportunity to be vaccinated with hepatitis B vaccine, at no charge to me. However, I decline the hepatitis B vaccination at ...
Control of Infection
... •All staff to understand and discharge their responsibilities in relation to infection control •Clinical teams to be responsible for infection control outcomes •Infection control programmes to be supported by adequately resourced infection control teams •Trusts to adopt comprehensive surveillance an ...
... •All staff to understand and discharge their responsibilities in relation to infection control •Clinical teams to be responsible for infection control outcomes •Infection control programmes to be supported by adequately resourced infection control teams •Trusts to adopt comprehensive surveillance an ...
Infection Prevention and Control Considerations for Patient Placement
... present with any clinical factors that would increase the likelihood of transmission? ...
... present with any clinical factors that would increase the likelihood of transmission? ...
2002 - THE ORAL CAVITY OF REPTILES
... The oral cavity is formed by the anterior-most parts of the gastrointestinal system and respiratory system and includes the mouth and the internal choane. Most reptiles have little in the way of a secondary palate. It is best developed in species that lack cranial kinesis (movement of the snout rela ...
... The oral cavity is formed by the anterior-most parts of the gastrointestinal system and respiratory system and includes the mouth and the internal choane. Most reptiles have little in the way of a secondary palate. It is best developed in species that lack cranial kinesis (movement of the snout rela ...
12/2 study guide ch 17 due
... to reduce this threat. 5. Describe the threats from (a) hepatitis B (b) West Nile (c) SARS viruses. 6. Describe the threat from malaria for 40% of the world’s people. How can we reduce this threat? 7. Give three examples of problems being studied in the new field of ecological medicine. What is Lyme ...
... to reduce this threat. 5. Describe the threats from (a) hepatitis B (b) West Nile (c) SARS viruses. 6. Describe the threat from malaria for 40% of the world’s people. How can we reduce this threat? 7. Give three examples of problems being studied in the new field of ecological medicine. What is Lyme ...
Chapter 4 Supplement
... of animals and humans. The indigenous microflora of humans contains many species of anaerobes, some of which are opportunistic pathogens. Anaerobes cause a wide variety of human diseases, including botulism, tetanus, gas gangrene, pulmonary infections, brain abscesses, and oral diseases. It was Loui ...
... of animals and humans. The indigenous microflora of humans contains many species of anaerobes, some of which are opportunistic pathogens. Anaerobes cause a wide variety of human diseases, including botulism, tetanus, gas gangrene, pulmonary infections, brain abscesses, and oral diseases. It was Loui ...
Scaling and Root Planning (SRP Gum Treatment) Periodontal (gum
... Scaling and Root Planning (SRP Gum Treatment) Periodontal (gum) disease is very common. Everyone’s mouth contains bacteria that cause gum disease. That's why it's the most common chronic bacterial infection in adults. In fact, nearly half of all Americans over age 30 and 70% of those age 65 or older ...
... Scaling and Root Planning (SRP Gum Treatment) Periodontal (gum) disease is very common. Everyone’s mouth contains bacteria that cause gum disease. That's why it's the most common chronic bacterial infection in adults. In fact, nearly half of all Americans over age 30 and 70% of those age 65 or older ...
Pneumonia - RNStrongresp
... pneumoniae will cause a sudden high fever. This fever is generally more than 103ºF. The fever is accompanied by other symptoms like chills and dizziness. The patient will also cough up the thick currant jelly sputum. This sputum may show streaks of blood. ...
... pneumoniae will cause a sudden high fever. This fever is generally more than 103ºF. The fever is accompanied by other symptoms like chills and dizziness. The patient will also cough up the thick currant jelly sputum. This sputum may show streaks of blood. ...
Diagnosis
... • most commonly LNs in the periportal region, followed by peripancreatic and mesenteric LNs. Hepatic lymph node involvement can lead to jaundice, portal vein thrombosis, and portal hypertension. ...
... • most commonly LNs in the periportal region, followed by peripancreatic and mesenteric LNs. Hepatic lymph node involvement can lead to jaundice, portal vein thrombosis, and portal hypertension. ...
Gonorrhea - Baltimore City Public Schools
... • Is a Sexual Transmitted Disease (STD) caused by bacteria called Neisseria Gonorrhea this can be passed from one person to another Vaginal, oral, and anal sex you can not catch gonorrhea from , towel, doorknob, and toilet seat ...
... • Is a Sexual Transmitted Disease (STD) caused by bacteria called Neisseria Gonorrhea this can be passed from one person to another Vaginal, oral, and anal sex you can not catch gonorrhea from , towel, doorknob, and toilet seat ...
Bacterial Pathogenesis
... • Host defenses can be damaged by destructing barriers or defective immune response – e.g. Cystic Fibrosis (囊腫纖維症) • Pseudomonas aerugionsa (綠膿桿菌)infection ...
... • Host defenses can be damaged by destructing barriers or defective immune response – e.g. Cystic Fibrosis (囊腫纖維症) • Pseudomonas aerugionsa (綠膿桿菌)infection ...
Haemophilus Influenzae Type B (Hib, H flu)
... What is Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease? Haemophilus influenzae type b is a serious bacterial disease that is sometimes fatal. Before effective vaccine became available, Haemophilus influenzae was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis (which is a swelling of the tissue that covers th ...
... What is Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease? Haemophilus influenzae type b is a serious bacterial disease that is sometimes fatal. Before effective vaccine became available, Haemophilus influenzae was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis (which is a swelling of the tissue that covers th ...
Prevalence of Ticks Infected with Human Pathogens in the Lehigh
... Overall B. burgdorferi infection rates for summer 2015 and 2016 are not significantly different from a similar study performed in 2014 at different sites in the Lehigh Valley which were 18.3% (20/109 nymphs, 95% CI: 11.6-26.9%) positive for this pathogen (Edwards et al. 2015). In summer 2015, B. mic ...
... Overall B. burgdorferi infection rates for summer 2015 and 2016 are not significantly different from a similar study performed in 2014 at different sites in the Lehigh Valley which were 18.3% (20/109 nymphs, 95% CI: 11.6-26.9%) positive for this pathogen (Edwards et al. 2015). In summer 2015, B. mic ...
Human Herpesviruses
... Capacity to establish latent and recurrent infections, in case of EBV immortalizing infections Ubiquitous Usually cause benign disease especially in children In immunosuppressed people they cause significant morbidity and mortality ...
... Capacity to establish latent and recurrent infections, in case of EBV immortalizing infections Ubiquitous Usually cause benign disease especially in children In immunosuppressed people they cause significant morbidity and mortality ...
Faculty of Infectious and Tropical Diseases
... the most efficient and cost-effective way to deliver health care; and health policy analysis. In addition to our many overseas collaborations, we have close links with the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, in purpose-built accommodation on the main UCL Hospital campus, five minutes walk from the Schoo ...
... the most efficient and cost-effective way to deliver health care; and health policy analysis. In addition to our many overseas collaborations, we have close links with the Hospital for Tropical Diseases, in purpose-built accommodation on the main UCL Hospital campus, five minutes walk from the Schoo ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.