Meters - Schuylkill Technology Center
... 2. Locates overloads and open circuits 3. Balances the loads on multiwire circuits 4. Locates electrical component malfunctions 5. Two types a. In-line In-line ammeters should always be connected in series with the circuit or component being tested. If direct current is being measured, always check ...
... 2. Locates overloads and open circuits 3. Balances the loads on multiwire circuits 4. Locates electrical component malfunctions 5. Two types a. In-line In-line ammeters should always be connected in series with the circuit or component being tested. If direct current is being measured, always check ...
Risk assessment of catastrophic failures in electric power systems L
... account of these blackouts can be found in the report prepared for the Transmission Reliability Program of the Department of Energy [8]. Besides the causes of the degradation of the power system reliability listed previously, there is the detrimental role played by the protection systems during larg ...
... account of these blackouts can be found in the report prepared for the Transmission Reliability Program of the Department of Energy [8]. Besides the causes of the degradation of the power system reliability listed previously, there is the detrimental role played by the protection systems during larg ...
“Reflowable” Alternative to Traditional Thermal Protection
... hot-lines begin forming on the trace causing delamination. If left unprotected, this can lead to a thermal event that ordinary electrical fuses and leaded thermal fuses cannot prevent. The RTP device gives the designer a greater degree of flexibility in protecting against damage from thermal runaway ...
... hot-lines begin forming on the trace causing delamination. If left unprotected, this can lead to a thermal event that ordinary electrical fuses and leaded thermal fuses cannot prevent. The RTP device gives the designer a greater degree of flexibility in protecting against damage from thermal runaway ...
Electrical Safety Guide For Non-Electrical Workers
... (8 A), a 100 W light bulb 1,000 mA and a coffee maker 7,000 mA. Under the right conditions, currents of only a few milli-amperes could lead to death. However, electric current does not occur without sufficient voltage available to motivate electrons to flow (current). Electrical equipment operating ...
... (8 A), a 100 W light bulb 1,000 mA and a coffee maker 7,000 mA. Under the right conditions, currents of only a few milli-amperes could lead to death. However, electric current does not occur without sufficient voltage available to motivate electrons to flow (current). Electrical equipment operating ...
Evaluation Board User Guide UG-339
... Because of its excellent sensitivity and low noise, the ADL5304 is capable of operation at currents easily influenced by stray magnetic fields. This can lead to unwanted signals coupling into the ADL5304 in unexpected ways. An example of this is shown in Figure 3. In a typical circuit testing enviro ...
... Because of its excellent sensitivity and low noise, the ADL5304 is capable of operation at currents easily influenced by stray magnetic fields. This can lead to unwanted signals coupling into the ADL5304 in unexpected ways. An example of this is shown in Figure 3. In a typical circuit testing enviro ...
MAX3030E–MAX3033E ±15kV ESD-Protected, 3.3V Quad RS-422 Transmitters General Description
... 200pF storage capacitor and zero discharge resistance. Its objective is to emulate the stress caused by contact that occurs with handling and assembly during manufacturing. Of course, all pins require this protection during manufacturing, not just inputs and outputs. Therefore, after PC board assemb ...
... 200pF storage capacitor and zero discharge resistance. Its objective is to emulate the stress caused by contact that occurs with handling and assembly during manufacturing. Of course, all pins require this protection during manufacturing, not just inputs and outputs. Therefore, after PC board assemb ...
Electromagnetic Force Modification in Fault Current Limiters under
... current limiters (FCL) will solve the aforementioned problems by limiting the fault currents to an acceptable limit. Thus, the expensive equipments and upgrades would not be necessary. FCLs are installed in series with electric lines. During normal conditions, FCL impedance is very small, but when a ...
... current limiters (FCL) will solve the aforementioned problems by limiting the fault currents to an acceptable limit. Thus, the expensive equipments and upgrades would not be necessary. FCLs are installed in series with electric lines. During normal conditions, FCL impedance is very small, but when a ...
.3Stakeholder Comparison Comment Rationale Matrix 2010-07-15 AESO AUTHORITATIVE DOCUMENT PROCESS
... referenced below. Such an initial indication assists in the AESO’s practical understanding of the receptivity of the industry to the proposed changes, and in that regard the AESO thanks, in advance, all market participants who choose to respond. With regard to the specific standard changes and their ...
... referenced below. Such an initial indication assists in the AESO’s practical understanding of the receptivity of the industry to the proposed changes, and in that regard the AESO thanks, in advance, all market participants who choose to respond. With regard to the specific standard changes and their ...
Stakeholder Comparison Comment Rationale Matrix 2010-07-15 AESO AUTHORITATIVE DOCUMENT PROCESS
... The purpose of this reliability Clarified the purpose to align with the standard is to ensure the content of the reliability standard. protective relay settings do not limit transmission loadability, do not interfere with system operators ability to take remedial action to protect system reliability ...
... The purpose of this reliability Clarified the purpose to align with the standard is to ensure the content of the reliability standard. protective relay settings do not limit transmission loadability, do not interfere with system operators ability to take remedial action to protect system reliability ...
Investigation Of Factors Affecting The Sustainability Of Arcs
... This exception does not direct workers to wear arc rated PPE for protection. It implies that there is no arc flash hazard because arc faults would either self-extinguish on such circuits or have insufficient incident energy to cause burns or ignite clothing. Note also that NFPA70E includes circuits ...
... This exception does not direct workers to wear arc rated PPE for protection. It implies that there is no arc flash hazard because arc faults would either self-extinguish on such circuits or have insufficient incident energy to cause burns or ignite clothing. Note also that NFPA70E includes circuits ...
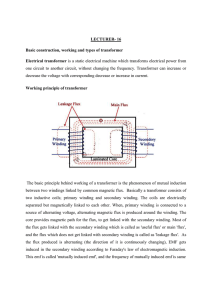
Chapter 13
... Physical parameters affecting inductance The inductance given by the equation in the previous slide is for the ideal case. In practice, inductors have winding resistance (RW) and winding capacitance (CW). An equivalent circuit for a practical inductor including these effects is: CW ...
... Physical parameters affecting inductance The inductance given by the equation in the previous slide is for the ideal case. In practice, inductors have winding resistance (RW) and winding capacitance (CW). An equivalent circuit for a practical inductor including these effects is: CW ...
PDF: 1.20MB
... 1.1 Features of MOSFET Super mini DIPIPM MOSFET Super mini DIPIPM (hereinafter called DIPIPM) is the transfer molding type intelligent power module (IPM) which integrates power chips, drive and protection circuits in one package. It is favorable for AC100-240Vinput class low power motor inverter con ...
... 1.1 Features of MOSFET Super mini DIPIPM MOSFET Super mini DIPIPM (hereinafter called DIPIPM) is the transfer molding type intelligent power module (IPM) which integrates power chips, drive and protection circuits in one package. It is favorable for AC100-240Vinput class low power motor inverter con ...
The Manitoba Electrical Code - 12th Edition
... (i) when the cost of labour and materials (excluding the cost of utilization equipment supplied by the circuitry) does not exceed two hundred dollars ($200) as determined by the inspection department in accordance with the current schedule of electrical permit fees; (ii) that are not associated with ...
... (i) when the cost of labour and materials (excluding the cost of utilization equipment supplied by the circuitry) does not exceed two hundred dollars ($200) as determined by the inspection department in accordance with the current schedule of electrical permit fees; (ii) that are not associated with ...
ER34881886
... steering DAC is simple and fast, needs no decoding logic. Hence this architecture is compact and efficient. But the main problem faced by this architecture is large DNL error, less monotonic, can be used up to only 10 bits. Lots of glitches in the output which affect the performance of DAC. In binar ...
... steering DAC is simple and fast, needs no decoding logic. Hence this architecture is compact and efficient. But the main problem faced by this architecture is large DNL error, less monotonic, can be used up to only 10 bits. Lots of glitches in the output which affect the performance of DAC. In binar ...
BD6164GUT
... BD6164GUT has no separate supply for the internal circuitry generally known as “Vdd”. The internal circuitry of the chip is supplied directly from the output voltage (VOUT). During battery-insertion, the VOUT node ramps up to battery voltage level (PMOS switch is ON initially). When the main system ...
... BD6164GUT has no separate supply for the internal circuitry generally known as “Vdd”. The internal circuitry of the chip is supplied directly from the output voltage (VOUT). During battery-insertion, the VOUT node ramps up to battery voltage level (PMOS switch is ON initially). When the main system ...
Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software
... Figure 12.28: The rectangle tool is used to fill in blank areas with ground planes. When making a board that will work at RF frequencies, a good rule of thumb is to have as much metal around which is at a ground voltage. These large areas of metal are called “ground planes” and help shield parts of ...
... Figure 12.28: The rectangle tool is used to fill in blank areas with ground planes. When making a board that will work at RF frequencies, a good rule of thumb is to have as much metal around which is at a ground voltage. These large areas of metal are called “ground planes” and help shield parts of ...
OSHA 29 CFR 1910.333, Selection and Use of Work Practices
... Note 1: Examples of increased or additional hazards include interruption of life support equipment, deactivation of emergency alarm systems, shutdown of hazardous location ventilation equipment, or removal of illumination for an area. Note 2: Examples of work that may be performed on or near energiz ...
... Note 1: Examples of increased or additional hazards include interruption of life support equipment, deactivation of emergency alarm systems, shutdown of hazardous location ventilation equipment, or removal of illumination for an area. Note 2: Examples of work that may be performed on or near energiz ...
FPF2024/5/6/7 Full Functional Load Switch With 100mA Current Limit F P
... The FPF2024/5/6/7 respond to an output overload condition by going into constant current mode where the output current is regulated by the load switch. If the overcurrent condition persists beyond the 10ms Blanking Time, FPF2024 and FPF2025 pull the fault signal pin (FLAGB) low and shut-off the swit ...
... The FPF2024/5/6/7 respond to an output overload condition by going into constant current mode where the output current is regulated by the load switch. If the overcurrent condition persists beyond the 10ms Blanking Time, FPF2024 and FPF2025 pull the fault signal pin (FLAGB) low and shut-off the swit ...