Chimeric Immune System
... viruses, and other foreign invaders Composed of chemicals and cells that attack and inactivate things that enter the body First line of defense is the skin, blocks invaders T cells and B cells: white blood cells, more specific forms of protection ...
... viruses, and other foreign invaders Composed of chemicals and cells that attack and inactivate things that enter the body First line of defense is the skin, blocks invaders T cells and B cells: white blood cells, more specific forms of protection ...
reduced expression of tissue transglutaminase in a human
... inhibited the incorporation of ["S]-sulphate into GAG chains, and greatly reduced the capacity of these cells to bind [lUI]-IFN-y; this was paralleled by decreased upregulation of class I1 MHC antigens by IFN-y stimulated cells that had been pre-treated with chlorate. This indicates that sulphated, ...
... inhibited the incorporation of ["S]-sulphate into GAG chains, and greatly reduced the capacity of these cells to bind [lUI]-IFN-y; this was paralleled by decreased upregulation of class I1 MHC antigens by IFN-y stimulated cells that had been pre-treated with chlorate. This indicates that sulphated, ...
Lesson 1: The Immune System - Lecture Notes | Vaccine Education
... • Antibodies are proteins produced by B lymphocytes to neutralize antigens and prepare them for destruction by phagocytes. They can also be known as immunoglobulins (Igs). • Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules with two distinct regions: a constant region and a variable region. The variable region allo ...
... • Antibodies are proteins produced by B lymphocytes to neutralize antigens and prepare them for destruction by phagocytes. They can also be known as immunoglobulins (Igs). • Antibodies are Y-shaped molecules with two distinct regions: a constant region and a variable region. The variable region allo ...
Immunology
... Also are immunologically active regions Sometimes called “antigenic determinants” Epitopes recognized by B cells are most accessible sites • Epitopes recognized by T cells are on the surface of APCs in association with MHC ...
... Also are immunologically active regions Sometimes called “antigenic determinants” Epitopes recognized by B cells are most accessible sites • Epitopes recognized by T cells are on the surface of APCs in association with MHC ...
No Slide Title
... functions of different types of immune cells • Summarize the roles of: – innate versus adapative immunity – cellular versus humoral immunity ...
... functions of different types of immune cells • Summarize the roles of: – innate versus adapative immunity – cellular versus humoral immunity ...
Inflammation in CNS
... An immune response in the CNS may be triggered also by endogenous ligands that stimulate TLRs. For example, signals from damaged cells (heat-shock proteins, components of the extracellular matrix degradation) or arising from molecules entering the brain through a damaged BBB may initiate an inflamma ...
... An immune response in the CNS may be triggered also by endogenous ligands that stimulate TLRs. For example, signals from damaged cells (heat-shock proteins, components of the extracellular matrix degradation) or arising from molecules entering the brain through a damaged BBB may initiate an inflamma ...
Immune System
... If a pathogen is able to get past the NSD of the Immune System (IS), then the IS reacts by launching an attack on the specific pathogen in specific defense (SD) ...
... If a pathogen is able to get past the NSD of the Immune System (IS), then the IS reacts by launching an attack on the specific pathogen in specific defense (SD) ...
Genomic Organization
... These extra copies cannot replicate and are broken down during early development. ...
... These extra copies cannot replicate and are broken down during early development. ...
link
... • Antibodies: Proteins made by immune cells that “recognize” or bind with particular antigens. Original diversity of antibodyproducing cells depends on recombination of genetic sequences during cell development • Macrophages: phagocytic cells in blood) • Cytotoxic T-cells: “killer” white blood cells ...
... • Antibodies: Proteins made by immune cells that “recognize” or bind with particular antigens. Original diversity of antibodyproducing cells depends on recombination of genetic sequences during cell development • Macrophages: phagocytic cells in blood) • Cytotoxic T-cells: “killer” white blood cells ...
HP_Tipaje Linfocitario_24 07 13
... These components are interconnected by blood and lymph vessels, constituting a single well-communicated system. The response mechanisms of the immune system are the innate or non-adaptive immunity (the natural killer cells, for example) and the acquired or specific immunity (such as the T and B lymp ...
... These components are interconnected by blood and lymph vessels, constituting a single well-communicated system. The response mechanisms of the immune system are the innate or non-adaptive immunity (the natural killer cells, for example) and the acquired or specific immunity (such as the T and B lymp ...
Reading Guide-InnateImmune (CH15)
... receptors) and indirectly (via opsonization….a process that happens when complement proteins are activated). Some really virulent pathogens have evolved mechanism to evade the process of phagocytosis…can you think of some ways in which an organism could evade phaogcytosis? Cells of the immune syste ...
... receptors) and indirectly (via opsonization….a process that happens when complement proteins are activated). Some really virulent pathogens have evolved mechanism to evade the process of phagocytosis…can you think of some ways in which an organism could evade phaogcytosis? Cells of the immune syste ...
organization of the immune system
... after puberty and lasts to middle age followed by a slower rate of involution extending to old age •DN cells do not proliferate and differentiate •Diversity of the TCR repertoire progressively becomes more limited •The thymic tissue is replaced by fat deposits •In old people naive peripheral T cells ...
... after puberty and lasts to middle age followed by a slower rate of involution extending to old age •DN cells do not proliferate and differentiate •Diversity of the TCR repertoire progressively becomes more limited •The thymic tissue is replaced by fat deposits •In old people naive peripheral T cells ...
Immune Primer - Life Sciences Outreach Program
... 2. Understands the chemical reactions involved in cell functions (e.g., food molecules taken into cells are broken down to provide the chemical constituents needed to synthesize other molecules; enzymes facilitate the breakdown and synthesis of ...
... 2. Understands the chemical reactions involved in cell functions (e.g., food molecules taken into cells are broken down to provide the chemical constituents needed to synthesize other molecules; enzymes facilitate the breakdown and synthesis of ...
Thesis Abstract Drug hypersensitivity reactions represent a major
... clinical characteristics are very heterogeneous as drugs can elicit all types of immune reactions. The antigenicity of drugs relies on the fact that small molecules can bind covalently to carrier proteins, which become modified and then behave like a foreign antigenic proteins inducing humoral and T ...
... clinical characteristics are very heterogeneous as drugs can elicit all types of immune reactions. The antigenicity of drugs relies on the fact that small molecules can bind covalently to carrier proteins, which become modified and then behave like a foreign antigenic proteins inducing humoral and T ...
Foundation Block Lecture Two Natural defense mechanism
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
... Microbial infections initiate inflammation As bacteria possess an array of pro-inflammatory molecules: e.g. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) ...
ch 43 clicker questions
... Recombinase genes RAG1 and RAG2 are found only in jawed vertebrates, supporting the hypothesis that a) jawless vertebrates have immune memory. b) jawless vertebrates employ combinatorial DNA rearrangements to increase antigen receptor diversity. c) sharks lack an adaptive immune system that respond ...
... Recombinase genes RAG1 and RAG2 are found only in jawed vertebrates, supporting the hypothesis that a) jawless vertebrates have immune memory. b) jawless vertebrates employ combinatorial DNA rearrangements to increase antigen receptor diversity. c) sharks lack an adaptive immune system that respond ...
Document
... 2. Lymphocytes that reach the thymus differentiate into T-cells/T-lymphocytes. 3. B lymphocytes/B-cells differentiate in the red bone marrow. ...
... 2. Lymphocytes that reach the thymus differentiate into T-cells/T-lymphocytes. 3. B lymphocytes/B-cells differentiate in the red bone marrow. ...
Immunity & Abnormal Responses
... – Those proteins made by the cell that are incorporated into the cell membrane & hold or present foreign antigenic material that has gotten into the cell – These are usually glycoproteins & everybody has different ones • Controlled by genes on chromosome 6 in region called MHC » MHC = major histocom ...
... – Those proteins made by the cell that are incorporated into the cell membrane & hold or present foreign antigenic material that has gotten into the cell – These are usually glycoproteins & everybody has different ones • Controlled by genes on chromosome 6 in region called MHC » MHC = major histocom ...
10 autoimmun
... Activation of APCs, which overcomes regulatory mechanisms and results in excessive T cell activation ...
... Activation of APCs, which overcomes regulatory mechanisms and results in excessive T cell activation ...
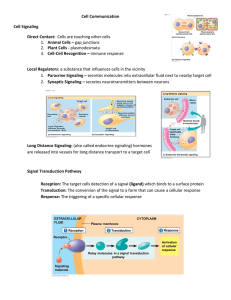
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Direct Contact: Cells are
... 1. G-Protein Coupled Receptors: a GTP binding protein with a secondary structure of 7 alpha-helices that acts as an on/off switch Ex. Epinephrine between neurons ...
... 1. G-Protein Coupled Receptors: a GTP binding protein with a secondary structure of 7 alpha-helices that acts as an on/off switch Ex. Epinephrine between neurons ...