Lymphatic and Immune Systems - Holding
... Your body responds to the presence of foreign particles and pathogens – Specific defenses – cellular level, specific to type of pathogen – Nonspecific responses – occur the same way to all pathogens Inflammation Fever ...
... Your body responds to the presence of foreign particles and pathogens – Specific defenses – cellular level, specific to type of pathogen – Nonspecific responses – occur the same way to all pathogens Inflammation Fever ...
The Human Body Systems
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
Immunity Talk selected slides
... T- and B-Cells are exposed to antigens in lymphoid tissue. This changes them so that they can act against specific pathogens, helped by and helping the ...
... T- and B-Cells are exposed to antigens in lymphoid tissue. This changes them so that they can act against specific pathogens, helped by and helping the ...
Congaplex Flyer L4905
... of the lymph system. There are many kinds of T lymphocytes and each has a specific role in immune response. ...
... of the lymph system. There are many kinds of T lymphocytes and each has a specific role in immune response. ...
"ISG15 regulates peritoneal macrophage functionality against viral
... Upon viral infection, the production of type I interferon (IFN) and the subsequent upregulation of IFN stimulated genes (ISGs) generate an antiviral state with an important role in the activation of innate and adaptive host immune responses. The ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) ISG15 is a critical IFN-i ...
... Upon viral infection, the production of type I interferon (IFN) and the subsequent upregulation of IFN stimulated genes (ISGs) generate an antiviral state with an important role in the activation of innate and adaptive host immune responses. The ubiquitin-like protein (UBL) ISG15 is a critical IFN-i ...
Questions: How does the body: fight a viral infection? a
... 4. Pathogens binding to the cell surface also turn on production of more antifungal proteins, more defensins and various cytokines. Cytokines are secreted molecules that can activate many processes including: a) attract inflammatory cells, b) trigger fever (most bacteria and viruses grow better at l ...
... 4. Pathogens binding to the cell surface also turn on production of more antifungal proteins, more defensins and various cytokines. Cytokines are secreted molecules that can activate many processes including: a) attract inflammatory cells, b) trigger fever (most bacteria and viruses grow better at l ...
31.3 Immune Responses
... 31.3 Immune Responses The immune system rejects foreign tissues. • Tissue rejection occurs in organ or tissue transplants – is the result of an immune response – immune system detects protein markers on the donor tissue – makes antibodies against the donor’s tissue ...
... 31.3 Immune Responses The immune system rejects foreign tissues. • Tissue rejection occurs in organ or tissue transplants – is the result of an immune response – immune system detects protein markers on the donor tissue – makes antibodies against the donor’s tissue ...
Document
... • Draw and label the parts of a neuron. • Name two types of glial cells and describe their general function. • Describe three types of neurons. • How can a hormone have different responses in different cells? • List three evolutionary trends of nervous system formation in animals. Describe each • L ...
... • Draw and label the parts of a neuron. • Name two types of glial cells and describe their general function. • Describe three types of neurons. • How can a hormone have different responses in different cells? • List three evolutionary trends of nervous system formation in animals. Describe each • L ...
The Immune System - The JAMA Network
... pathogens. Pathogens have molecules called antigens on their surface. Antigens provide a unique signature for the pathogen that enables immune system cells to recognize different pathogens and distinguish pathogens from the body’s own cells and tissues. When a pathogen gets into the body, the immune ...
... pathogens. Pathogens have molecules called antigens on their surface. Antigens provide a unique signature for the pathogen that enables immune system cells to recognize different pathogens and distinguish pathogens from the body’s own cells and tissues. When a pathogen gets into the body, the immune ...
The immune response against dying tumor cells: avoid
... cohesion of the multicellular ensemble. Paradoxically, one of the most primitive antimicrobial responses consists of the sacrifice via programmed cell death (PCD) of infected cells; a response that is found in all metazoan phyla including plants (which do not possess any mobile cells and hence lack ...
... cohesion of the multicellular ensemble. Paradoxically, one of the most primitive antimicrobial responses consists of the sacrifice via programmed cell death (PCD) of infected cells; a response that is found in all metazoan phyla including plants (which do not possess any mobile cells and hence lack ...
Chapter 24: The Immune System
... 1o Ab function: bind Ag to B lymphocyte and initiate production of additional antibodies (usually IgM) Other Ab functions: bind to pathogens and target them for destruction (via several different mechanisms!) ...
... 1o Ab function: bind Ag to B lymphocyte and initiate production of additional antibodies (usually IgM) Other Ab functions: bind to pathogens and target them for destruction (via several different mechanisms!) ...
Chapter 17
... Ag fragments + ____________________________ (MHC II) proteins together = presented or “processed” antigen Triggers __________________ (IL-2) production from T cells This stimulates B cells further and creates memory cells Known as _______________________, usually proteins ...
... Ag fragments + ____________________________ (MHC II) proteins together = presented or “processed” antigen Triggers __________________ (IL-2) production from T cells This stimulates B cells further and creates memory cells Known as _______________________, usually proteins ...
Lecture Notes for Med. Tech. Class
... Neonatal exposure leads to life-long tolerance to the otherwise foreign cells. Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, ...
... Neonatal exposure leads to life-long tolerance to the otherwise foreign cells. Medawar’s Experiment of Neonatal Tolerance Induction • Neonatal exposure of allogeneic blood cells causes tolerance to the skin grafts from the blood donor. Central and Peripheral Immunological Tolerance • Theoretically, ...
immune system - immunology.unideb.hu
... 1.Vasodilation: leads to greater blood flow to the area of inflammation, resulting in redness and heat. 2.Vascular permeability: endothelial cells become "leaky" from either direct endothelial cell injury or via chemical mediators. 3.Exudation: fluid, proteins, red blood cells, and white blood cells ...
... 1.Vasodilation: leads to greater blood flow to the area of inflammation, resulting in redness and heat. 2.Vascular permeability: endothelial cells become "leaky" from either direct endothelial cell injury or via chemical mediators. 3.Exudation: fluid, proteins, red blood cells, and white blood cells ...
File
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
... • Our immune system “remembers” bad pathogens it has fought in the past • It has weapons built up so the next time the pathogen enters your body, you are ready to defend ...
irc seminar - MedUni Wien
... Molecular Cell Biology and Immunology at the VUMC in Amsterdam. She is an associate professor since 2015. Her group is studying different types of macrophages and DCs that are present in lymphoid organs and how they can activate immune responses. Previously, she discovered a unique role for mouse CD ...
... Molecular Cell Biology and Immunology at the VUMC in Amsterdam. She is an associate professor since 2015. Her group is studying different types of macrophages and DCs that are present in lymphoid organs and how they can activate immune responses. Previously, she discovered a unique role for mouse CD ...
doc 3.2.4 immunity notes Student notes for section 3.2.4
... Are derived from stem cells in the bone marrow. These cells secrete antibodies into the blood plasma, tissue fluid and lymph once they are activated. Plasma cells actively secrete antibodies. Memory cells are inactive cells ready to be activated should the need arise. T lymphocytes: These get their ...
... Are derived from stem cells in the bone marrow. These cells secrete antibodies into the blood plasma, tissue fluid and lymph once they are activated. Plasma cells actively secrete antibodies. Memory cells are inactive cells ready to be activated should the need arise. T lymphocytes: These get their ...
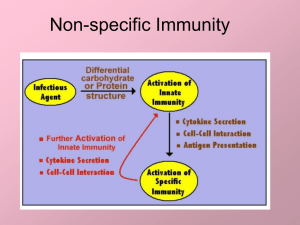
Non-specific Immunity
... Muscular contraction and constriction of skin blood vessels cause core temperature to rise ...
... Muscular contraction and constriction of skin blood vessels cause core temperature to rise ...
Ch 12 Adaptive Defense Overview
... Another human’s cells can trigger an immune response because they are foreign Blood type is a great example as agglutination takes place with a mismatch ...
... Another human’s cells can trigger an immune response because they are foreign Blood type is a great example as agglutination takes place with a mismatch ...
Dendreon: Pipeline Largely Based on Active Cellular Immunotherapy
... cassette technology that results in a fusion protein of the cancer-specific antigen (i.e., protein enriched on cancer cells) linked to GM-CSF, an important immune system activating protein. The fusion protein, when combined with harvested immune system cells from a patient, activates the resting ant ...
... cassette technology that results in a fusion protein of the cancer-specific antigen (i.e., protein enriched on cancer cells) linked to GM-CSF, an important immune system activating protein. The fusion protein, when combined with harvested immune system cells from a patient, activates the resting ant ...
Detailed Outline and Resources for Lesson Planning
... o Secondary lymphoid organs are sites of immune responses and include (Fig 12-1): Lymph nodes Filtering stations for foreign particles (macrophages eat) Pathogens recognized by lymphocytes set off response and node swells Spleen Left upper quadrant above stomach Similar function to nodes ...
... o Secondary lymphoid organs are sites of immune responses and include (Fig 12-1): Lymph nodes Filtering stations for foreign particles (macrophages eat) Pathogens recognized by lymphocytes set off response and node swells Spleen Left upper quadrant above stomach Similar function to nodes ...
Ch 35 Disease Fighting mechanisms Pre test key 2
... 14. Malaria and tuberculosis are two examples of diseases that have A. been totally eliminated from the human population. B. evolved resistance to many antibiotics. C. increased because of a lack of understanding of how vaccines work. D. recently been discovered in the United States. 15. Failing to ...
... 14. Malaria and tuberculosis are two examples of diseases that have A. been totally eliminated from the human population. B. evolved resistance to many antibiotics. C. increased because of a lack of understanding of how vaccines work. D. recently been discovered in the United States. 15. Failing to ...