Optimizing the Periosteal Flap for Lateral Eyelid Reconstruction
... width of the flap should measure 6-7 mm which compensates for primary contracture while maintaining strength of the periosteum. The periosteum is then secured with 5-0 Vicryl to the lateral edge of the tarsal plate with enough tension that the lid approximates the globe. ...
... width of the flap should measure 6-7 mm which compensates for primary contracture while maintaining strength of the periosteum. The periosteum is then secured with 5-0 Vicryl to the lateral edge of the tarsal plate with enough tension that the lid approximates the globe. ...
as a pdf
... If the radical vulvectomy and groin dissection are performed through separate incisions, the lateral vulvar incision is basically elliptical. Each incision should commence on the mons pubis anteriorly and extend through the fat and superficial fascia to the fascia over the pubic symphysis. It is the ...
... If the radical vulvectomy and groin dissection are performed through separate incisions, the lateral vulvar incision is basically elliptical. Each incision should commence on the mons pubis anteriorly and extend through the fat and superficial fascia to the fascia over the pubic symphysis. It is the ...
PPT
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
Slides 7
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
superior mesenteric artery
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
... It is a blind-ended pouch Site: situated in the right iliac fossa , above the lat ½ of inguinal ligament Size: It is about 3 inch in diameter Completely covered with peritoneum. It possesses a considerable amount of mobility, although it does not have a mesentery. Attached to : - Ascending colon - p ...
Differential Diagnosis of Temporal Bone and Skull Base
... demonstrates a reddish-blue pulsatile retrotympanic mass. Positive pressure with pneumatic otoscopy may cause blanching known as the Brown sign. The pulsatile nature of the lesion may be diminished with pressure over the ipsilateral carotid artery which is known as the Aquino sign. A bruit may be au ...
... demonstrates a reddish-blue pulsatile retrotympanic mass. Positive pressure with pneumatic otoscopy may cause blanching known as the Brown sign. The pulsatile nature of the lesion may be diminished with pressure over the ipsilateral carotid artery which is known as the Aquino sign. A bruit may be au ...
Surgery of Skull Base Tumors Extending to the Orbit, Paranasal
... It should be noted that there is no anatomical concept of the "craniofacial region". The term "craniofacial tumor" is conditional. It means a neoplasm of the skull base extending both intracranially and to extracranial structures of the facial skeleton [7, 10]. Upon that, the source of growth may be ...
... It should be noted that there is no anatomical concept of the "craniofacial region". The term "craniofacial tumor" is conditional. It means a neoplasm of the skull base extending both intracranially and to extracranial structures of the facial skeleton [7, 10]. Upon that, the source of growth may be ...
Document
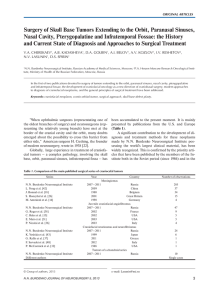
... Hepatitis C, alcoholism as well as multiple additional comorbidities presented initially to an outside hospital. An MRI in October 2012 demonstrated an irregularly enhancing lesion in segment V with a pseudocapsule and foci of washout. The patient was referred to our facility for further evaluation. ...
... Hepatitis C, alcoholism as well as multiple additional comorbidities presented initially to an outside hospital. An MRI in October 2012 demonstrated an irregularly enhancing lesion in segment V with a pseudocapsule and foci of washout. The patient was referred to our facility for further evaluation. ...
Large Intestine
... Large Intestine Anatomical Structures Like the small intestine, the mucosa of the large intestine has intestinal glands that contain both absorptive and goblet cells. However, there are several notable differences between the walls of the large and small intestines. For example, other than the anal ...
... Large Intestine Anatomical Structures Like the small intestine, the mucosa of the large intestine has intestinal glands that contain both absorptive and goblet cells. However, there are several notable differences between the walls of the large and small intestines. For example, other than the anal ...
Diverticulosis and Diverticulitis
... pouches becomes thin and ruptures allowing bacteria normally contained inside the colon to seep out through the wall and cause infection on the outside of the colon. When this occurs, it is called diverticulitis. Diverticulitis can be mild with only slight discomfort in the left lower abdomen - or i ...
... pouches becomes thin and ruptures allowing bacteria normally contained inside the colon to seep out through the wall and cause infection on the outside of the colon. When this occurs, it is called diverticulitis. Diverticulitis can be mild with only slight discomfort in the left lower abdomen - or i ...
Hernias, and Intraperitoneal abscess
... • covering tissue: skin, subcutanous tissue • hernial sac: protrusion of peritonum, neck of the sac: is narrow where the sac emerges from the abdomen body of the sac • hernial contents: small intestine, major omentum ...
... • covering tissue: skin, subcutanous tissue • hernial sac: protrusion of peritonum, neck of the sac: is narrow where the sac emerges from the abdomen body of the sac • hernial contents: small intestine, major omentum ...
Diverticulitis in the left lower quadrant
... stool, the colon has to work harder to move stool out of the colon. This puts pressure on the weak portions of the colonic wall, where the blood vessels enter and the pressure creates small pouches. One theory is that the stool becomes trapped in these pouches where bacteria grows, which may lead to ...
... stool, the colon has to work harder to move stool out of the colon. This puts pressure on the weak portions of the colonic wall, where the blood vessels enter and the pressure creates small pouches. One theory is that the stool becomes trapped in these pouches where bacteria grows, which may lead to ...
LabPracticalIBio242LGRCC
... 28. Name the vessel labeled 9 on the sheep heart above. 29. Name the structure indicated by number 14 on the anterior/ventral view of the heart. ...
... 28. Name the vessel labeled 9 on the sheep heart above. 29. Name the structure indicated by number 14 on the anterior/ventral view of the heart. ...
Read more
... Normal tilt is less than 10º Tilt more than 10 º Or 5º tilt more than normal side is significant ATFL and MCFL are torn ...
... Normal tilt is less than 10º Tilt more than 10 º Or 5º tilt more than normal side is significant ATFL and MCFL are torn ...
Ocular Pathology Review © 2014 Ralph C. Eagle, Jr., M.D.
... and white blood cells from the blood into extravascular tissues. This is frequently an expression of the host's attempt to localize and eliminate metabolically altered cells, foreign particles, microorganisms or antigens Cardinal manifestions of Inflammation, i.e. redness, heat, pain and diminished ...
... and white blood cells from the blood into extravascular tissues. This is frequently an expression of the host's attempt to localize and eliminate metabolically altered cells, foreign particles, microorganisms or antigens Cardinal manifestions of Inflammation, i.e. redness, heat, pain and diminished ...
See p. Op305 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... Typical pathway is TRANSSPHENOIDAL APPROACH – gold standard – high safety and efficiency (incl. MICROADENOMAS confined to sella and larger tumors that, in past, could be approached only by subfrontal craniotomy)! possible for fairly large medial suprasellar extensions, as long as tumor is soft (us ...
... Typical pathway is TRANSSPHENOIDAL APPROACH – gold standard – high safety and efficiency (incl. MICROADENOMAS confined to sella and larger tumors that, in past, could be approached only by subfrontal craniotomy)! possible for fairly large medial suprasellar extensions, as long as tumor is soft (us ...
PARAGANGLIOMAS OF THE HEAD AND NECK : review
... carotid body (53%) and glomus jugular (32%). They present as slow-growing tumors, with few symptoms, and imaging tests as well defined and hypervascular masses. The relationship with the vessels is a key factor in the differential diagnosis. We show the best examples of each subtype illustrated and ...
... carotid body (53%) and glomus jugular (32%). They present as slow-growing tumors, with few symptoms, and imaging tests as well defined and hypervascular masses. The relationship with the vessels is a key factor in the differential diagnosis. We show the best examples of each subtype illustrated and ...
TUMORS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS
... TUMORS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS ANATOMY - PAROTID THE PAROTID DUCT LIES ON AN IMAGINARY LINE BETWEEN THE EXTERNAL NARES AND THE TRAGUS OF THE EAR. ...
... TUMORS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS ANATOMY - PAROTID THE PAROTID DUCT LIES ON AN IMAGINARY LINE BETWEEN THE EXTERNAL NARES AND THE TRAGUS OF THE EAR. ...
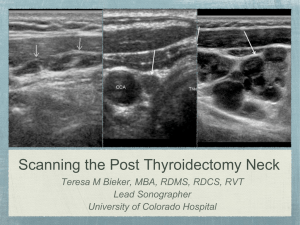
Scanning the Post Thyroidectomy Neck
... T0: No evidence of primary tumor. T1: Tumor ≤2 cm in greatest dimension limited to the thyroid. T1a: Tumor ≤1 cm, limited to the thyroid. T1b: Tumor >1 cm but ≤2 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid. T2: Tumor >2 cm but ≤4 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid. T3: Tumor >4 cm ...
... T0: No evidence of primary tumor. T1: Tumor ≤2 cm in greatest dimension limited to the thyroid. T1a: Tumor ≤1 cm, limited to the thyroid. T1b: Tumor >1 cm but ≤2 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid. T2: Tumor >2 cm but ≤4 cm in greatest dimension, limited to the thyroid. T3: Tumor >4 cm ...
BREAST CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORTS
... • When staging a known breast cancer and there are satellite lesions an FNA should be done to not get malignant cells in a large core bx, so FNA is more direct. ...
... • When staging a known breast cancer and there are satellite lesions an FNA should be done to not get malignant cells in a large core bx, so FNA is more direct. ...
eL BPH+PCa - UMF IASI 2015
... most patients with early-stage CaP are asymptomatic; presence of symptoms often suggests locally advanced or metastatic disease local growth into the urethra or bladder neck or direct extension into the trigone obstructive or irritative voiding complaints metastatic disease bone pain and s ...
... most patients with early-stage CaP are asymptomatic; presence of symptoms often suggests locally advanced or metastatic disease local growth into the urethra or bladder neck or direct extension into the trigone obstructive or irritative voiding complaints metastatic disease bone pain and s ...
Document
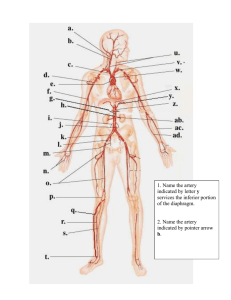
... The main bld. Supply to the abdomin comes from: Abdominal Aorta Starts in aortic hiatus opposite to T12 Ends opposite to L4 by dividing into: 2 common iliac arteries ...
... The main bld. Supply to the abdomin comes from: Abdominal Aorta Starts in aortic hiatus opposite to T12 Ends opposite to L4 by dividing into: 2 common iliac arteries ...
dr.mohamed farouk Cervical cancer
... The cervix is attached to the lateral pelvic wall by a pair of ligaments at the base of the broad ligament referred to as the cardinal ligaments This ligament contains the uterine arteries and veins. The uterine arteries pass over the ureters on each side in close proximity to the cervix Most cervic ...
... The cervix is attached to the lateral pelvic wall by a pair of ligaments at the base of the broad ligament referred to as the cardinal ligaments This ligament contains the uterine arteries and veins. The uterine arteries pass over the ureters on each side in close proximity to the cervix Most cervic ...
Primary Parapharyngeal Tumors
... Many surgeons prefer the transcervical-transparotid approach. A standard parotidectomy incision is made and carried into the lateral neck. The main trunk and lower division of the facial nerve are identified. The posterior belly of the digastric and stylohyoid muscle are divided, allowing for visual ...
... Many surgeons prefer the transcervical-transparotid approach. A standard parotidectomy incision is made and carried into the lateral neck. The main trunk and lower division of the facial nerve are identified. The posterior belly of the digastric and stylohyoid muscle are divided, allowing for visual ...
barium enema position
... bag is no more than 24 inches (60cm) above the table. Ensure tubing stopcock is in the closed position and no barium flows into the pt. ...
... bag is no more than 24 inches (60cm) above the table. Ensure tubing stopcock is in the closed position and no barium flows into the pt. ...
Neoplasm

Neoplasm (from Ancient Greek νέος- neo ""new"" and πλάσμα plasma ""formation, creation"") is an abnormal growth of tissue, and when also forming a mass is commonly referred to as a tumor or tumour. This abnormal growth (neoplasia) usually but not always forms a mass.The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers.Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia do not always progress to neoplasia.