II. T cell activation
... Th-independent: virus infected DC that highly express co-stimulatory molecules can directly stimulate CD8+ T cells. ...
... Th-independent: virus infected DC that highly express co-stimulatory molecules can directly stimulate CD8+ T cells. ...
Immune System - Mr. Mazza's BioResource
... cell-mediated immunity Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) kill only cells that are infected with a virus Helper T-cells (Th) release chemicals called cytokines to activate B-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and macrophages Suppressor T-cells (TS) slow down activity of B and T cells once the antigen has been destroyed ...
... cell-mediated immunity Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) kill only cells that are infected with a virus Helper T-cells (Th) release chemicals called cytokines to activate B-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and macrophages Suppressor T-cells (TS) slow down activity of B and T cells once the antigen has been destroyed ...
BSC 361
... Cytokine-soluble molecule that helps regulate immune functions. TNF, IL-I, IL-6, IL-10 etc. Inflammation-host immune response that is includes increased localized temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B ...
... Cytokine-soluble molecule that helps regulate immune functions. TNF, IL-I, IL-6, IL-10 etc. Inflammation-host immune response that is includes increased localized temperature, increased permeability of the capillaries, increased blood flow. Leukocyte-any "white blood cell" Lymphocytes-T-cells and B ...
APSpring14_142Q2Aans..
... In response to short-term stress, post-ganglionic adrenergic neurons release epinephrine Feedback of CRH release is inhibited by ACTH Secretions produced by the zona glomerulosa increase gluconeogenesis Secretions produced by the zona fasiculata are controlled by the anterior pituitary gland Hormone ...
... In response to short-term stress, post-ganglionic adrenergic neurons release epinephrine Feedback of CRH release is inhibited by ACTH Secretions produced by the zona glomerulosa increase gluconeogenesis Secretions produced by the zona fasiculata are controlled by the anterior pituitary gland Hormone ...
Gastrointestinal tract barrier function
... tight junction function in the GIT. Recent data have emphasized the presence of immune mechanisms that maintain mucosal homeostasis despite barrier dysfunction, and some data suggest that the epithelium orchestrates these immunoregulatory events through direct interactions with innate immune cells. ...
... tight junction function in the GIT. Recent data have emphasized the presence of immune mechanisms that maintain mucosal homeostasis despite barrier dysfunction, and some data suggest that the epithelium orchestrates these immunoregulatory events through direct interactions with innate immune cells. ...
Immune System PowerPoint
... system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. ● The causes of these disorders are unknown for the most part. ● We suspect some are caused by bacteria, some by drugs, and some people may just have a genetic predisposition. ● Examples of autoimmune diseases are: ...
... system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. ● The causes of these disorders are unknown for the most part. ● We suspect some are caused by bacteria, some by drugs, and some people may just have a genetic predisposition. ● Examples of autoimmune diseases are: ...
Innate Immunity - Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine
... molecular patterns (PAMP) via pattern recognition receptors such as CD14/Toll receptors and produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. • Microbial substances (LPS,LTA,PPG) may directly activate plasma complement proteins stimulating inflammation ...
... molecular patterns (PAMP) via pattern recognition receptors such as CD14/Toll receptors and produce proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. • Microbial substances (LPS,LTA,PPG) may directly activate plasma complement proteins stimulating inflammation ...
Characterization of disease-causing dendritic cells in Crohn`s
... Lay Summary: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder with no known cure. The inflammation characteristic of CD can be found anywhere along the digestive tract, and is thought to result from an inappropriate immune response in genetically-prone individuals. Its incidence is ...
... Lay Summary: Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder with no known cure. The inflammation characteristic of CD can be found anywhere along the digestive tract, and is thought to result from an inappropriate immune response in genetically-prone individuals. Its incidence is ...
Innate Immunity - Ohio University
... – Intact skin, epithelial layers, cough, fever Nonspecific chemical factors – Antimicrobial peptides & fatty acids, gastric pH, ...
... – Intact skin, epithelial layers, cough, fever Nonspecific chemical factors – Antimicrobial peptides & fatty acids, gastric pH, ...
Document
... B. function in the removal of damaged erythrocytes from the circulation. C. act as the major source of stem cells and thus help to maintain hematopoiesis. D. provide an infrastructure that on antigenic stimulation contains large populations of B lymphocytes and plasma cells. E. are the sites of NK-c ...
... B. function in the removal of damaged erythrocytes from the circulation. C. act as the major source of stem cells and thus help to maintain hematopoiesis. D. provide an infrastructure that on antigenic stimulation contains large populations of B lymphocytes and plasma cells. E. are the sites of NK-c ...
Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal cell-mediated
... The HPA axis is a sophisticated psychoneuroendocrine system that is activated by and responds to a variety of stressors, including challenges to cellular immunity. CMI in turn regulates HPA responses. Stressors can be physical, mental or immunological in nature, and induce a finely coordinated HPA-C ...
... The HPA axis is a sophisticated psychoneuroendocrine system that is activated by and responds to a variety of stressors, including challenges to cellular immunity. CMI in turn regulates HPA responses. Stressors can be physical, mental or immunological in nature, and induce a finely coordinated HPA-C ...
The Immune System
... • Invasive virulence factors – help bacterial pathogens invade across the mucous membranes into the tissue space below. • Capsule – armor-like coating made of polysaccharides or proteins that protect bacterial pathogens from being engulfed and digested by the body’s phagocytic white blood cells, neu ...
... • Invasive virulence factors – help bacterial pathogens invade across the mucous membranes into the tissue space below. • Capsule – armor-like coating made of polysaccharides or proteins that protect bacterial pathogens from being engulfed and digested by the body’s phagocytic white blood cells, neu ...
Cellular Immune Response
... Any defect in the immune system decreases a person's ability to fight infections. A person with an immunodeficiency disorder may get more frequent infections, heal more slowly, and have a higher incidence of some cancers. ...
... Any defect in the immune system decreases a person's ability to fight infections. A person with an immunodeficiency disorder may get more frequent infections, heal more slowly, and have a higher incidence of some cancers. ...
immune system - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Viral and bacterial infections are by far the most common causes of illness for most people. They cause things like colds, influenza, measles, mumps, malaria, AIDS and so on. The job of your immune system is to protect your body from these infections. The immune system protects you in three diffe ...
... • Viral and bacterial infections are by far the most common causes of illness for most people. They cause things like colds, influenza, measles, mumps, malaria, AIDS and so on. The job of your immune system is to protect your body from these infections. The immune system protects you in three diffe ...
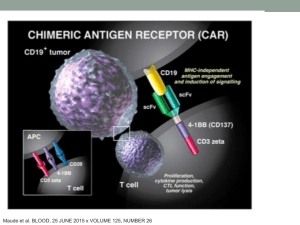
CAR T cell lecture 11.25
... • Found on B cell malignant cells (NHL, CLL, ALL, etc) • Expressed on early B cells but NOT stem cells ...
... • Found on B cell malignant cells (NHL, CLL, ALL, etc) • Expressed on early B cells but NOT stem cells ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.