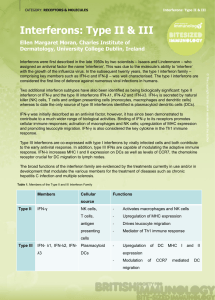
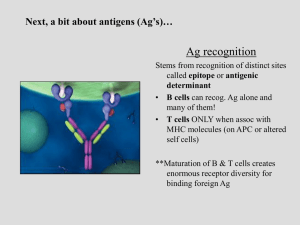
hypersensitivities ppt
... Bacterial Virulence and Infectivity • Bacteremia or septicemia • Presence of bacteria in the blood as a result of a failure of the body’s defense mechanisms • Usually caused by gram-negative bacteria • Toxins released in the blood cause the release of vasoactive peptides and cytokines that produce ...
... Bacterial Virulence and Infectivity • Bacteremia or septicemia • Presence of bacteria in the blood as a result of a failure of the body’s defense mechanisms • Usually caused by gram-negative bacteria • Toxins released in the blood cause the release of vasoactive peptides and cytokines that produce ...
INFECTIOUS BIOFE
... Please record the ways in which you can be infected with HIV as a class. Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person. That is all types of sex, where bodily fluid is released for either gender. - Contact with an infected person's blood - From mother to child (Breastmilk) ...
... Please record the ways in which you can be infected with HIV as a class. Unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected person. That is all types of sex, where bodily fluid is released for either gender. - Contact with an infected person's blood - From mother to child (Breastmilk) ...
You will need
... the whole bottle. Any bacteria who are out of the game may re-enter on any available square only the edges. 6) I went to visit a sick friend and was exposed to more pathogens. Two viruses who got captured may re-enter the game at any available edge space. 7) When I got sick this time, I really took ...
... the whole bottle. Any bacteria who are out of the game may re-enter on any available square only the edges. 6) I went to visit a sick friend and was exposed to more pathogens. Two viruses who got captured may re-enter the game at any available edge space. 7) When I got sick this time, I really took ...
lymphocytes
... • They present the antigen on their surface (APC) for the lymphocytes to identify • Macrophages release chemicals called monokines (a type of cytokine) to attract neutrophils and activate lymphocytes ...
... • They present the antigen on their surface (APC) for the lymphocytes to identify • Macrophages release chemicals called monokines (a type of cytokine) to attract neutrophils and activate lymphocytes ...
Nutritional Supplementation in HIV-Infected
... of Clinical Research, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Chennai, India; United Nations’ World Food Programme, Italy ...
... of Clinical Research, Tuberculosis Research Centre, Chennai, India; United Nations’ World Food Programme, Italy ...
Economics
... Psychophysical illness – “mind-body” illness; any stress-related physical illness, such as hypertension and some headaches (Note: this is distinct from hypochondriasis.) Hypochondriasis – a misinterpretation of normal physical sensations as symptoms of disease Lymphocytes – the two types of white bl ...
... Psychophysical illness – “mind-body” illness; any stress-related physical illness, such as hypertension and some headaches (Note: this is distinct from hypochondriasis.) Hypochondriasis – a misinterpretation of normal physical sensations as symptoms of disease Lymphocytes – the two types of white bl ...
中六生物科教材
... A type of white blood cell, produced by bone marrow which are important in immunity of the body. 4. Explain the meaning of the term memory cell. These are lymphocytes produced during the formation of plasma cells. They greatly amplify the process of plasma cell formation and antibody secretion when ...
... A type of white blood cell, produced by bone marrow which are important in immunity of the body. 4. Explain the meaning of the term memory cell. These are lymphocytes produced during the formation of plasma cells. They greatly amplify the process of plasma cell formation and antibody secretion when ...
MMG 301 Lec 33 Host Defenses Questions for today: 1. What are
... 4. What is non-specific immunity and how does it work? 5. How does specific immunity work? (2 types: antibody-mediated vs. cell-mediated immunity) Non-immune host defense against infections Resistance to microbial infections is highly variable and depends on the overall health of the host. • Factors ...
... 4. What is non-specific immunity and how does it work? 5. How does specific immunity work? (2 types: antibody-mediated vs. cell-mediated immunity) Non-immune host defense against infections Resistance to microbial infections is highly variable and depends on the overall health of the host. • Factors ...
and t-lymphocyte immune deficiencies
... infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract The most common causative organisms are bacteria such as S. pneumoniae and H. influenza Severe inherited disorders of antibody production are rare usually present at 5-6 months of age, when the protective benefit of transfe ...
... infections, particularly of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract The most common causative organisms are bacteria such as S. pneumoniae and H. influenza Severe inherited disorders of antibody production are rare usually present at 5-6 months of age, when the protective benefit of transfe ...
bacteria engage in a hazardous hide-and
... Some people experience relapses of streptococcal infections time and again interrupted by only brief intervals. Despite treating the infections with antibiotics - which appears to be successful. The underlying reason: Streptococci colonise on the inside of human cells and thus evade the immune syste ...
... Some people experience relapses of streptococcal infections time and again interrupted by only brief intervals. Despite treating the infections with antibiotics - which appears to be successful. The underlying reason: Streptococci colonise on the inside of human cells and thus evade the immune syste ...
AP Biology - Al Young Studios
... 11. Explain how B cells and T cells recognize specific antigens. 12. Explain how the particular structure of a lymphocyte's receptor is determined. 13. Describe the mechanism of clonal selection. Distinguish between effector cells and memory cells. 14. Distinguish between the primary and secondary i ...
... 11. Explain how B cells and T cells recognize specific antigens. 12. Explain how the particular structure of a lymphocyte's receptor is determined. 13. Describe the mechanism of clonal selection. Distinguish between effector cells and memory cells. 14. Distinguish between the primary and secondary i ...
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
... Fever – systemic response triggered by pyrogens (chemicals) secreted by white blood cells. Fever can inhibit multiplication of bacteria and enhance body repair processes. ...
... Fever – systemic response triggered by pyrogens (chemicals) secreted by white blood cells. Fever can inhibit multiplication of bacteria and enhance body repair processes. ...
Slide 1
... which is called the adrenomedullary response. The other route is through the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis and involves all these structures. The response of the hypothalamus prompts the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids, including cortisol. (See Figure 5.4 fo ...
... which is called the adrenomedullary response. The other route is through the hypothalamicpituitary-adrenal axis and involves all these structures. The response of the hypothalamus prompts the pituitary to stimulate the adrenal cortex to produce glucocorticoids, including cortisol. (See Figure 5.4 fo ...
A De Novo Variant in CTLA-4 Confers Responsiveness to Abatacept
... human or knockout of the gene in mouse leads to immune dysregulation. Here we report a human patient with severe multiple autoimmune features due to a de novo point mutation in the ligand-binding motif of CTLA-4, which effectively abolished the essential immuno-suppressive function of the protein. S ...
... human or knockout of the gene in mouse leads to immune dysregulation. Here we report a human patient with severe multiple autoimmune features due to a de novo point mutation in the ligand-binding motif of CTLA-4, which effectively abolished the essential immuno-suppressive function of the protein. S ...
Immunogerontology Ed`s update
... diabetes, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s, the common carcinomas). To my knowledge, these claims have without exception failed to find real support. This is not surprising, since none is characteristic of any of the known hereditary immunodeficiency diseases, which now number over 100. Increased levels of ...
... diabetes, osteoporosis, Alzheimer’s, the common carcinomas). To my knowledge, these claims have without exception failed to find real support. This is not surprising, since none is characteristic of any of the known hereditary immunodeficiency diseases, which now number over 100. Increased levels of ...
Lecture 21: Virus offence meets host defense
... • We literally swim in viruses and other microbes • We’ve evolved numerous, ovelapping active and passive defenses to enable us to ward off infection ...
... • We literally swim in viruses and other microbes • We’ve evolved numerous, ovelapping active and passive defenses to enable us to ward off infection ...
Helper T cells - Plain Local Schools
... b. Rheumatoid arthritis – the immune system attacks cartilage and bone joints causing damage and painful debilitating inflammation c. Multiple Sclerosis- T cells attack parts of nerve cells and interfere with the transmission of nerve signals – symptoms range from fatigue and numbness to difficultie ...
... b. Rheumatoid arthritis – the immune system attacks cartilage and bone joints causing damage and painful debilitating inflammation c. Multiple Sclerosis- T cells attack parts of nerve cells and interfere with the transmission of nerve signals – symptoms range from fatigue and numbness to difficultie ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.