Biology Topic 10
... pathogens are the ones with receptors able to recognize the antigens these pathogens produce. Those B cells whose receptors bind with antigens are selcted and made in multiple copies. ...
... pathogens are the ones with receptors able to recognize the antigens these pathogens produce. Those B cells whose receptors bind with antigens are selcted and made in multiple copies. ...
Organization of the Nervous System
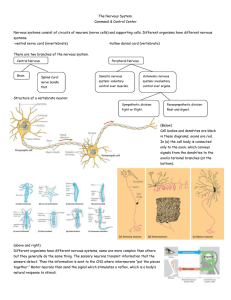
... A Closer Look @ Nervous System Cells GLIAL CELLS– support, protect, and maintain nerve tissue Most abundant cells in the nervous system CNS production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 types (PNS) Satellite Cells Schwann Cells ...
... A Closer Look @ Nervous System Cells GLIAL CELLS– support, protect, and maintain nerve tissue Most abundant cells in the nervous system CNS production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2 types (PNS) Satellite Cells Schwann Cells ...
Autoimmune disease
... • Disruption of self or tissue barrier • Infection of antigen presenting cell • Binding of pathogen to self antigen ...
... • Disruption of self or tissue barrier • Infection of antigen presenting cell • Binding of pathogen to self antigen ...
Chapter 48: The Nervous System
... Chapter 48: The Nervous System The nervous system & endocrine system work to regulate the organism & maintain homeostasis. Nervous system Involves: Sensory ...
... Chapter 48: The Nervous System The nervous system & endocrine system work to regulate the organism & maintain homeostasis. Nervous system Involves: Sensory ...
Preface - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B
... For these reasons, the cell cycle can be considered as a microcosm for many aspects of life. It embraces temporal and spatial development, reproduction, the replication and segregation of hereditary material, and evolutionary change. It is also important for the growth and development of multi-cellu ...
... For these reasons, the cell cycle can be considered as a microcosm for many aspects of life. It embraces temporal and spatial development, reproduction, the replication and segregation of hereditary material, and evolutionary change. It is also important for the growth and development of multi-cellu ...
The Immune System
... • Cancerous or infected cells no longer express this protein; natural killer (NK) cells attack these damaged cells ...
... • Cancerous or infected cells no longer express this protein; natural killer (NK) cells attack these damaged cells ...
... Histamine is secreted by basophils, white blood cells found in connective tissue. Vasodilation(dilation of blood vessels), stimulated by histamine, increases blood supply to the damaged area and allows for easier movement of white blood cells through blood vessel walls. This also causes redness, an ...
Foundations in Microbiology
... encounter with a foreign molecule, called an antigen • Two features that characterize specific immunity: – specificity – antibodies produced, function only against the antigen that they were produced in response to – memory – lymphocytes are programmed to “recall” their first encounter with an antig ...
... encounter with a foreign molecule, called an antigen • Two features that characterize specific immunity: – specificity – antibodies produced, function only against the antigen that they were produced in response to – memory – lymphocytes are programmed to “recall” their first encounter with an antig ...
What we`ve already established
... • Binding changes the shape of the receptor, eliciting a chemical/physiological response • Receptors are proteins (form = function) • Action of steroid hormones occurs inside the cell, while peptide and amine hormones bind with receptors on the cellular ...
... • Binding changes the shape of the receptor, eliciting a chemical/physiological response • Receptors are proteins (form = function) • Action of steroid hormones occurs inside the cell, while peptide and amine hormones bind with receptors on the cellular ...
Sandy Yuan - Crohn's Disease
... • About 20% runs in families • Complex trait (several genes at different locaHons may contribute to disease) • CombinaHon of inherited genes and immune system’s response to anHgens in environment (some unknown risk factors?) • SuscepHbility locus mapped to Chromosome 16 – CD19, involved in ...
... • About 20% runs in families • Complex trait (several genes at different locaHons may contribute to disease) • CombinaHon of inherited genes and immune system’s response to anHgens in environment (some unknown risk factors?) • SuscepHbility locus mapped to Chromosome 16 – CD19, involved in ...
2012 Cellular imaging at 3 T
... Cellular imaging at 3 T: Detecting Cells in Inflammation using Active Labeling with Super paramagnetic Iron oxide Azhar Hosein Faraz Medical Biophysics Western University Robarts Research Institute Under supervision of: Dr. Paula Foster ...
... Cellular imaging at 3 T: Detecting Cells in Inflammation using Active Labeling with Super paramagnetic Iron oxide Azhar Hosein Faraz Medical Biophysics Western University Robarts Research Institute Under supervision of: Dr. Paula Foster ...
20.380 S10 Introduction: the Immune System– the basics, inflammation in health
... Chemokines are secreted at sites of inflammation and infection by resident tissue cells, resident and recruited leukocytes, and cytokine-activated endothelial cells. Chemokines are locally retained on matrix and cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans, establishing a chemokine concentration gradi ...
... Chemokines are secreted at sites of inflammation and infection by resident tissue cells, resident and recruited leukocytes, and cytokine-activated endothelial cells. Chemokines are locally retained on matrix and cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans, establishing a chemokine concentration gradi ...
Lymphatic system Lecture #2
... Round bean-shaped structures found at certain points along lymphatic vessels A fibrous capsule divided into nodules containing sinuses (open spaces) filled with macrophages and lymphocytes. Two distinct regions: cortex & medulla As lymph passes through the sinuses in the nodules it is cleansed ...
... Round bean-shaped structures found at certain points along lymphatic vessels A fibrous capsule divided into nodules containing sinuses (open spaces) filled with macrophages and lymphocytes. Two distinct regions: cortex & medulla As lymph passes through the sinuses in the nodules it is cleansed ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... 1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. _____ 2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as the activation of skeletal muscles. ______ 3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves and ganglia. ____ 4. Subd ...
... 1. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord. _____ 2. Subdivision of the PNS that controls voluntary activities such as the activation of skeletal muscles. ______ 3. Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the cranial and spinal nerves and ganglia. ____ 4. Subd ...
a. active site is covered (toxin)
... a. B-cells – made in the bone marrow -- make and secrete antibodies b. T-cells – made in the thymus (gland in your neck) -- two types: T-helper – organize other white blood cells to fight infections ...
... a. B-cells – made in the bone marrow -- make and secrete antibodies b. T-cells – made in the thymus (gland in your neck) -- two types: T-helper – organize other white blood cells to fight infections ...
The Human Body Systems
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
Immune system
... filter of Ag (microorganisms, tumor cells) coming in the lymph before its return to blood circulation recirculation: lymphocytes return to node via high endothelial venules reticular connective tissue stroma cortex (lymphatic nodules, B-lymph) paracortex (T-lymph) ...
... filter of Ag (microorganisms, tumor cells) coming in the lymph before its return to blood circulation recirculation: lymphocytes return to node via high endothelial venules reticular connective tissue stroma cortex (lymphatic nodules, B-lymph) paracortex (T-lymph) ...
Nervous
... Knowledge of these events may be applied one day to stimulate axonal regrowth following CNS damage. Neural Stem Cells The adult human brain contains stem cells that can differentiate into mature neurons. The induction of stem cell differentiation and transplantation of cultured stem cells are potent ...
... Knowledge of these events may be applied one day to stimulate axonal regrowth following CNS damage. Neural Stem Cells The adult human brain contains stem cells that can differentiate into mature neurons. The induction of stem cell differentiation and transplantation of cultured stem cells are potent ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.