Concept Analysis Diagram
... Explanation of the Analysis Diagram for Metabolism Concept. The definition of the concept is written in the middle (circle) of the diagram. Nursing Care is printed slightly above the rest of the Concept Diagram because it incorporates all aspects of the diagram prior to determining the care required ...
... Explanation of the Analysis Diagram for Metabolism Concept. The definition of the concept is written in the middle (circle) of the diagram. Nursing Care is printed slightly above the rest of the Concept Diagram because it incorporates all aspects of the diagram prior to determining the care required ...
Laboratory of Viral Immunology
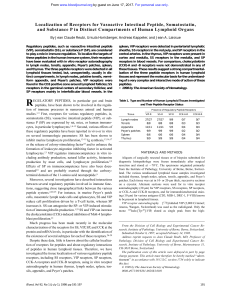
... inflammatory cytokine IL-1a • HESN have lower levels of the T cell migratory factors MIG and IP-10. ...
... inflammatory cytokine IL-1a • HESN have lower levels of the T cell migratory factors MIG and IP-10. ...
TLR3 Signaling in Human BDCA-3 Dendritic Cells Results in the
... elusive. TLR2 has been shown to recognize a wide variety of bacterial cell wall components through heterodimerization with either TLR1 or TLR6 (Kadowaki et al., 2001). TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA typically generated by actively replicating viruses and upon activation results in the productio ...
... elusive. TLR2 has been shown to recognize a wide variety of bacterial cell wall components through heterodimerization with either TLR1 or TLR6 (Kadowaki et al., 2001). TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA typically generated by actively replicating viruses and upon activation results in the productio ...
Effects of supplementation with tocotrienol-rich fraction on
... on animal and human immune systems. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF) supplementation on immune response following tetanus toxoid (TT) vaccine challenge in healthy female volunteers. Subjects/Methods: In this double-blinded, placebo-controlled c ...
... on animal and human immune systems. The objective of this study was to assess the effects of tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF) supplementation on immune response following tetanus toxoid (TT) vaccine challenge in healthy female volunteers. Subjects/Methods: In this double-blinded, placebo-controlled c ...
Learning and Optimization Using the Clonal Selection Principle
... In a T cell dependent immune response, the repertoire of antigen-activated B cells is diversified basically by two mechanisms: hypermutation and receptor editing [20]−[23]. Antibodies present in a memory response have, on average, a higher affinity than those of the early primary response. This phen ...
... In a T cell dependent immune response, the repertoire of antigen-activated B cells is diversified basically by two mechanisms: hypermutation and receptor editing [20]−[23]. Antibodies present in a memory response have, on average, a higher affinity than those of the early primary response. This phen ...
New advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of ITP 2014 ASH
... – Anti-GPIbα antibodies cause platelet desialylation, leading to Fc-independent platelet clearance in the liver. – Patients with anti-GPIbα-mediated ITP who present with significant platelet desialylation may be identified as likely nonresponders to conventional first-line treatments and splenectomy ...
... – Anti-GPIbα antibodies cause platelet desialylation, leading to Fc-independent platelet clearance in the liver. – Patients with anti-GPIbα-mediated ITP who present with significant platelet desialylation may be identified as likely nonresponders to conventional first-line treatments and splenectomy ...
Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia (IMT)
... shapes of proteins present on a cell’s surface. These shapes are similar to ID cards. The immune system recognizes shapes defined as “self” and does not attack but when it sees a cell expressing protein shapes that are “non-self,” it will respond. If the immune system is responding to a blood parasi ...
... shapes of proteins present on a cell’s surface. These shapes are similar to ID cards. The immune system recognizes shapes defined as “self” and does not attack but when it sees a cell expressing protein shapes that are “non-self,” it will respond. If the immune system is responding to a blood parasi ...
Lymphatic
... help activate T cells Dendritic cells – spiny-looking cells with functions similar to macrophages Reticular cells – fibroblastlike cells that produce a stroma, or network, that supports other cell types in lymphoid organs ...
... help activate T cells Dendritic cells – spiny-looking cells with functions similar to macrophages Reticular cells – fibroblastlike cells that produce a stroma, or network, that supports other cell types in lymphoid organs ...
Pathways Molecule-Dependent and
... optimal antiviral responses, many viruses target these events to prevent the development of antiviral immunity and boost viral survival. The recognition mechanisms that initiate and control innate reactions to viruses remain poorly understood. Accumulating evidence suggests that membrane-bound cell- ...
... optimal antiviral responses, many viruses target these events to prevent the development of antiviral immunity and boost viral survival. The recognition mechanisms that initiate and control innate reactions to viruses remain poorly understood. Accumulating evidence suggests that membrane-bound cell- ...
Defense Mechanisms against Influenza Virus Infection in the
... SUMMARY: The respiratory tract mucosa is not only the site of infection for influenza viruses but also the site of defense against virus infection. Viruses are initially detected and destroyed non-specifically by innate immune mechanisms, but if the viruses escape the early defense mechanisms, they ...
... SUMMARY: The respiratory tract mucosa is not only the site of infection for influenza viruses but also the site of defense against virus infection. Viruses are initially detected and destroyed non-specifically by innate immune mechanisms, but if the viruses escape the early defense mechanisms, they ...
Immunodeficient Mouse Models
... combined immunodeficiency mouse strain described [12]. The DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is necessary for joining non-homologous ends of double-stranded DNA and this defect impairs the production of functional B and T cells, thus mice do not respond to either B or T cell mitogens. Nonetheles ...
... combined immunodeficiency mouse strain described [12]. The DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) is necessary for joining non-homologous ends of double-stranded DNA and this defect impairs the production of functional B and T cells, thus mice do not respond to either B or T cell mitogens. Nonetheles ...
Bio-pesticide BT (Bacillus Turengensis)
... studies have been made on lumenal bacterial communities in the gut, less work has been carried out on organisms growing in biofilms, where individual groups of bacteria exist in a multiplicity of different microhabitats and metabolic niches associated with the mucosa, the mucus layer and particulate ...
... studies have been made on lumenal bacterial communities in the gut, less work has been carried out on organisms growing in biofilms, where individual groups of bacteria exist in a multiplicity of different microhabitats and metabolic niches associated with the mucosa, the mucus layer and particulate ...
Identification of Immunomodulatory Cells Induced By 670 nm Light
... myelin sheath, whereas MOG, a minor contributor to myelin, is a type I transmembrane protein located on the outer surface of the myelin sheath and oligodendrocytes [12-14]. Due to its external location, MOG is considered a candidate antigen for the initiation of MS/EAE, whereas PLP and MBP are thoug ...
... myelin sheath, whereas MOG, a minor contributor to myelin, is a type I transmembrane protein located on the outer surface of the myelin sheath and oligodendrocytes [12-14]. Due to its external location, MOG is considered a candidate antigen for the initiation of MS/EAE, whereas PLP and MBP are thoug ...
Focus Article
... Sustained inflammation may bring about time-dependent changes in dorsal horn function, favoring nociceptive facilitation where previously there was inhibition.52 Vanegas and Schaible208 identified the periaqueductal gray and rostal ventromedial medulla as an efferent channel for nociceptive control ...
... Sustained inflammation may bring about time-dependent changes in dorsal horn function, favoring nociceptive facilitation where previously there was inhibition.52 Vanegas and Schaible208 identified the periaqueductal gray and rostal ventromedial medulla as an efferent channel for nociceptive control ...
GrayetalBBI - University of Aberdeen
... disease and dementia (Samieri et al., 2008). Amongst the possible mechanisms of action through which dietary fish can protect against cardiovascular disease, their anti-inflammatory properties seem to play a major role (Thies et al., 2003). PUFAs are essential constituents of cell membranes of immun ...
... disease and dementia (Samieri et al., 2008). Amongst the possible mechanisms of action through which dietary fish can protect against cardiovascular disease, their anti-inflammatory properties seem to play a major role (Thies et al., 2003). PUFAs are essential constituents of cell membranes of immun ...
Passive vs active & vaccines
... Natural immunity: active and passive • An infection is an example of acquiring natural immunity. It is called ACTIVE as your body needs to work to produce the necessary antibodies • When a mother breast feeds her baby she passes antibodies to it. This is a way of acquiring PASSIVE immunity as it is ...
... Natural immunity: active and passive • An infection is an example of acquiring natural immunity. It is called ACTIVE as your body needs to work to produce the necessary antibodies • When a mother breast feeds her baby she passes antibodies to it. This is a way of acquiring PASSIVE immunity as it is ...
Full-Text PDF
... multitude of players and interactions. Tumors promote immune tolerance through down-regulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules and tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), thereby preventing recognition by T cells [6]. In addition, preclinical studies have indicated that tumoric ...
... multitude of players and interactions. Tumors promote immune tolerance through down-regulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules and tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), thereby preventing recognition by T cells [6]. In addition, preclinical studies have indicated that tumoric ...
Tuberculous Meningitis - TB-IPCP
... • Delays initiation of adaptive immunity (delays DC response to CCR7 to lymph node • Adaptive immunity ability to clear organism reduced: – Reduced MHC11 ass Ag presentation – Reduced activation by IGN gamma – Lipoxin 4A generated (anti-inflammatory) ...
... • Delays initiation of adaptive immunity (delays DC response to CCR7 to lymph node • Adaptive immunity ability to clear organism reduced: – Reduced MHC11 ass Ag presentation – Reduced activation by IGN gamma – Lipoxin 4A generated (anti-inflammatory) ...
Innate immune system

The innate immune system, also known as the nonspecific immune system, is an important subsystem of the overall immune system that comprises the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms. The cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way, but, unlike the adaptive immune system (which is found only in vertebrates), it does not confer long-lasting or protective immunity to the host. Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. They include both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.The innate immune system is an evolutionarily older defense strategy, and is the dominant immune system found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms.The major functions of the vertebrate innate immune system include: Recruiting immune cells to sites of infection, through the production of chemical factors, including specialized chemical mediators, called cytokines Activation of the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells The identification and removal of foreign substances present in organs, tissues, the blood and lymph, by specialised white blood cells Activation of the adaptive immune system through a process known as antigen presentation Acting as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents.↑ ↑ ↑