UNIT 2: The Chemistry of Life
... Example: Solution A has a pH of 8. Solution B has a pH of 3. Because Solution B has a lower pH, it has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions present. The more acidic a solution is, the greater the concentration of hydrogen ions. 1. An unknown solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ion ...
... Example: Solution A has a pH of 8. Solution B has a pH of 3. Because Solution B has a lower pH, it has a greater concentration of hydrogen ions present. The more acidic a solution is, the greater the concentration of hydrogen ions. 1. An unknown solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ion ...
Enzymes - Mr. hawkins
... a) Prosthetic group: Organic molecule that is permanently attached to an enzyme. ...
... a) Prosthetic group: Organic molecule that is permanently attached to an enzyme. ...
1. Vmax, the maximum velocity, of an enzyme-catalyzed
... 1. Vmax, the maximum velocity, of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is a. the rate observed when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate. b. independent of the amount of enzyme present. c. the rate observed at the highest substrate concentration that can be experimentally obtained. d. the in ...
... 1. Vmax, the maximum velocity, of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is a. the rate observed when all enzyme active sites are saturated with substrate. b. independent of the amount of enzyme present. c. the rate observed at the highest substrate concentration that can be experimentally obtained. d. the in ...
Michaelis-Menten Equation
... What is Michaelis-Menton good for? • Application: Any process involving an Enzyme (E) that converts a resource material (substrate, S) into another form product (P) • Biochemist use the shape of the curve to determine the binding specificity of an enzyme for a substrate • Km is called the Michaelis ...
... What is Michaelis-Menton good for? • Application: Any process involving an Enzyme (E) that converts a resource material (substrate, S) into another form product (P) • Biochemist use the shape of the curve to determine the binding specificity of an enzyme for a substrate • Km is called the Michaelis ...
Microbiology Lab Experiment Changes
... mix the bacteria into the peroxide. Alternately, you may put the bacteria on the slide first then add a drop of peroxide. Either way works. 4. Observe for the presence of bubbles. 5. Do Not put peroxide on the slant! Note: Bacillus species sometimes do not appear to be strong catalase producers. (Lo ...
... mix the bacteria into the peroxide. Alternately, you may put the bacteria on the slide first then add a drop of peroxide. Either way works. 4. Observe for the presence of bubbles. 5. Do Not put peroxide on the slant! Note: Bacillus species sometimes do not appear to be strong catalase producers. (Lo ...
ENZYMES
... - because of all this movement, molecules are always colliding with one another, and upon colliding, KE decreases and potential energy (PE) increases proportionally. - two things can happen as the result of a collision: 1) The reactant molecules collide but either they do not have enough KE, which, ...
... - because of all this movement, molecules are always colliding with one another, and upon colliding, KE decreases and potential energy (PE) increases proportionally. - two things can happen as the result of a collision: 1) The reactant molecules collide but either they do not have enough KE, which, ...
HANDOUT- Enzymes! (Enzyme Reaction Rates)
... substrate molecules is usually so large compared with the number of enzyme molecules that changing the substrate concentrate does not (for a short period at least) affect the number of successful collisions between substrate and enzyme. During this early period, the enzyme is acting on substrate mol ...
... substrate molecules is usually so large compared with the number of enzyme molecules that changing the substrate concentrate does not (for a short period at least) affect the number of successful collisions between substrate and enzyme. During this early period, the enzyme is acting on substrate mol ...
Enzyme Inhibition
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TLr7_2wnIXU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z8lG8X9ZvxQ&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CZD5xsOKres&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTUm-75-PL4 ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TLr7_2wnIXU http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z8lG8X9ZvxQ&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CZD5xsOKres&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XTUm-75-PL4 ...
Enzymes - Kevan Kruger
... smaller ones. b) two substrates to form a bond (in a synthetic reaction). Another word for this is ANABOLISM: making big molecules from small. Note: ANABOLISM and CATABOLISM make up METABOLISM. 4) Specific groove shapes and chemical groups in an active site means that enzymes can only bond with one ...
... smaller ones. b) two substrates to form a bond (in a synthetic reaction). Another word for this is ANABOLISM: making big molecules from small. Note: ANABOLISM and CATABOLISM make up METABOLISM. 4) Specific groove shapes and chemical groups in an active site means that enzymes can only bond with one ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Occurs in muscles during exercise because they go into oxygen debt. Soreness due to H+ from lactic acid Metabolism in muscles returns to normal when oxygen replenished ...
... Occurs in muscles during exercise because they go into oxygen debt. Soreness due to H+ from lactic acid Metabolism in muscles returns to normal when oxygen replenished ...
digestzyme-v - Ortho Molecular Products
... estimated 30% of Americans suffer from low levels of acidity. The depletion of stomach acidity due to medications and age, are further compounded by the age-related decline of enzyme production which both influence the breakdown of foods into absorbable nutrients.[2] This can lead to suboptimal nutr ...
... estimated 30% of Americans suffer from low levels of acidity. The depletion of stomach acidity due to medications and age, are further compounded by the age-related decline of enzyme production which both influence the breakdown of foods into absorbable nutrients.[2] This can lead to suboptimal nutr ...
enzymes
... more rarely, of its tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor. Phenylalanine accumulates in all body fluids because it cannot be converted into tyrosine. Normally, three-quarters of the phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine, and the other quarter becomes incorporated into proteins. The accumulation of phenylp ...
... more rarely, of its tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor. Phenylalanine accumulates in all body fluids because it cannot be converted into tyrosine. Normally, three-quarters of the phenylalanine is converted into tyrosine, and the other quarter becomes incorporated into proteins. The accumulation of phenylp ...
Enzyme Kinetics Lab
... The Enzyme Kinetics Lab Without enzymes, the dynamic steady state called “you” would quickly cease to exist. Reactions simply would not proceed fast enough for the body to process food, send signals among brain cells, make muscles contract, and do everything else to stay alive. Enzymes are a class o ...
... The Enzyme Kinetics Lab Without enzymes, the dynamic steady state called “you” would quickly cease to exist. Reactions simply would not proceed fast enough for the body to process food, send signals among brain cells, make muscles contract, and do everything else to stay alive. Enzymes are a class o ...
ENZYMES - Bio12.com
... Irreversible inhibitors: Combine with the functional groups of the amino acids in the active site, irreversibly Examples: nerve gases and pesticides, containing organophosphorus, combine with serine residues in the enzyme acetylcholine ...
... Irreversible inhibitors: Combine with the functional groups of the amino acids in the active site, irreversibly Examples: nerve gases and pesticides, containing organophosphorus, combine with serine residues in the enzyme acetylcholine ...
Exploration Activity: Enzymes
... Below you’ll find graphs that show how pH affects four different enzymes. For each, explain the trend you see, and where the enzyme is most efficient, shown by the optimum, or best pH. I. Chymotrypsin (enzyme that digests proteins):: ...
... Below you’ll find graphs that show how pH affects four different enzymes. For each, explain the trend you see, and where the enzyme is most efficient, shown by the optimum, or best pH. I. Chymotrypsin (enzyme that digests proteins):: ...
Slide 1
... ATP is the end product of glycolysis as well as it is substrate for PFK-1. In presence of high concentration of ATP, ATP binds to inhibition site of PFK, and thereby decreases the activity of enzyme. AMP, ADP and Fructose 2, 6 biphosphate act as allosteric activators of this enzyme. Activation of en ...
... ATP is the end product of glycolysis as well as it is substrate for PFK-1. In presence of high concentration of ATP, ATP binds to inhibition site of PFK, and thereby decreases the activity of enzyme. AMP, ADP and Fructose 2, 6 biphosphate act as allosteric activators of this enzyme. Activation of en ...
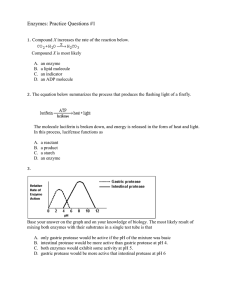
Enzymes: Practice Questions #1
... reactions that are controlled by catalysts enzymes that are stored in mitochondria the production of catalysts in vacuoles enzymes that have the same genetic base sequence ...
... reactions that are controlled by catalysts enzymes that are stored in mitochondria the production of catalysts in vacuoles enzymes that have the same genetic base sequence ...
Adding Enzymes To Dairy Diets
... variable, but encouraging, results. In a recent trial conducted at the University of Idaho, mid lactation cows were fed an alfalfa hay and silagebased total mixed ration (TMR), where the forage was sprayed with an enzyme preparation 24 hours before feeding. Daily production by the cows fed the enzym ...
... variable, but encouraging, results. In a recent trial conducted at the University of Idaho, mid lactation cows were fed an alfalfa hay and silagebased total mixed ration (TMR), where the forage was sprayed with an enzyme preparation 24 hours before feeding. Daily production by the cows fed the enzym ...
Why Doctor Bond Performs the Zinc Taste Test
... Why Doctors Hilgartner Perform the Zinc Taste Test Zinc is an essential trace element. It is one of the most important trace elements needed by the body. Of the many hundreds of protein enzymes present in the body which allow its chemistry to work, zinc is required by over two hundred of them. Thus, ...
... Why Doctors Hilgartner Perform the Zinc Taste Test Zinc is an essential trace element. It is one of the most important trace elements needed by the body. Of the many hundreds of protein enzymes present in the body which allow its chemistry to work, zinc is required by over two hundred of them. Thus, ...
A group on the enzyme acts as an acid or base
... for catalyst to be regenerated in original form. Examples of general acid/base catalysts among protein functional groups: His imidazole a-amino group thiol of Cys R group carboxyls of Glu, Asp Sidechain amino group of Lys Aromatic OH of Tyr Guanidino group of Arg ...
... for catalyst to be regenerated in original form. Examples of general acid/base catalysts among protein functional groups: His imidazole a-amino group thiol of Cys R group carboxyls of Glu, Asp Sidechain amino group of Lys Aromatic OH of Tyr Guanidino group of Arg ...
biology lab: enzyme activity
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
... BACKGROUND INFORMATION: (Summarize the information below in your own words.) "Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts that affect the rate of biochemical reactions. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substance to be acted upon, the substrate (S), binds to the active site of the enzyme (E). One ...
Glycolysis: Derived from Greek words
... from the reduced form (NADH), this reaction takes place in muscle cells. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reduces pyruvate to lactate using NADH and thereby oxidizing it to NAD+ . Other than regenerating NAD+ for running GAPDH reaction, LDH reaction is a waste of energy, and its product lactic acid bring ...
... from the reduced form (NADH), this reaction takes place in muscle cells. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reduces pyruvate to lactate using NADH and thereby oxidizing it to NAD+ . Other than regenerating NAD+ for running GAPDH reaction, LDH reaction is a waste of energy, and its product lactic acid bring ...
Alcohol dehydrogenase

Alcohol dehydrogenases (ADH) (EC 1.1.1.1) are a group of dehydrogenase enzymes that occur in many organisms and facilitate the interconversion between alcohols and aldehydes or ketones with the reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+ to NADH). In humans and many other animals, they serve to break down alcohols that otherwise are toxic, and they also participate in generation of useful aldehyde, ketone, or alcohol groups during biosynthesis of various metabolites. In yeast, plants, and many bacteria, some alcohol dehydrogenases catalyze the opposite reaction as part of fermentation to ensure a constant supply of NAD+.