The Biotechnology Age: Issues and Impacts
... • 2. Enzymes: activity make and burn energy. Stimulate growth and biomass production. • 1000’s different enzymes -> unique activities ...
... • 2. Enzymes: activity make and burn energy. Stimulate growth and biomass production. • 1000’s different enzymes -> unique activities ...
No Slide Title
... Classes of enzyme-linked receptors: 1. Receptor tyrosine kinases - signals (secreted factors, cell-surface-bound molecules) bind extracellular domains - intracellular tyrosine kinase domain ...
... Classes of enzyme-linked receptors: 1. Receptor tyrosine kinases - signals (secreted factors, cell-surface-bound molecules) bind extracellular domains - intracellular tyrosine kinase domain ...
Phosphatases - Georgia Institute of Technology
... phosphorylase, activates GS – Phospho-GM does not bind PP1 ...
... phosphorylase, activates GS – Phospho-GM does not bind PP1 ...
Defining immortality of stem cells to identify novel anti
... cellular protein content. This ability declines during the aging process, inducing the accumulation of damaged and misfolded proteins that can lead to cell death or malfunction. Several neurodegenerative age-related disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are linked to a d ...
... cellular protein content. This ability declines during the aging process, inducing the accumulation of damaged and misfolded proteins that can lead to cell death or malfunction. Several neurodegenerative age-related disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are linked to a d ...
Identification of cAMP-dependent phosphorylated proteins involved
... 2014). The encystment-dependent phosphorylation of a Colpoda RISP (p27) may be involved in the disappearance of the mitochondrial membrane potential through the regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition. The tails of the histone proteins including histone H4 can be epigenetically modif ...
... 2014). The encystment-dependent phosphorylation of a Colpoda RISP (p27) may be involved in the disappearance of the mitochondrial membrane potential through the regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition. The tails of the histone proteins including histone H4 can be epigenetically modif ...
Document
... However, water is not considered a biochemical or organic compound. Organisms are not bonded to water, instead water is contained within the ...
... However, water is not considered a biochemical or organic compound. Organisms are not bonded to water, instead water is contained within the ...
Macromolecules
... The result is a messenger RNA that provides instructions straight from the DNA on how to ‘make’ hemoglobin Other proteins ‘translate’ the mRNA instructions into another form – an actual 3D protein ...
... The result is a messenger RNA that provides instructions straight from the DNA on how to ‘make’ hemoglobin Other proteins ‘translate’ the mRNA instructions into another form – an actual 3D protein ...
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm which work to keep the cell alive Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... is a message that codes for a protein Proteins are made in the cytoplasm which work to keep the cell alive Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
Discovering Macromolecular Interactions
... The quality of the sample that is used for IP applications critically depends on the right lysis buffer, which stabilizes native protein conformation, inhibits enzymatic activity, minimizes antibody binding site denaturation and maximizes the release of proteins from the cells or tissue. The lysis b ...
... The quality of the sample that is used for IP applications critically depends on the right lysis buffer, which stabilizes native protein conformation, inhibits enzymatic activity, minimizes antibody binding site denaturation and maximizes the release of proteins from the cells or tissue. The lysis b ...
Cell Communication Study Guide
... 8. Explain the term ligand. Give an example of how a ligand is used. ...
... 8. Explain the term ligand. Give an example of how a ligand is used. ...
Document
... a single protein or indistinguishable protein group. Protein nodes are represented by large circles, and are colored in a range from white (0% sequence coverage) to dark blue (100%). The edges are colored in a range from red (0.0 NSP-adjusted probability) to white (0.5) to bright green (1.0); their ...
... a single protein or indistinguishable protein group. Protein nodes are represented by large circles, and are colored in a range from white (0% sequence coverage) to dark blue (100%). The edges are colored in a range from red (0.0 NSP-adjusted probability) to white (0.5) to bright green (1.0); their ...
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
... Once the protein is activated, the process cannot be reversed. Active protein can only be controlled by other kinds of regulation, such as inhibition or inactivation. ...
... Once the protein is activated, the process cannot be reversed. Active protein can only be controlled by other kinds of regulation, such as inhibition or inactivation. ...
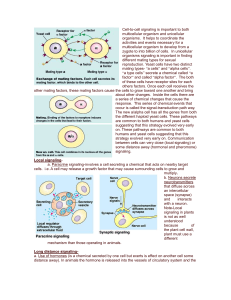
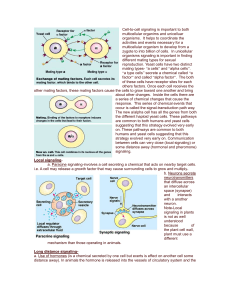
Long distance signaling
... activated. Once this occurs, the Gprotein cleaves a phosphate group from GTP and makes it GDP and thus the G-protein becomes inactivated. These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. Thes ...
... activated. Once this occurs, the Gprotein cleaves a phosphate group from GTP and makes it GDP and thus the G-protein becomes inactivated. These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. Thes ...
HW2
... where η is the viscosity which for water is ηwater = 10−3 P a s and a is the radius of the diffusing particle, estimate the diffusion constant for a protein in water and make a log-log plot of diffusion time vs distance (with distances ranging from 1 nm to 1 µm) and comment on its biological signifi ...
... where η is the viscosity which for water is ηwater = 10−3 P a s and a is the radius of the diffusing particle, estimate the diffusion constant for a protein in water and make a log-log plot of diffusion time vs distance (with distances ranging from 1 nm to 1 µm) and comment on its biological signifi ...
Cell Communication
... characteristics • Transcription factors – control which genes are turned on (transcribed into mRNA) ...
... characteristics • Transcription factors – control which genes are turned on (transcribed into mRNA) ...
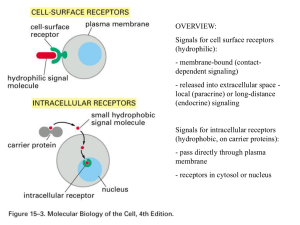
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... activated. Once this occurs, the Gprotein cleaves a phosphate group from GTP and makes it GDP and thus the G-protein becomes inactivated. These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. Thes ...
... activated. Once this occurs, the Gprotein cleaves a phosphate group from GTP and makes it GDP and thus the G-protein becomes inactivated. These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. Thes ...
The Prokaryotes Simplest organisms All unicellular
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
Introductory presentation(, 3.5 MB)
... FUNCTION FINDERS Discover how DNA sequences code for proteins with different roles and functions yourgenome.org ...
... FUNCTION FINDERS Discover how DNA sequences code for proteins with different roles and functions yourgenome.org ...
Chapter Two Mineral Nutrition of Plant
... protein. Their roles are tansport , structure.and transfer message etc. ·Phospholipid include polar head group composition: cholin, phosphate and glycerd. (nature: water-loving or called hydrophilic ) and nonpoplar tail group (14~24 carbon atoms long-chain fatty acids. Nature: water-fearing or calle ...
... protein. Their roles are tansport , structure.and transfer message etc. ·Phospholipid include polar head group composition: cholin, phosphate and glycerd. (nature: water-loving or called hydrophilic ) and nonpoplar tail group (14~24 carbon atoms long-chain fatty acids. Nature: water-fearing or calle ...
Summer 2011 Proposal for UNCA Undergraduate Research
... pathways. Due to the nature of its function, G12 has the potential to promote malignant, uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis, classifying it as a proto-oncoprotein. Indeed, analysis of cDNA libraries collected from sarcoma tissue samples has implicated G12 as a strong transforming oncoprotein ...
... pathways. Due to the nature of its function, G12 has the potential to promote malignant, uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis, classifying it as a proto-oncoprotein. Indeed, analysis of cDNA libraries collected from sarcoma tissue samples has implicated G12 as a strong transforming oncoprotein ...
DOC - Uni Basel Research Database
... Exploring the proteome on a system-wide level is essential for obtaining information on the molecular mechanisms of diseases and fundamental biological processes. Proteomics has made tremendous advances to study the cellular repertoire of proteins in its entirety, but capturing representative proteo ...
... Exploring the proteome on a system-wide level is essential for obtaining information on the molecular mechanisms of diseases and fundamental biological processes. Proteomics has made tremendous advances to study the cellular repertoire of proteins in its entirety, but capturing representative proteo ...
SP600125 Selectively Inhibits Histone H3
... INTRODUCTION. The role played by histone modifications in transcriptional regulation is one recent area of interest in the study of gene expression. These modifications collectively influence a web of regulatory events, and their interconnectedness has led to the hypothesis that there is a “histone ...
... INTRODUCTION. The role played by histone modifications in transcriptional regulation is one recent area of interest in the study of gene expression. These modifications collectively influence a web of regulatory events, and their interconnectedness has led to the hypothesis that there is a “histone ...
Lecture 13-Effects of glycosylation on protein structure and function
... Comparison of rat and human CD2 • Rat CD2 is not glycosylated at the posi3on corresponding to Asn-‐65 in human CD2 • In human protein, lysine at 61, 69, and 71 all project from the same sid ...
... Comparison of rat and human CD2 • Rat CD2 is not glycosylated at the posi3on corresponding to Asn-‐65 in human CD2 • In human protein, lysine at 61, 69, and 71 all project from the same sid ...
The eukaryotic cell cycle
... Isolation of cell-division cycle (CDC) genes from a S. cerevisiae genomic library by functional complementation of cdc mutants ...
... Isolation of cell-division cycle (CDC) genes from a S. cerevisiae genomic library by functional complementation of cdc mutants ...
Supplemental Materials and Methods
... Linked heterodimer fusion protein constructs for Bcl-xL–Bak, Mcl1–Bak, and Bax–Bcl-2 were made using synthetic DNA (Life Technologies) with Gateway attB1 and attB2 sites flanking the insert region. His6MBP (maltose binding protein) tags were used to enhance solubility and permit affinity purificatio ...
... Linked heterodimer fusion protein constructs for Bcl-xL–Bak, Mcl1–Bak, and Bax–Bcl-2 were made using synthetic DNA (Life Technologies) with Gateway attB1 and attB2 sites flanking the insert region. His6MBP (maltose binding protein) tags were used to enhance solubility and permit affinity purificatio ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.