Deep Space Objects
... spirals, or “irregular” objects. Imagine something the size of an AA battery emitting the power of a nuclear reactor – that basically the idea behind quasars. A quasar is generally a galactic nucleus in the energetic early stages of formation, emitting up to two trillion Suns’ worth of energy from a ...
... spirals, or “irregular” objects. Imagine something the size of an AA battery emitting the power of a nuclear reactor – that basically the idea behind quasars. A quasar is generally a galactic nucleus in the energetic early stages of formation, emitting up to two trillion Suns’ worth of energy from a ...
Galaxy Notes Presentation
... giant spiral galaxy including our Sun The disk’s diameter is 100,000 light years Mass is 1,000 to 2,000 billion times the mass of the Sun The Sun lies a little more than 30,000 light years from the center Cannot actually count the number of stars in the galaxy, can estimate as roughly 100 bi ...
... giant spiral galaxy including our Sun The disk’s diameter is 100,000 light years Mass is 1,000 to 2,000 billion times the mass of the Sun The Sun lies a little more than 30,000 light years from the center Cannot actually count the number of stars in the galaxy, can estimate as roughly 100 bi ...
What is the net result of the proton-proton chain? a. 2 protons make
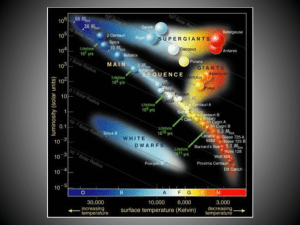
... What are the two most important intrinsic properties used to classify stars: a. Mass and age b. Luminosity and surface temperature c. Distance and luminosity d. Distance and surface temperature e. Distance and color Stars that have masses similar to the Sun and sizes similar to the Earth are: a. Mai ...
... What are the two most important intrinsic properties used to classify stars: a. Mass and age b. Luminosity and surface temperature c. Distance and luminosity d. Distance and surface temperature e. Distance and color Stars that have masses similar to the Sun and sizes similar to the Earth are: a. Mai ...
PHYSICS 015
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
... For the most massive stars, the Schwarzschild radius is already too big. For example, if you wanted to allow a 10-solar-mass star to settle down as a neutron star, about 10 km in diameter, it already inside its Schwarzschild radius and is doomed to collapse! Stars can’t ‘know’ that they should shed ...
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... Giants are dying stars; white dwarfs are dead stars • Evidence on giants from star clusters • Compare members of a population. (Twin study) ...
... Giants are dying stars; white dwarfs are dead stars • Evidence on giants from star clusters • Compare members of a population. (Twin study) ...
Unit 1
... of a single interstellar cloud of gas and dust • These groups are called star clusters • Open clusters have a low density of stars – there is lots of space between the cluster’s members • They can contain up to a few thousand stars in a volume 14 to 40 light years across • The Pleiades is a very fam ...
... of a single interstellar cloud of gas and dust • These groups are called star clusters • Open clusters have a low density of stars – there is lots of space between the cluster’s members • They can contain up to a few thousand stars in a volume 14 to 40 light years across • The Pleiades is a very fam ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... Clumps of glowing gas called Herbig-Haro objects are sometimes found along these jets and at their ends ...
... Clumps of glowing gas called Herbig-Haro objects are sometimes found along these jets and at their ends ...
Irregular Galaxies
... are said to be “clustered” together. • There are two types of star clusters. • Open Clusters: Unorganized clusters of stars with hundreds of stars. • Globular Clusters: Clusters of stars that are grouped in a spherical shape and often contain more than 100,000 stars ...
... are said to be “clustered” together. • There are two types of star clusters. • Open Clusters: Unorganized clusters of stars with hundreds of stars. • Globular Clusters: Clusters of stars that are grouped in a spherical shape and often contain more than 100,000 stars ...
Lecture 7 Stars and Galaxies and Nebula, (Oh My!) Feb 18 2003
... Outer layers of gas are blown off from the core of a star. The core often goes on to become a white dwarf. The eject gas is illuminated by the remaining star. This is the fate of most stars, including our own Sun. ...
... Outer layers of gas are blown off from the core of a star. The core often goes on to become a white dwarf. The eject gas is illuminated by the remaining star. This is the fate of most stars, including our own Sun. ...
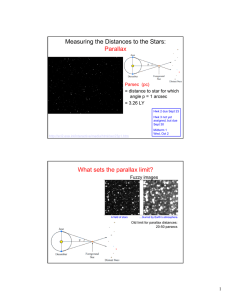
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
Last time: Star Clusters (sec. 19.6)
... depth, so hottest in center nuclear reactions H He “core H-burning”. Two nuclear reaction procceses: proton-proton (dominates in stars ~ sun’s mass and lower), and CNO cycle (dominates in stars more massive than sun; see More Precisely 20-1). Stable, lasts most of star’s lifetime. (Will explain ...
... depth, so hottest in center nuclear reactions H He “core H-burning”. Two nuclear reaction procceses: proton-proton (dominates in stars ~ sun’s mass and lower), and CNO cycle (dominates in stars more massive than sun; see More Precisely 20-1). Stable, lasts most of star’s lifetime. (Will explain ...
More on Cluster HR diagrams - University of Texas Astronomy
... the same (old) age, and are still “in one piece” (not dissolved), while not a single open cluster is older than about 5 billion years, and nearly all of them are younger than about 100 million years? Does this suggest that there were few open clusters forming until recently, with our Galaxy in a “lu ...
... the same (old) age, and are still “in one piece” (not dissolved), while not a single open cluster is older than about 5 billion years, and nearly all of them are younger than about 100 million years? Does this suggest that there were few open clusters forming until recently, with our Galaxy in a “lu ...
Lecture 16 - Yet More Evolution of Stars
... Core collapse • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, ...
... Core collapse • Iron core is degenerate • Core grows until it is too heavy to support itself • Core collapses, density increases, normal iron nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, ...
doc
... have about the same (old) age, and are still “in one piece” (not dissolved), while not a single open cluster is older than about 5 billion years, and nearly all of them are younger than about 100 million years? Does this suggest that there were few open clusters forming until recently, with our ...
... have about the same (old) age, and are still “in one piece” (not dissolved), while not a single open cluster is older than about 5 billion years, and nearly all of them are younger than about 100 million years? Does this suggest that there were few open clusters forming until recently, with our ...
Galaxies
... • Spiral structure has been determined through radio observations – Radio observations have shown how the spiral arms move around the center of the galaxy ...
... • Spiral structure has been determined through radio observations – Radio observations have shown how the spiral arms move around the center of the galaxy ...
Slide 1
... of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clusters including Local Grp. We are falling toward Virgo Cluster, which has three supergiant ellipticals (M87 contains accretion disk indicating BH or WH in center--a quadrillion solar masses!) The Pisces-Cetus Complex: may include 400 ric ...
... of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clusters including Local Grp. We are falling toward Virgo Cluster, which has three supergiant ellipticals (M87 contains accretion disk indicating BH or WH in center--a quadrillion solar masses!) The Pisces-Cetus Complex: may include 400 ric ...
Jeopardy Questions
... A: X-ray observations of hot gas in galaxy clusters, gravitational lensing from galaxy clusters, flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies ...
... A: X-ray observations of hot gas in galaxy clusters, gravitational lensing from galaxy clusters, flat rotation curves of spiral galaxies ...
Astrophysics
... This enables us to study the relationship between the mass and the other properties of stars It is found that there is a simple massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars The luminosity increases with the cube of the mass (this is consistent with other clues about the size, density and mass ...
... This enables us to study the relationship between the mass and the other properties of stars It is found that there is a simple massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars The luminosity increases with the cube of the mass (this is consistent with other clues about the size, density and mass ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... Because we are within the Galaxy, it is difficult to map out its structure. This is especially true when looking in the Galactic plane, because of all the dust. We are not near the center of the Galaxy, but where is the center? How far away is it? ...
... Because we are within the Galaxy, it is difficult to map out its structure. This is especially true when looking in the Galactic plane, because of all the dust. We are not near the center of the Galaxy, but where is the center? How far away is it? ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... The prominent pentagon of Auriga (awe-RYE-guh), the Charioteer, visible nearly overhead in March, is home to three beautiful open clusters that lend themselves well to low-magnification observing. Once the pentagon is identified, all three clusters are easy to find. However, since all of the Auriga ...
... The prominent pentagon of Auriga (awe-RYE-guh), the Charioteer, visible nearly overhead in March, is home to three beautiful open clusters that lend themselves well to low-magnification observing. Once the pentagon is identified, all three clusters are easy to find. However, since all of the Auriga ...
A-105 Homework 1
... orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
... orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
18.1 NOTES How are stars formed? Objective: Describe how stars
... white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how hot in temperature it is. Stars differ in size, brightness, and surface temperature. How large and massive a star is determines what will eventually happen to it. Most stars are composed ...
... white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how hot in temperature it is. Stars differ in size, brightness, and surface temperature. How large and massive a star is determines what will eventually happen to it. Most stars are composed ...
Open cluster

An open cluster, also known as galactic cluster, is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the galactic center, resulting in a migration to the main body of the galaxy as well as a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring.Young open clusters may still be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region. Over time, radiation pressure from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity and extinction) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades, Hyades or the Alpha Persei Cluster are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars or telescopes. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, is an example.