Galaxy / Cluster Ecosystem Ming Sun (University of Alabama in Huntsville)
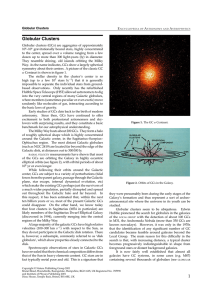
... Galaxy’svelocity vs.Perseus’s: + 2170 km/s --Mach number of ~ 3 --- a Bullet galaxy ! Soft X-ray Radio Optical Sun, Jerius & Jones 2005 ...
... Galaxy’svelocity vs.Perseus’s: + 2170 km/s --Mach number of ~ 3 --- a Bullet galaxy ! Soft X-ray Radio Optical Sun, Jerius & Jones 2005 ...
19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... • A strong X-ray source at the center from high velocity collisions in the accretion disk ...
... • A strong X-ray source at the center from high velocity collisions in the accretion disk ...
Globular Clusters
... the appropriate statistical significance among the GC stars. This allows a direct check on the validity of the detailed evolution theory. When GCs are considered just as a million or so pointlike masses in a small volume, subject to internal and external dynamical interactions, they represent an ide ...
... the appropriate statistical significance among the GC stars. This allows a direct check on the validity of the detailed evolution theory. When GCs are considered just as a million or so pointlike masses in a small volume, subject to internal and external dynamical interactions, they represent an ide ...
Part 2 - Aryabhat
... ring or donut. Epsilon Lyrae appears to the naked-eye as a double star, but through a small telescope you can see that the two individual stars are themselves double! Epsilon Lyrae is popularly known as the "double double." Vega is a hydrogen-burning dwarf star, 54 times more luminous and 1.5 times ...
... ring or donut. Epsilon Lyrae appears to the naked-eye as a double star, but through a small telescope you can see that the two individual stars are themselves double! Epsilon Lyrae is popularly known as the "double double." Vega is a hydrogen-burning dwarf star, 54 times more luminous and 1.5 times ...
presentation source
... “[Even though T Tauri associations could all have similar colors implying young age by coincidence], it is of course, tempting to search for a connection between the T Tauri stars and Bok’s ‘globules,’ but we must admit that at present there is no evidence of any objects intermediate between the two ...
... “[Even though T Tauri associations could all have similar colors implying young age by coincidence], it is of course, tempting to search for a connection between the T Tauri stars and Bok’s ‘globules,’ but we must admit that at present there is no evidence of any objects intermediate between the two ...
Binocular Objects (MS Word)
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
... Sagittarius contains more Messier objects than any other constellation. The best way to identify them is to take them one by one. The beginner will have to be careful not to confuse the various objects. The principal stars of Sagittarius form the famous “Teapot” asterism. The brightest part of the M ...
Our Galaxy, The Milky Way
... Thus, by measuring radial velocities, if we knew the distances, we could map out the differential rotation pattern ...
... Thus, by measuring radial velocities, if we knew the distances, we could map out the differential rotation pattern ...
Observational properties of stars
... Prad=10 Pgas. The other boundaries are found by equating the pressure relationships and solving the formulae so that they are only functions of density and temperature. So those boundaries mark locations where the dominant form of the gas transitions from one form to another. In reality you will not ...
... Prad=10 Pgas. The other boundaries are found by equating the pressure relationships and solving the formulae so that they are only functions of density and temperature. So those boundaries mark locations where the dominant form of the gas transitions from one form to another. In reality you will not ...
Solutions
... 2. Type Ia and Type II Supernovae are each explosions that signify the death of a star and which are briefly as luminous as an entire galaxy. However, they are very different sorts of objects. What is the original source of the energy which powers each type of explosion? (I.e. where did the energy ...
... 2. Type Ia and Type II Supernovae are each explosions that signify the death of a star and which are briefly as luminous as an entire galaxy. However, they are very different sorts of objects. What is the original source of the energy which powers each type of explosion? (I.e. where did the energy ...
The Southern Fall PDF - Treasures of the Southern Sky
... The vast Carina Nebula contains over a dozen stars with masses between 50 to 100 times that of the Sun, and these are the main source of illumination of the nebula itself. However, by far the most exotic star here is Eta Carinae. It is shrouded in a tiny nebula — the expanding, dumbbell-shaped Homu ...
... The vast Carina Nebula contains over a dozen stars with masses between 50 to 100 times that of the Sun, and these are the main source of illumination of the nebula itself. However, by far the most exotic star here is Eta Carinae. It is shrouded in a tiny nebula — the expanding, dumbbell-shaped Homu ...
Hall Scorpius constellation (11) Jacob Hall Physics 1040, sec 002
... and at an estimated distance of 32,600 light-years, M80's spatial diameter is about 95 light-years. It contains several hundred thousand stars, and is among the more densely populated globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy. M80 contains a relatively large number of blue stragglers, stars that app ...
... and at an estimated distance of 32,600 light-years, M80's spatial diameter is about 95 light-years. It contains several hundred thousand stars, and is among the more densely populated globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy. M80 contains a relatively large number of blue stragglers, stars that app ...
Abundances of RGB stars in NGC 6752 Grundahl
... The primordial scenario, and variations on it, has been proposed and discussed several times before in the literature (see for example Cottrell & Da Costa 1981, and Cannon et al. 1998). The small star–to–star scatter in the iron peak elements (as observed in this work) indicates that the contributio ...
... The primordial scenario, and variations on it, has been proposed and discussed several times before in the literature (see for example Cottrell & Da Costa 1981, and Cannon et al. 1998). The small star–to–star scatter in the iron peak elements (as observed in this work) indicates that the contributio ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... – pressure due to fusion in core • hydrogen in the core eventually converted to helium nuclear reactions stop! • gravity takes over and the core shrinks • outside layers also collapse • layers closer to the center collapse faster than those near the surface. • As the layers collapses, the gas comp ...
... – pressure due to fusion in core • hydrogen in the core eventually converted to helium nuclear reactions stop! • gravity takes over and the core shrinks • outside layers also collapse • layers closer to the center collapse faster than those near the surface. • As the layers collapses, the gas comp ...
129 DYNAMICAL STREAMS IN THE SOLAR NEIGHBOURHOOD B
... Nevertheless, De Simone et al. (2004) have shown that the structure of the local distribution function could well be due to a lumpy potential related to the presence of strong transient spiral waves. Besides those simulations, a recent model of gas flows in the Galaxy (Bissantz et al. 2003) indicate ...
... Nevertheless, De Simone et al. (2004) have shown that the structure of the local distribution function could well be due to a lumpy potential related to the presence of strong transient spiral waves. Besides those simulations, a recent model of gas flows in the Galaxy (Bissantz et al. 2003) indicate ...
The cosmic distance scale
... spectrum. The HI gas in a spiral follows very closely circular orbits at a speed Vc . If the galaxy is inclined at an angle i to the line of sight, the observed line of sight velocity will vary from + Vc sin i to - Vc sin i relative to the systemic velocity of the galaxy. This results in a double ho ...
... spectrum. The HI gas in a spiral follows very closely circular orbits at a speed Vc . If the galaxy is inclined at an angle i to the line of sight, the observed line of sight velocity will vary from + Vc sin i to - Vc sin i relative to the systemic velocity of the galaxy. This results in a double ho ...
1705 Star Charts
... Antares is a red-giant star like Betelgeuse: around 20 times the mass of the sun but wider than Earth's orbit. It is 600 light years away and 19 000 times brighter than the sun. Arcturus is the brightest red star in the sky but, at 37 light years, is much closer than Antares. It is about 120 times b ...
... Antares is a red-giant star like Betelgeuse: around 20 times the mass of the sun but wider than Earth's orbit. It is 600 light years away and 19 000 times brighter than the sun. Arcturus is the brightest red star in the sky but, at 37 light years, is much closer than Antares. It is about 120 times b ...
Good Vibrations and Stellar Pulsations - Physics
... In 1913, Hertzsprung calculated that the distance to the Small Magellanic Cloud was 33,000 light years. This was the greatest distance ever determined for an astronomical object. In 1917, Harlow Shapley used Hertzsprung’s calibration of the period-luminosity relation to determine the distance to th ...
... In 1913, Hertzsprung calculated that the distance to the Small Magellanic Cloud was 33,000 light years. This was the greatest distance ever determined for an astronomical object. In 1917, Harlow Shapley used Hertzsprung’s calibration of the period-luminosity relation to determine the distance to th ...
Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... 1. Stars are born in the cold (20K), giant molecular clouds (GMCs) found in the Galaxy. Astronomers estimate that our Galaxy contains 5,000 GMCs. 2. The average density of a GMC is about 200 molecules/cm3; a typical cloud may be 50 pc across and contain as much as a million solar masses of material. ...
... 1. Stars are born in the cold (20K), giant molecular clouds (GMCs) found in the Galaxy. Astronomers estimate that our Galaxy contains 5,000 GMCs. 2. The average density of a GMC is about 200 molecules/cm3; a typical cloud may be 50 pc across and contain as much as a million solar masses of material. ...
Frontiers: Intermediate-Mass Black Holes For our final lecture we will
... maybe aspects of star formation. Basically, you can pair IMBHs with stellar-mass objects (specifically BHs or NSs); with other IMBHs; or with SMBHs. In a stellar cluster, the third growth mechanism above requires mergers with stellar-mass black holes or neutron stars. There are a lot of uncertaintie ...
... maybe aspects of star formation. Basically, you can pair IMBHs with stellar-mass objects (specifically BHs or NSs); with other IMBHs; or with SMBHs. In a stellar cluster, the third growth mechanism above requires mergers with stellar-mass black holes or neutron stars. There are a lot of uncertaintie ...
Powerpoint
... Observation of such events suggests that low-mass white dwarfs could account for about half of the mass needed. The rest is mystery. ...
... Observation of such events suggests that low-mass white dwarfs could account for about half of the mass needed. The rest is mystery. ...
Open cluster

An open cluster, also known as galactic cluster, is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the galactic center, resulting in a migration to the main body of the galaxy as well as a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring.Young open clusters may still be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region. Over time, radiation pressure from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity and extinction) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades, Hyades or the Alpha Persei Cluster are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars or telescopes. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, is an example.