![Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014331057_1-996ec6eddf93071c5e835624d4620c7e-300x300.png)
Cosmic variance in [O/Fe] in the Galactic disk
... Stars in the thin and thick disks can be statistically distinguished based on their distance to the plane, age, kinematics, or chemical compositions. The kinematic properties of both disks overlap, and the available distances are not very accurate. On the other hand, the intrinsic uncertainties in t ...
... Stars in the thin and thick disks can be statistically distinguished based on their distance to the plane, age, kinematics, or chemical compositions. The kinematic properties of both disks overlap, and the available distances are not very accurate. On the other hand, the intrinsic uncertainties in t ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... Clusters of Galaxies Rather than occurring individually in space, galaxies are grouped in clusters ranging in size from a few dozens to thousands of galaxies. The Coma Cluster, shown at right, is 300 million light years from the Milky Way and contains more than 1,000 (and possibly as many as 10,000 ...
... Clusters of Galaxies Rather than occurring individually in space, galaxies are grouped in clusters ranging in size from a few dozens to thousands of galaxies. The Coma Cluster, shown at right, is 300 million light years from the Milky Way and contains more than 1,000 (and possibly as many as 10,000 ...
Gaps
... • The discontinuity in the rotation rate seems to coincide with the luminosity jump - All the stars with Teff > 11 500 K have vsin i < 12 km/s - Stars with Teff < 11 500 K show a range of rotational velocities, with some stars showing vsin i up to 30km/s. ...
... • The discontinuity in the rotation rate seems to coincide with the luminosity jump - All the stars with Teff > 11 500 K have vsin i < 12 km/s - Stars with Teff < 11 500 K show a range of rotational velocities, with some stars showing vsin i up to 30km/s. ...
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
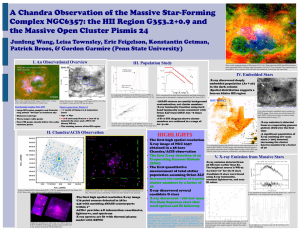
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
Lecture-25 Notes - Georgia Southern University Astrophysics
... These massive galaxies (and their super-massive black holes) had formed before the universe was 1-billion years old!! A z = 7.1 QSO has recently been discovered. It formed ~300-million years after the creation of the universe!! ...
... These massive galaxies (and their super-massive black holes) had formed before the universe was 1-billion years old!! A z = 7.1 QSO has recently been discovered. It formed ~300-million years after the creation of the universe!! ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that initially more massive stars circumvent the R ...
... star leaves the main sequence and becomes a blue supergiant, and ultimately a red supergiant (RSG) for stars with initial mass up to perhaps 20–30 MA. Observationally, there is an absence of luminous RSGs, known as the Humphreys-Davidson limit, such that initially more massive stars circumvent the R ...
Chapter 16
... Mutual gravitation between the cloud’s parts pulled it together. 2. The center portion was the first to become dense enough for stars to form. Dense pockets in orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating ...
... Mutual gravitation between the cloud’s parts pulled it together. 2. The center portion was the first to become dense enough for stars to form. Dense pockets in orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating ...
WORD - Astrophysics
... overcome crowding, and a 100m class telescope is required to study the brighter galaxies at their half-light radius - without it work is limited to the less representative outer regions where crowding is less of an issue. The more luminous elliptical ...
... overcome crowding, and a 100m class telescope is required to study the brighter galaxies at their half-light radius - without it work is limited to the less representative outer regions where crowding is less of an issue. The more luminous elliptical ...
Lect15-3-23-11-stars..
... Now you can understand that these low-mass stars have not yet reached the main sequence for the Pleiades cluster. The previous slide indicates that only stars of about one solar mass or more have had time to reach the main sequence by now. ...
... Now you can understand that these low-mass stars have not yet reached the main sequence for the Pleiades cluster. The previous slide indicates that only stars of about one solar mass or more have had time to reach the main sequence by now. ...
Exploration of the Milky Way and Nearby galaxies
... stars produced the metals found in dwarf galaxies and the Galactic halo. Frebel et al. showed that the overall abundance pattern mirrors that seen in lowmetallicity halo stars, including alpha-elements. Such chemical similarity indicates that the systems destroyed to form the halo billions of years ...
... stars produced the metals found in dwarf galaxies and the Galactic halo. Frebel et al. showed that the overall abundance pattern mirrors that seen in lowmetallicity halo stars, including alpha-elements. Such chemical similarity indicates that the systems destroyed to form the halo billions of years ...
The Galactic Halo The Galactic Disk Height and Thickness of MW
... Shapley’s Center of the Galaxy " To find the center of the Galaxy, Shapley measured the distance to each cluster using RR Lyrae stars and produced a three dimensional plot of the clusters’ positions. The center of the Galaxy was then identified by the average position of the clusters. " We now know ...
... Shapley’s Center of the Galaxy " To find the center of the Galaxy, Shapley measured the distance to each cluster using RR Lyrae stars and produced a three dimensional plot of the clusters’ positions. The center of the Galaxy was then identified by the average position of the clusters. " We now know ...
Using Photometric Data to Derive an HR Diagram
... M-16 is located in the next spiral arm of our Milky Way Galaxy, looking toward the galactic center. That means there is a lot of DUST in the way, and dust causes the visual magnitudes to be greater than they otherwise would be (i.e., dimmer). Dust also causes starlight to appear REDDER than it other ...
... M-16 is located in the next spiral arm of our Milky Way Galaxy, looking toward the galactic center. That means there is a lot of DUST in the way, and dust causes the visual magnitudes to be greater than they otherwise would be (i.e., dimmer). Dust also causes starlight to appear REDDER than it other ...
PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... • Mass has a lower cutoff and upper cutoff. This is because lower mass objects can not initiate nuclear burning while higher mass stars are unstable. • The luminosity range varies by about 11 orders of magnitude, much larger than any other parameters. Some stars are extremely luminous, while others ...
... • Mass has a lower cutoff and upper cutoff. This is because lower mass objects can not initiate nuclear burning while higher mass stars are unstable. • The luminosity range varies by about 11 orders of magnitude, much larger than any other parameters. Some stars are extremely luminous, while others ...
The Milky Way
... In order to get a good outside view of the Milky Way, you are trying to send a spacecraft high above the plane of the Milky Way, to a height equal to our distance from the Galactic center. If you had a spacecraft that could travel at almost the speed of light, how long would it take it to get there ...
... In order to get a good outside view of the Milky Way, you are trying to send a spacecraft high above the plane of the Milky Way, to a height equal to our distance from the Galactic center. If you had a spacecraft that could travel at almost the speed of light, how long would it take it to get there ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... The GalEx All-sky Imaging Survey(AIS) will provide an unprecedented view into the near- and far-ultraviolet universe. One area of astronomical research that is not well-served by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2 ...
... The GalEx All-sky Imaging Survey(AIS) will provide an unprecedented view into the near- and far-ultraviolet universe. One area of astronomical research that is not well-served by the AIS, due to avoidance of the galactic plane, is young stars. According to Fischer (1998; PhD Thesis, UCSC) only 1% (2 ...
PH607lec10
... monitored. However, in spite of all efforts, no unambiguous NIR counterpart of SgrA* could be detected up to 2003. On the 9th of May, during routine observations of the GC star cluster at 1.7 microns with NAOS/CONICA at the VLT, we witnessed a powerful flare at the location of the black hole. Within ...
... monitored. However, in spite of all efforts, no unambiguous NIR counterpart of SgrA* could be detected up to 2003. On the 9th of May, during routine observations of the GC star cluster at 1.7 microns with NAOS/CONICA at the VLT, we witnessed a powerful flare at the location of the black hole. Within ...
shirley - Yancy L. Shirley`s Webpage
... Dense cores with no known internal luminosity source SEDs peak longer than 100 m Study the initial conditions of low-mass SF ...
... Dense cores with no known internal luminosity source SEDs peak longer than 100 m Study the initial conditions of low-mass SF ...
File
... stars in elliptical galaxies are old, cool, low-mass stars, making them look reddish. There is little gas and dust, and little formation of new stars. Elliptical galaxies range greatly in size, from ten million solar masses to one hundred times the mass of the Milky Way. Irregular Galaxies ...
... stars in elliptical galaxies are old, cool, low-mass stars, making them look reddish. There is little gas and dust, and little formation of new stars. Elliptical galaxies range greatly in size, from ten million solar masses to one hundred times the mass of the Milky Way. Irregular Galaxies ...
Nebulae - Innovative Teachers BG
... a in a same cloud. Such processes have been observed in the Orion Nebula, so there are now seeing many bright and hot stars. Evidence of star formation in the same place are stellar clusters. The Galactic Stellar Clusters have a relatively small number (a few hundreds) of bright hot stars. These ast ...
... a in a same cloud. Such processes have been observed in the Orion Nebula, so there are now seeing many bright and hot stars. Evidence of star formation in the same place are stellar clusters. The Galactic Stellar Clusters have a relatively small number (a few hundreds) of bright hot stars. These ast ...
Properties of Ellipticals and Spirals
... Ellipticals: Velocities of stars in ellipticals are more or less random Velocity dispersions are responsible for the overall shape of galaxies. Oblate and Prolate Ellipticals – how that? Spiral: Velocities of stars in spirals are more ordered. Stars rotate around the galactic center in a disk surrou ...
... Ellipticals: Velocities of stars in ellipticals are more or less random Velocity dispersions are responsible for the overall shape of galaxies. Oblate and Prolate Ellipticals – how that? Spiral: Velocities of stars in spirals are more ordered. Stars rotate around the galactic center in a disk surrou ...
THE GALACTIC GAZETTE The Astronomical Society of Southern New England Next Meeting
... helpful characteristic: The stars are all the same distance away. That means if a star is brighter than another in the cluster, it really is more luminous. That makes comparing the stars directly to each other easier. At first it was assumed that all globulars are very old—as old as the Milky Way it ...
... helpful characteristic: The stars are all the same distance away. That means if a star is brighter than another in the cluster, it really is more luminous. That makes comparing the stars directly to each other easier. At first it was assumed that all globulars are very old—as old as the Milky Way it ...
harrold_kajubi_astro1
... Mees Telescope with Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Camera Photometry with ATV ...
... Mees Telescope with Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Camera Photometry with ATV ...
what are stars made of?
... Gravity brings global clusters together Global clusters are large groups of stars that are held together by their own gravity. These groups of stars are very old and often have millions of members. ...
... Gravity brings global clusters together Global clusters are large groups of stars that are held together by their own gravity. These groups of stars are very old and often have millions of members. ...
Small galaxies are growing smaller
... have the spectacular appearance we see in “coffee table” books. Indeed, in the early days of extragalactic astronomy it was thought that most galaxies were of rather similar (large) luminosities. Specifically, Edwin Hubble (1936) and his contemporaries believed that the luminosity function (LF) of g ...
... have the spectacular appearance we see in “coffee table” books. Indeed, in the early days of extragalactic astronomy it was thought that most galaxies were of rather similar (large) luminosities. Specifically, Edwin Hubble (1936) and his contemporaries believed that the luminosity function (LF) of g ...
Astronomical Distance Determination • etc.
... seen from far away. (They are not main sequence stars). A complication though is that there are two populations of Cepheids and they have different period luminosity ...
... seen from far away. (They are not main sequence stars). A complication though is that there are two populations of Cepheids and they have different period luminosity ...
Open cluster

An open cluster, also known as galactic cluster, is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the galactic center, resulting in a migration to the main body of the galaxy as well as a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring.Young open clusters may still be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region. Over time, radiation pressure from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity and extinction) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades, Hyades or the Alpha Persei Cluster are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars or telescopes. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, is an example.