Lecture 8a Star Formation 10/15/2014
... • How they “die” depends on mass " large stars blow up Supernovas • Understand stars’ lifecycles by studying their properties and also groups of stars ...
... • How they “die” depends on mass " large stars blow up Supernovas • Understand stars’ lifecycles by studying their properties and also groups of stars ...
Chapter 8: The Pennsylvanian Period in Alabama: Looking Up
... While watching the fast-moving frames, we would see stars moving in all directions. The sky would be filled with movement. Some stars would get brighter as they approach us, others would get dimmer as they recede. Some stars would, relatively speaking, ``pop" into view, and before you knew it would ...
... While watching the fast-moving frames, we would see stars moving in all directions. The sky would be filled with movement. Some stars would get brighter as they approach us, others would get dimmer as they recede. Some stars would, relatively speaking, ``pop" into view, and before you knew it would ...
The Pennsylvanian Period in Alabama: Looking Up Astronomy and
... from us and its direction in the sky vary considerably over time. 310 million years ago, it was 2,900 light years away and not visible to the naked eye. Extrapolating back we discover that Rigel Kent is closer to us now than it has ever been, at least since the Devonian. Rigel Kent is a fine visual ...
... from us and its direction in the sky vary considerably over time. 310 million years ago, it was 2,900 light years away and not visible to the naked eye. Extrapolating back we discover that Rigel Kent is closer to us now than it has ever been, at least since the Devonian. Rigel Kent is a fine visual ...
SGHS Faulkes ASISTM Star Cluster Photometry
... This will give you a set of visible magnitudes V so you will then have a B and V value for each star. Note: It is very important that you match the B and V values for each star in each image. The B value you measured for star 1 must be recorded with the V value for that same star. The spreadsheet I ...
... This will give you a set of visible magnitudes V so you will then have a B and V value for each star. Note: It is very important that you match the B and V values for each star in each image. The B value you measured for star 1 must be recorded with the V value for that same star. The spreadsheet I ...
The formation of the galaxy is believed to be similar
... The position of the Sun in the Milky Way Galaxy is best described as a) in the disk, slightly more than halfway out from the center. b) very close to the center. c) in an open cluster in the disk. d) in a globular cluster in the halo. ...
... The position of the Sun in the Milky Way Galaxy is best described as a) in the disk, slightly more than halfway out from the center. b) very close to the center. c) in an open cluster in the disk. d) in a globular cluster in the halo. ...
–1– 2. Milky Way We know a great deal, perhaps more than any
... Fig. 1.— Panorama of the Milky Way (credit: Lund Observatory). Notice the dark patches caused by dust extinction. A Panorama of the Milky Way is shown in Fig. 1. The Galaxy appears as a thin band with dark patches which are caused by dust extinction. Many past astronomers often ignored such obvious ...
... Fig. 1.— Panorama of the Milky Way (credit: Lund Observatory). Notice the dark patches caused by dust extinction. A Panorama of the Milky Way is shown in Fig. 1. The Galaxy appears as a thin band with dark patches which are caused by dust extinction. Many past astronomers often ignored such obvious ...
CHP 15
... d. they only observed stars in the disk of the galaxy and not the halo. e. they did not know about interstellar dust clouds. 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stars of the disk component of our galaxy? a. circular orbits. b. randomly inclined orbits. c. higher metal abundance. ...
... d. they only observed stars in the disk of the galaxy and not the halo. e. they did not know about interstellar dust clouds. 2. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the stars of the disk component of our galaxy? a. circular orbits. b. randomly inclined orbits. c. higher metal abundance. ...
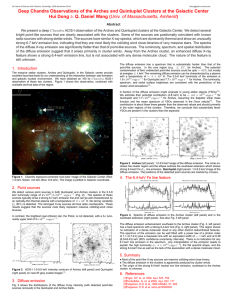
Deep Chandra Observations of the Arches and Quintuplet Clusters at... Hui Dong Q. Daniel Wang ( &
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
Chapter 11
... understand how stars work. For instance, what stops a contracting star and gives it stability? We can understand this phenomenon because we understand some of the basic laws of physics. ...
... understand how stars work. For instance, what stops a contracting star and gives it stability? We can understand this phenomenon because we understand some of the basic laws of physics. ...
question - UW Canvas
... elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that these stars fuse all elements simultaneously; that is, all at the same time. b.The ...
... elements without any of these stages resulting in degeneracy or any flashes like the helium flash that occurs in solar-type stars? a. The cores of massive stars are so hot, have such high densities and pressures, that these stars fuse all elements simultaneously; that is, all at the same time. b.The ...
Spagna
... for F 18 and J 19 (|b|>20) predicted by the Mendez’s Galaxy model extended to the GSC-II photometric system. ...
... for F 18 and J 19 (|b|>20) predicted by the Mendez’s Galaxy model extended to the GSC-II photometric system. ...
hst/stis spectroscopy of the environment in the starburst core of m82
... The structure of M82 central region: Confirm the presence of a stellar bar. The interaction of x1-orbits with the perpendicular x2-orbits lead to a buildup of gas and dust along the leading x1-orbits. By comparing CO observations to an HST broadband colour composite of M82, the authors identify that ...
... The structure of M82 central region: Confirm the presence of a stellar bar. The interaction of x1-orbits with the perpendicular x2-orbits lead to a buildup of gas and dust along the leading x1-orbits. By comparing CO observations to an HST broadband colour composite of M82, the authors identify that ...
Document
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
32Brightness
... higher energy levels and spontaneously fall to lower levels, emitting light in the process • Absorption from cooler gases in front of continuum source, where discrete colors are absorbed by atoms – From emission and absorption lines, get composition of objects and also their temperature ...
... higher energy levels and spontaneously fall to lower levels, emitting light in the process • Absorption from cooler gases in front of continuum source, where discrete colors are absorbed by atoms – From emission and absorption lines, get composition of objects and also their temperature ...
Open clusters in the Third Galactic Quadrant III. Alleged binary
... members, some sequences are not satisfactorily reproduced by one single isochrone, as said above, and a range of them has been indicated in each cluster of Table 4. Known reasons to fail the fitting include the effect of un-resolved binaries, stellar rotation and variable reddening due to remaining m ...
... members, some sequences are not satisfactorily reproduced by one single isochrone, as said above, and a range of them has been indicated in each cluster of Table 4. Known reasons to fail the fitting include the effect of un-resolved binaries, stellar rotation and variable reddening due to remaining m ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Consequently, the large-scale structure of the Galaxy must be inferred from observations made at infrared and radio wavelengths. The central bar and spiral structure in the stellar disc, generate significant non-axisymmetric gravitational forces that make the gas disc and its embedded star formation ...
... Consequently, the large-scale structure of the Galaxy must be inferred from observations made at infrared and radio wavelengths. The central bar and spiral structure in the stellar disc, generate significant non-axisymmetric gravitational forces that make the gas disc and its embedded star formation ...
THE HR DIAGRAM
... Late in the nineteenth century, astronomers had tools that revealed a great deal about stars. By that time, advances in telescope design and photographic emulsions were becoming mature. They were able to take spectral images of stars which revealed their composition and th ...
... Late in the nineteenth century, astronomers had tools that revealed a great deal about stars. By that time, advances in telescope design and photographic emulsions were becoming mature. They were able to take spectral images of stars which revealed their composition and th ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... dust and gas strongly concentrated in the disk plane. • The Sun orbits around the Galactic centre at a speed of about 220 km s-1. • It takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit ...
... dust and gas strongly concentrated in the disk plane. • The Sun orbits around the Galactic centre at a speed of about 220 km s-1. • It takes about 220 million years to complete one orbit ...
PH607lec12
... QSOs, we have speculated on whether the centre of our galaxy might contain a black hole "Galactic Centre" here will mean the central ~10 parsecs of the Galaxy. It contains: 1. Young stars: the stellar population including evidence for star formation there in the last 50 million years or even less 2 ...
... QSOs, we have speculated on whether the centre of our galaxy might contain a black hole "Galactic Centre" here will mean the central ~10 parsecs of the Galaxy. It contains: 1. Young stars: the stellar population including evidence for star formation there in the last 50 million years or even less 2 ...
observing cards - NC Science Festival
... that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of stars up to 8 times the mass of our Sun. If we compared that period in a Sun-like star’s life to a human lifetime, it would correspond to about the last h ...
... that these were not planets, but the name stuck. The planetary nebula phase of a star’s life represents a short but important time in the life of stars up to 8 times the mass of our Sun. If we compared that period in a Sun-like star’s life to a human lifetime, it would correspond to about the last h ...
Mass and the Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... very small x requires that p ≥ h / x be very large. – Very large uncertainty in the momentum of the electrons means that their velocity varies over a very large range (recall the definition of momentum: p = mv) – A very large range in the possible range of velocity of a large collection of partic ...
... very small x requires that p ≥ h / x be very large. – Very large uncertainty in the momentum of the electrons means that their velocity varies over a very large range (recall the definition of momentum: p = mv) – A very large range in the possible range of velocity of a large collection of partic ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
Virgo constellation
... dense swarm of globular star clusters orbiting the galaxy. More than 2000 have been counted. The Sombrero is believed to have a central supermassive black hole at its heart. X-ray emission from the region suggests some material is still being absorbed by the hole. ...
... dense swarm of globular star clusters orbiting the galaxy. More than 2000 have been counted. The Sombrero is believed to have a central supermassive black hole at its heart. X-ray emission from the region suggests some material is still being absorbed by the hole. ...
two dozen compact sources and a massive disk
... cluster begins to emerge MIR - mm 4. Young cluster cluster has emerged from cloud ...
... cluster begins to emerge MIR - mm 4. Young cluster cluster has emerged from cloud ...
Open cluster

An open cluster, also known as galactic cluster, is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the galactic center, resulting in a migration to the main body of the galaxy as well as a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring.Young open clusters may still be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region. Over time, radiation pressure from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity and extinction) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades, Hyades or the Alpha Persei Cluster are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars or telescopes. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, is an example.