Lecture Notes - Mutual Inductance and Linear Transformers File
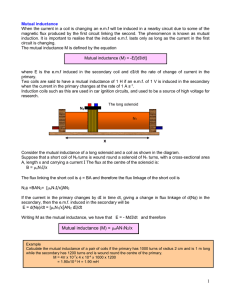
... When two coils are placed close to each other, a changing flux in one coil will cause an induced voltage in the second coil. The coils are said to have mutual inductance M, which can either add or subtract from the total inductance depending on if the fields are aiding or opposing. Mutual induct ...
... When two coils are placed close to each other, a changing flux in one coil will cause an induced voltage in the second coil. The coils are said to have mutual inductance M, which can either add or subtract from the total inductance depending on if the fields are aiding or opposing. Mutual induct ...
Lecture Notes - Mutual Inductance and Linear Transformers File
... When two coils are placed close to each other, a changing flux in one coil will cause an induced voltage in the second coil. The coils are said to have mutual inductance M, which can either add or subtract from the total inductance depending on if the fields are aiding or opposing. Mutual induct ...
... When two coils are placed close to each other, a changing flux in one coil will cause an induced voltage in the second coil. The coils are said to have mutual inductance M, which can either add or subtract from the total inductance depending on if the fields are aiding or opposing. Mutual induct ...
Mutual / Self-Induction * Learning Outcomes
... Mutual induction occurs when two coils are adjacent to each other. If the magnetic field in one coil changes, an emf is induced in the other. This happens with a.c. The size of the induced emf depends on: the distance between the coils (closer yields more emf), whether the coils have the sam ...
... Mutual induction occurs when two coils are adjacent to each other. If the magnetic field in one coil changes, an emf is induced in the other. This happens with a.c. The size of the induced emf depends on: the distance between the coils (closer yields more emf), whether the coils have the sam ...
transformer
... A magnetically (inductively) coupled inductor circuit consists of more than one coil of inductive wire wound on the same magnetic core. The flux linkage of the z-turn coil is defined as flux Φ times the number of turns z. Each coils has its own flux linkage. The total flux linking each coil is the s ...
... A magnetically (inductively) coupled inductor circuit consists of more than one coil of inductive wire wound on the same magnetic core. The flux linkage of the z-turn coil is defined as flux Φ times the number of turns z. Each coils has its own flux linkage. The total flux linking each coil is the s ...
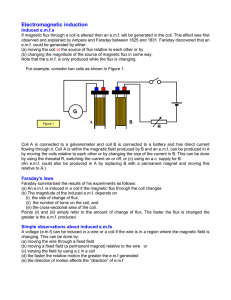
Electromagnetic Induction
... In the writing process, information is firstly converted into an a.c. signals. The a.c. magnetize and rearrange the grains on the platter in as certain pattern as the patter passes over the head. In the reading process, the magnetic field of the grains induces a certain a.c. in the head as the platt ...
... In the writing process, information is firstly converted into an a.c. signals. The a.c. magnetize and rearrange the grains on the platter in as certain pattern as the patter passes over the head. In the reading process, the magnetic field of the grains induces a certain a.c. in the head as the platt ...
Electromagnetic Induction Study Guide
... 4. You have a generator that is made from 450 circular wire loops that are 3 cm in diameter and rotate in a magnetic field of 1.7 T from permanent magnets. How quickly would the loop have to rotate to produce an emf with an amplitude of 15 V? 5. When it is turning at operating speed, a motor with 7 ...
... 4. You have a generator that is made from 450 circular wire loops that are 3 cm in diameter and rotate in a magnetic field of 1.7 T from permanent magnets. How quickly would the loop have to rotate to produce an emf with an amplitude of 15 V? 5. When it is turning at operating speed, a motor with 7 ...
Transformers Practice #1
... Some transmission lines carry electricity at 138 kV and 7.25 A. There are transformers to convert the electricity before it reaches residential power lines. The primary coil has 238 loops. The secondary coil voltage is 4.06 kV. a. What type of transformer is this? b. How many loops are in the second ...
... Some transmission lines carry electricity at 138 kV and 7.25 A. There are transformers to convert the electricity before it reaches residential power lines. The primary coil has 238 loops. The secondary coil voltage is 4.06 kV. a. What type of transformer is this? b. How many loops are in the second ...
Transformers and Electromagnetic Waves Practice Problems
... 8. The circuit components inside an electronic device operate at 20 V and 0.50 A. The power adapter for the device contains a transformer with 300 turns in its primary coil that is used to convert 120 V household electricity to the proper voltage. a) How many turns must the secondary coil have? b) H ...
... 8. The circuit components inside an electronic device operate at 20 V and 0.50 A. The power adapter for the device contains a transformer with 300 turns in its primary coil that is used to convert 120 V household electricity to the proper voltage. a) How many turns must the secondary coil have? b) H ...
Chapter 17-3 Electric Currents
... • An electric current can be produced in a circuit by a changing magnetic field ...
... • An electric current can be produced in a circuit by a changing magnetic field ...
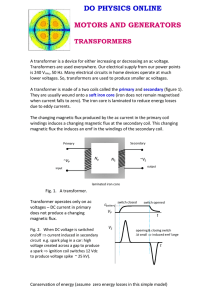
Electricity Distribution
... The voltage induced in the secondary (output) coil depends on the number of turns on the primary and secondary coils. ...
... The voltage induced in the secondary (output) coil depends on the number of turns on the primary and secondary coils. ...
Mutual inductance
... Mutual inductance (M) = -E/[dI/dt] where E is the e.m.f induced in the secondary coil and dI/dt the rate of change of current in the primary. Two coils are said to have a mutual inductance of 1 H if an e.m.f. of 1 V is induced in the secondary when the current in the primary changes at the rate of 1 ...
... Mutual inductance (M) = -E/[dI/dt] where E is the e.m.f induced in the secondary coil and dI/dt the rate of change of current in the primary. Two coils are said to have a mutual inductance of 1 H if an e.m.f. of 1 V is induced in the secondary when the current in the primary changes at the rate of 1 ...
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits
... Transformers work only if the current is changing; this is one reason why electricity is transmitted as ac. ...
... Transformers work only if the current is changing; this is one reason why electricity is transmitted as ac. ...
Ch13_PPT_Fund_Elec_Circ_5e
... • The general rule for eliminating the transformer and reflecting the secondary circuit to the primary side is: Divide the secondary impedance by n2, divide the secondary voltage by n, and multiply the secondary current by n. • The rule for eliminating the transformer and reflecting the primary circ ...
... • The general rule for eliminating the transformer and reflecting the secondary circuit to the primary side is: Divide the secondary impedance by n2, divide the secondary voltage by n, and multiply the secondary current by n. • The rule for eliminating the transformer and reflecting the primary circ ...
Resonant inductive coupling
Resonant inductive coupling or electrodynamic induction is the near field wireless transmission of electrical energy between two magnetically coupled coils that are part of resonant circuits tuned to resonate at the same frequency. This process occurs in a resonant transformer, an electrical component which consists of two high Q coils wound on the same core with capacitors connected across the windings to make two coupled LC circuits. Resonant transformers are widely used in radio circuits as bandpass filters, and in switching power supplies. Resonant inductive coupling is also being used in wireless power systems. Here the two LC circuits are in different devices; a transmitter coil in one device transmits electric power across an intervening space to a resonant receiver coil in another device. This technology is being developed for powering and charging portable devices such as cellphones and tablet computers at a distance, without being tethered to an outlet.Resonant transfer works by making a coil ring with an oscillating current. This generates an oscillating magnetic field. Because the coil is highly resonant, any energy placed in the coil dies away relatively slowly over very many cycles; but if a second coil is brought near it, the coil can pick up most of the energy before it is lost, even if it is some distance away. The fields used are predominately non-radiative, near fields (sometimes called evanescent waves), as all hardware is kept well within the 1/4 wavelength distance they radiate little energy from the transmitter to infinity.One of the applications of the resonant transformer is for the CCFL inverter. Another application of the resonant transformer is to couple between stages of a superheterodyne receiver, where the selectivity of the receiver is provided by tuned transformers in the intermediate-frequency amplifiers. The Tesla coil is a resonant transformer circuit used to generate very high voltages, and is able to provide much higher current than high voltage electrostatic machines such as the Van de Graaff generator. Resonant energy transfer is the operating principle behind proposed short range (up to 2 metre) wireless electricity systems such as WiTricity or Rezence and systems that have already been deployed, such as Qi power transfer, passive RFID tags and contactless smart cards.