A Brief Discussion of Color
... correspondingly higher energy of light is needed to do this. If the excited state is closer in energy to the ground state, a correspondingly lower energy of light is needed. For molecules having conjugated systems of electrons, the ground states and excited states of the electrons are closer in ene ...
... correspondingly higher energy of light is needed to do this. If the excited state is closer in energy to the ground state, a correspondingly lower energy of light is needed. For molecules having conjugated systems of electrons, the ground states and excited states of the electrons are closer in ene ...
A Simple Applet
... (0, 0) is the top left corner (50, 0) is 50 pixels to the right of (0, 0) (0, 20) is 20 pixels down from (0, 0) (w - 1, h - 1) is just inside the bottom right corner, where w is the width of the window and h is its height ...
... (0, 0) is the top left corner (50, 0) is 50 pixels to the right of (0, 0) (0, 20) is 20 pixels down from (0, 0) (w - 1, h - 1) is just inside the bottom right corner, where w is the width of the window and h is its height ...
Vocabulary Chapter 3C Transmission: The passage of a wave
... Polarization: Way of filtering light so that all of the waves vibrate in the same direction. Prism: An optical tool that uses refraction to separate the different wavelengths that make up white light. Primary colors: Three colors of light-red, green, and blue- that can be mixed to produce all possib ...
... Polarization: Way of filtering light so that all of the waves vibrate in the same direction. Prism: An optical tool that uses refraction to separate the different wavelengths that make up white light. Primary colors: Three colors of light-red, green, and blue- that can be mixed to produce all possib ...
Section 1
... scatters more green light than other colours, which it absorbs more. 2. C. Light travels slower than sound. Tip: Light waves travel really fast at 3,000,000,00 meters every second. They do not need to travel through a medium like air. 3. D. Red, green and blue. Tip: Red, green, and blue are the prim ...
... scatters more green light than other colours, which it absorbs more. 2. C. Light travels slower than sound. Tip: Light waves travel really fast at 3,000,000,00 meters every second. They do not need to travel through a medium like air. 3. D. Red, green and blue. Tip: Red, green, and blue are the prim ...
Bloomfield_CMSept16
... Why are Things Different Colors? The origin of color can be understood by investigating what happens at the atomic scale. Atoms are not colored in themselves. Carbon in graphite (pencil lead) is metallic gray and in its other well-known form, diamond, it is transparent and colorless. The colors we s ...
... Why are Things Different Colors? The origin of color can be understood by investigating what happens at the atomic scale. Atoms are not colored in themselves. Carbon in graphite (pencil lead) is metallic gray and in its other well-known form, diamond, it is transparent and colorless. The colors we s ...
Light - WordPress.com
... Primary colors: 3 colors that can combine to make any other color. (Red, Yellow, & Blue) Secondary Color: 2 primary colors combine in equal amounts When the 3 primary colors of light are combined in equal amounts, they produce white light A primary and a secondary color can combine to make white lig ...
... Primary colors: 3 colors that can combine to make any other color. (Red, Yellow, & Blue) Secondary Color: 2 primary colors combine in equal amounts When the 3 primary colors of light are combined in equal amounts, they produce white light A primary and a secondary color can combine to make white lig ...
Prisms Lab - Mr. Ahearn`s Science
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
... • Prisms are typically made out of glass, but can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelength for which they are designed. • A prism can be used to break light up into its spectral colors (ROY G BIV). Prisms can also be used to reflect light, or to split light into components. ...
Applet - CIS UPenn
... (0, 0) is the top left corner (50, 0) is 50 pixels to the right of (0, 0) (0, 20) is 20 pixels down from (0, 0) (w - 1, h - 1) is just inside the bottom right corner, where w is the width of the window and h is its height ...
... (0, 0) is the top left corner (50, 0) is 50 pixels to the right of (0, 0) (0, 20) is 20 pixels down from (0, 0) (w - 1, h - 1) is just inside the bottom right corner, where w is the width of the window and h is its height ...
Light The Electromagnetic Spectrum
... 3. Astronomy – stars are made of Hydrogen + Helium which have characteristic bright line spectra at known frequencies: ...
... 3. Astronomy – stars are made of Hydrogen + Helium which have characteristic bright line spectra at known frequencies: ...
Chapter19a
... • Infrared images can provide a threedimensional view of the clouds: ♦ Height of the cloud ♦ Temperature of the cloud ...
... • Infrared images can provide a threedimensional view of the clouds: ♦ Height of the cloud ♦ Temperature of the cloud ...
ch01
... following ray from source to viewer Light travels in straight line until it hits surface Surface point then acts as new point source Ray behavior determined by trig laws Infinite possibilities but only those that reach viewer matter ...
... following ray from source to viewer Light travels in straight line until it hits surface Surface point then acts as new point source Ray behavior determined by trig laws Infinite possibilities but only those that reach viewer matter ...
Plants Seeing Red
... information about their environment. For example, green leaves reflect a lot of light in the far red region. Therefore, when a given plant’s phytochromes sense a high ratio of far red to red light wavelengths, the plant knows that it has many neighbors—many other plants around it are reflecting red ...
... information about their environment. For example, green leaves reflect a lot of light in the far red region. Therefore, when a given plant’s phytochromes sense a high ratio of far red to red light wavelengths, the plant knows that it has many neighbors—many other plants around it are reflecting red ...
LAB, A2 Color, Polarized Light
... Copyright 2009 CPO Science Can be duplicated for classroom use ...
... Copyright 2009 CPO Science Can be duplicated for classroom use ...
Notes
... We can access basic colors with Color.orange, Color.blue, etc. Pictures .jpg .bmp .gif .png - different formats for storing image files Java cannot work with every file type: jpg and gif are the best file types for java. If you have an image type that does not work with java you can use Paint to con ...
... We can access basic colors with Color.orange, Color.blue, etc. Pictures .jpg .bmp .gif .png - different formats for storing image files Java cannot work with every file type: jpg and gif are the best file types for java. If you have an image type that does not work with java you can use Paint to con ...
Experiment 5 The Atomic Spectrum of Hydrogen
... beam of white light is passed through a prism, the different wavelengths travel through the glass at different rates. As a result, white light is diffracted into its components, ranging from red to violet, or 400 nm to 700 nm. ...
... beam of white light is passed through a prism, the different wavelengths travel through the glass at different rates. As a result, white light is diffracted into its components, ranging from red to violet, or 400 nm to 700 nm. ...
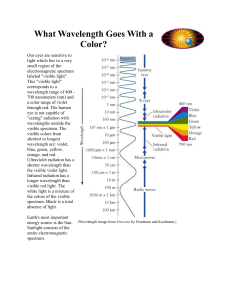
What Wavelength Goes With a Color?
... Energy with wavelengths too short to see is "bluer than blue". Light with such short wavelengths is called "Ultraviolet" light. How do we know this light exists? One way is that this kind of light causes sunburns. Our skin is sensitive to this kind of light. If we stay out in this light without sunb ...
... Energy with wavelengths too short to see is "bluer than blue". Light with such short wavelengths is called "Ultraviolet" light. How do we know this light exists? One way is that this kind of light causes sunburns. Our skin is sensitive to this kind of light. If we stay out in this light without sunb ...
Vision
... the wavelength of incoming light, the eye can determine what color it is looking at. The (normal) eye contains 3 types of cone cells, each containing a different pigment: The L-cone detecting long wavelength light (peaking in the yellows – but also responsible for reds). The M-cone detecting med ...
... the wavelength of incoming light, the eye can determine what color it is looking at. The (normal) eye contains 3 types of cone cells, each containing a different pigment: The L-cone detecting long wavelength light (peaking in the yellows – but also responsible for reds). The M-cone detecting med ...
absorbance, a - srmbiotech25
... shifts in the position of a chemical or physical equilibrium involving the absorbing species. • A common example of this behavior is found with acid/base indicators. • Deviations arising from chemical factors can only be observed when concentrations are changed. eg:dichromate ions on dilution. Cr2O7 ...
... shifts in the position of a chemical or physical equilibrium involving the absorbing species. • A common example of this behavior is found with acid/base indicators. • Deviations arising from chemical factors can only be observed when concentrations are changed. eg:dichromate ions on dilution. Cr2O7 ...
الشريحة 1
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
PowerPoint Slides Chapter 6
... – Spatial frequency: cells vary firing rate according to the sine wave frequency of the stimulus (different levels of information ...
... – Spatial frequency: cells vary firing rate according to the sine wave frequency of the stimulus (different levels of information ...
UNIT 4: Sensation and Perception I. Overview A. Sensation
... Parallel processing – brain cell teams process combined information about color, movement, form, and depth e. Recognition – brain interprets the constructed image based on information from stored images Color Vision ...
... Parallel processing – brain cell teams process combined information about color, movement, form, and depth e. Recognition – brain interprets the constructed image based on information from stored images Color Vision ...
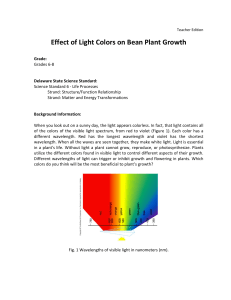
Effect of Light Colors on Bean Plant Growth
... ensure that at least one grows. After they sprout, snip one of them off so that there will be one per cup. This project will take several weeks to measure plant growth. The beans should sprout within a few days. During this experiment, explain figure 1 - that the line graph indicates the wavelengths ...
... ensure that at least one grows. After they sprout, snip one of them off so that there will be one per cup. This project will take several weeks to measure plant growth. The beans should sprout within a few days. During this experiment, explain figure 1 - that the line graph indicates the wavelengths ...
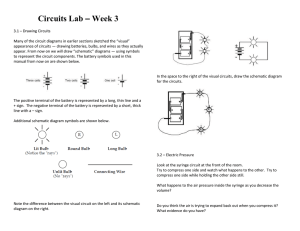
Section 3
... Why do you think wires are given uniform colors? Colors can be used to represent electric pressure values in circuits. Colorcoding a circuit enables you to visualize pressure differences. It will help you to see which light bulbs light and their relative brightness. The following is the color system ...
... Why do you think wires are given uniform colors? Colors can be used to represent electric pressure values in circuits. Colorcoding a circuit enables you to visualize pressure differences. It will help you to see which light bulbs light and their relative brightness. The following is the color system ...
Sensation and Perception
... • Perception- the process by which sensations are organized and interpreted to form an inner representation of the world, is almost normal. • She recognizes people from their hair, etc., but not face ...
... • Perception- the process by which sensations are organized and interpreted to form an inner representation of the world, is almost normal. • She recognizes people from their hair, etc., but not face ...
Interactions of Light - Ms. Gravette and the Mad Scientists
... light does not pass through it, so we cannot see behind it ...
... light does not pass through it, so we cannot see behind it ...
Color

Color, or colour—see spelling differences—is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, blue, yellow, etc. Color derives from the spectrum of light (distribution of light power versus wavelength) interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors. Color categories and physical specifications of color are also associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates.Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance.The science of color is sometimes called chromatics, colorimetry, or simply color science. It includes the perception of color by the human eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electromagnetic radiation in the visible range (that is, what we commonly refer to simply as light).