Visible light is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is
... while violet has the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths.Blackbody radiation from the Sun peaks in the visible part of the spectrum but is more intense in the red than in the violet, making the Sun yellowish in appearance. Colors that can be produced by visible light of a narrow band of wa ...
... while violet has the highest frequencies and shortest wavelengths.Blackbody radiation from the Sun peaks in the visible part of the spectrum but is more intense in the red than in the violet, making the Sun yellowish in appearance. Colors that can be produced by visible light of a narrow band of wa ...
Refractive index
... 4. Adjust the middle light ray parallel to the horizontal axis (as is shown in figure). ...
... 4. Adjust the middle light ray parallel to the horizontal axis (as is shown in figure). ...
intro to spectroscopy - Mount Holyoke College
... when activated by the jellyfish's nervous system) and glowing safety light sticks (in which a chemical reaction, usually induced by breaking a glass tube in the stick, produces light). More commonly, however, materials around us which appear "colored" are absorbing particular colors form the visible ...
... when activated by the jellyfish's nervous system) and glowing safety light sticks (in which a chemical reaction, usually induced by breaking a glass tube in the stick, produces light). More commonly, however, materials around us which appear "colored" are absorbing particular colors form the visible ...
Practical Laboratory #2: Emission Spectra 2
... The discrete bright (dark) lines in the emission (absorption) spectrum can be explained by treating light as a photon that is emitted (absorbed) by an atom, as shown in Fig. 2.3. (For this lab we are going to concentrate on emission spectra.) In the quantum model of the atom, electrons exist only in ...
... The discrete bright (dark) lines in the emission (absorption) spectrum can be explained by treating light as a photon that is emitted (absorbed) by an atom, as shown in Fig. 2.3. (For this lab we are going to concentrate on emission spectra.) In the quantum model of the atom, electrons exist only in ...
Solar Lamps Evaluation
... Brightness is a description of light output, which is measured in lumens (not watts). Two important measurements of white light (sunlight) quality are correlated color temperature (CCT) and color rendering index (CRI). CCT describes whether white light appears warm (reddish), neutral, or cool (bluis ...
... Brightness is a description of light output, which is measured in lumens (not watts). Two important measurements of white light (sunlight) quality are correlated color temperature (CCT) and color rendering index (CRI). CCT describes whether white light appears warm (reddish), neutral, or cool (bluis ...
Unit 4 Sensation & Perception
... receptors (cones) each of which is most sensitive to one of the primary colors. When combined in differing amounts, they can produce the perception of any color ...
... receptors (cones) each of which is most sensitive to one of the primary colors. When combined in differing amounts, they can produce the perception of any color ...
Part I Basic terminology
... process like hand-tinting, they “painted” colors on great movies meant by their creators to be seen in black and white. Generally, this process is currently frowned upon, as it seems to trample on the original artist’s vision when they made the original film. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZKtRvBZx ...
... process like hand-tinting, they “painted” colors on great movies meant by their creators to be seen in black and white. Generally, this process is currently frowned upon, as it seems to trample on the original artist’s vision when they made the original film. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZKtRvBZx ...
PHYS 101 Light, Department of Physics EXAM 1 – Solutions Name
... Q45. The dominant wavelength for the color depicted at the left is (A)615 (B)635 (C)655 (D)665 (E)700 nm. Read it off the graph at the left. Find the peak and drop down to estimate the wavelength number. Q46. In the Munsell color system, colors get less saturated as you (A)proceed up the color tree ...
... Q45. The dominant wavelength for the color depicted at the left is (A)615 (B)635 (C)655 (D)665 (E)700 nm. Read it off the graph at the left. Find the peak and drop down to estimate the wavelength number. Q46. In the Munsell color system, colors get less saturated as you (A)proceed up the color tree ...
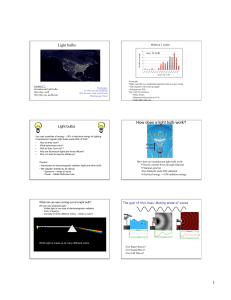
Light bulbs How does a light bulb work?
... • Make sure that you understand questions that you got wrong. • This material will come up again! • Solutions on D2L, • See web for resources: • office hours, • helproom (not just by us 9-5), • email,after class etc.. ...
... • Make sure that you understand questions that you got wrong. • This material will come up again! • Solutions on D2L, • See web for resources: • office hours, • helproom (not just by us 9-5), • email,after class etc.. ...
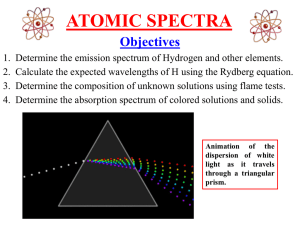
Atomic_spectra
... the midst of the rainbow of colors was a series of black lines. These dark lines were later determined to be the result of the absorption of selected frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation by an atom or molecule. ...
... the midst of the rainbow of colors was a series of black lines. These dark lines were later determined to be the result of the absorption of selected frequencies of the electromagnetic radiation by an atom or molecule. ...
Reflections On Golden Scarabs
... are stimulated in equal proportion, we perceive the color white. If none of the three are stimulated, we perceive the color black. In the absence of cones, we would see the world as most mammals or colorblind people do: in shades of gray. Interestingly, birds have four types of cones: three respondi ...
... are stimulated in equal proportion, we perceive the color white. If none of the three are stimulated, we perceive the color black. In the absence of cones, we would see the world as most mammals or colorblind people do: in shades of gray. Interestingly, birds have four types of cones: three respondi ...
Vision Stations - Raleigh Charter High School
... What you have just seen is called an after-image. Opponent-processes refer to any two processes that work opposite of one another. An example of this is the sympathetic (arousing) and parasympathetic (calming) nervous systems. According to the opponent-process theory of color vision, there are four ...
... What you have just seen is called an after-image. Opponent-processes refer to any two processes that work opposite of one another. An example of this is the sympathetic (arousing) and parasympathetic (calming) nervous systems. According to the opponent-process theory of color vision, there are four ...
The Eye
... neither rods or cone can survive in the dark for long, blindness is a definite possibility The photoreceptors found in dark light are rods A. Factors that affect Dark Light - Intensity and duration of the pre- adapting light ...
... neither rods or cone can survive in the dark for long, blindness is a definite possibility The photoreceptors found in dark light are rods A. Factors that affect Dark Light - Intensity and duration of the pre- adapting light ...
Light - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... Frosted glasses are good examples of translucent materials. ...
... Frosted glasses are good examples of translucent materials. ...
light1
... Theory of Light Keep taking away colors until you wind up w/ one Objects absorb every color other than the color it appears However, most colors we see are various combinations of colors Ex. A blue shirt may reflect mostly blue, some purple, maybe some green, depending on the shade it appers ...
... Theory of Light Keep taking away colors until you wind up w/ one Objects absorb every color other than the color it appears However, most colors we see are various combinations of colors Ex. A blue shirt may reflect mostly blue, some purple, maybe some green, depending on the shade it appers ...
Hearing - RaduegeAP
... receptors (cones) each of which is most sensitive to one of the primary colors. When combined in differing amounts, they can produce the perception of any color ...
... receptors (cones) each of which is most sensitive to one of the primary colors. When combined in differing amounts, they can produce the perception of any color ...
Drawing pictures with Java
... • The Color class contains constants named for each of its predefined colors; they include Color.BLUE, Color.RED, Color.YELLOW, Color.WHITE, Color.BLACK, Color.CYAN, Color.GREEN, Color.MAGENTA, Color.ORANGE, Color.PINK and three shades of GRAY • You can create your own Color objects using these cons ...
... • The Color class contains constants named for each of its predefined colors; they include Color.BLUE, Color.RED, Color.YELLOW, Color.WHITE, Color.BLACK, Color.CYAN, Color.GREEN, Color.MAGENTA, Color.ORANGE, Color.PINK and three shades of GRAY • You can create your own Color objects using these cons ...
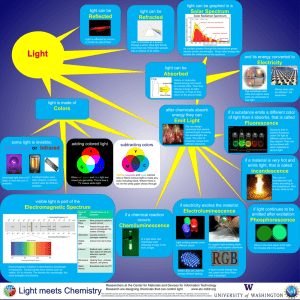
Basiclight_poster
... This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0120967. Any opinions, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. ...
... This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0120967. Any opinions, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. ...
Luminescence Electromagnetic Spectrum Colors
... solution fluoresce under UV light at different colors than they absorb. They can be combined with other materials to absorb light. ...
... solution fluoresce under UV light at different colors than they absorb. They can be combined with other materials to absorb light. ...
Properties of Light
... • opaque: Does not allow light to pass through. All light is either absorbed or reflected. • translucent: Can be seen through, but not clearly. Allows some light to go through, but some is also absorbed or reflected. (such as waxed paper) • transparent: Allows almost all light to go through, so can ...
... • opaque: Does not allow light to pass through. All light is either absorbed or reflected. • translucent: Can be seen through, but not clearly. Allows some light to go through, but some is also absorbed or reflected. (such as waxed paper) • transparent: Allows almost all light to go through, so can ...
الشريحة 1
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
... electromagnetic spectrum and it includes the colors commonly observed (red, yellow, green, blue and violet). -The visible spectrum consists of electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths range from 400 nm to nearly 800 nm ...
Introductory Psychology: Sensation
... (Hermann von Helmholtz & Thomas Young) The theory that the retina contains three different color receptors – red, green and blue When stimulated in combination, these receptors can produce the perception of any color ...
... (Hermann von Helmholtz & Thomas Young) The theory that the retina contains three different color receptors – red, green and blue When stimulated in combination, these receptors can produce the perception of any color ...
Elements of Art - Carroll County Schools
... • Tint: A lighter value of a hue made by adding small amount of another color to it. • Shade: Variations in the dark and light of color by adding black to the color. ...
... • Tint: A lighter value of a hue made by adding small amount of another color to it. • Shade: Variations in the dark and light of color by adding black to the color. ...
Light – Reflection & Mirrors
... the light it reflects. 14.Objects and White Light – Objects that appear white reflect all the colors of the visible light spectrum. Objects that appear black absorb all the colors of the visible light spectrum. 15.Primary Colors of White Light– Red, Green, and Blue can be combined to form secondary ...
... the light it reflects. 14.Objects and White Light – Objects that appear white reflect all the colors of the visible light spectrum. Objects that appear black absorb all the colors of the visible light spectrum. 15.Primary Colors of White Light– Red, Green, and Blue can be combined to form secondary ...
Color

Color, or colour—see spelling differences—is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, blue, yellow, etc. Color derives from the spectrum of light (distribution of light power versus wavelength) interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors. Color categories and physical specifications of color are also associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates.Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance.The science of color is sometimes called chromatics, colorimetry, or simply color science. It includes the perception of color by the human eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electromagnetic radiation in the visible range (that is, what we commonly refer to simply as light).