Psychoses induced by exceptional states of consciousness
... clouding, lethargy and the different levels of coma). Also fitting into these are states of exaltation of the consciousness, generally accompanied by distortions of it. These were described for the first time as pervitin psychoses, induced by amphetamines in German Soldiers during the Second World W ...
... clouding, lethargy and the different levels of coma). Also fitting into these are states of exaltation of the consciousness, generally accompanied by distortions of it. These were described for the first time as pervitin psychoses, induced by amphetamines in German Soldiers during the Second World W ...
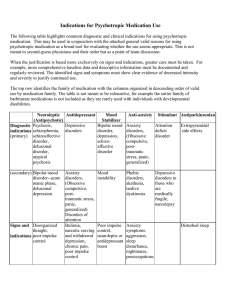
Indications for Psychotropic Medication Use
... This is perhaps the most contentious and challenging rationale. The risk of it being used as a “garbage can” to justify medication for a variety of unpleasant, obnoxious, even hurtful behaviors that serve clear functional means for an individual is inherent. This rationale should be accompanied by a ...
... This is perhaps the most contentious and challenging rationale. The risk of it being used as a “garbage can” to justify medication for a variety of unpleasant, obnoxious, even hurtful behaviors that serve clear functional means for an individual is inherent. This rationale should be accompanied by a ...
Computational Psychiatry
... Figure 1 A hierarchical generative model, illustrated using the ‘beads’ or ‘urn’ task. On the left, two jars are hidden behind a screen, one containing mostly green and some red balls, the other the converse. A sequence of balls is being drawn from one of these jars, in view of an observer, who is a ...
... Figure 1 A hierarchical generative model, illustrated using the ‘beads’ or ‘urn’ task. On the left, two jars are hidden behind a screen, one containing mostly green and some red balls, the other the converse. A sequence of balls is being drawn from one of these jars, in view of an observer, who is a ...
DSM-5: The Future of Psychiatric Diagnosis
... class will consider the bio-psycho-social etiological base for the major psychological disorders (i.e. Axis I disorders- thought disorder, mood disorders, and anxiety disorders), as well as Axis II or personality disorders as well. Rigorous biological determinism has long been the cultural fashion i ...
... class will consider the bio-psycho-social etiological base for the major psychological disorders (i.e. Axis I disorders- thought disorder, mood disorders, and anxiety disorders), as well as Axis II or personality disorders as well. Rigorous biological determinism has long been the cultural fashion i ...
bipolar disorder - mrsashleymhelmsclass
... The prognosis for bipolar disorder differs amongst people considering there are three different types of bipolar disorder which are bipolar I, bipolar II, and cyclothymia. In some cases it can be very severe and longterm or mild with less episodes occurring. The depressive states and manic states di ...
... The prognosis for bipolar disorder differs amongst people considering there are three different types of bipolar disorder which are bipolar I, bipolar II, and cyclothymia. In some cases it can be very severe and longterm or mild with less episodes occurring. The depressive states and manic states di ...
Bipolar Disorder
... minimize negativity in relationships, recognize the first symptoms that indicate onset of a full-blown episode (prodromal symptoms), and work on the factors that help maintain the "normal" periods for as long as possible. CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy), psycho-education and family-focused therap ...
... minimize negativity in relationships, recognize the first symptoms that indicate onset of a full-blown episode (prodromal symptoms), and work on the factors that help maintain the "normal" periods for as long as possible. CBT (cognitive behavioral therapy), psycho-education and family-focused therap ...
Causes of bipolar disorder
... in hours of bright sunshine is thought to trigger depression and mania (a severely high mood where an individual often experiences delusions and/or hallucinations) or hypomania (a less severe high without any delusions and/or hallucinations) by affecting the pineal gland (which is responsible for th ...
... in hours of bright sunshine is thought to trigger depression and mania (a severely high mood where an individual often experiences delusions and/or hallucinations) or hypomania (a less severe high without any delusions and/or hallucinations) by affecting the pineal gland (which is responsible for th ...
Lecture 7
... S Age: suicide is higher in persons older than 50. S Gender: males higher than females S Ethnicity: white higher than Native Americans. S Marital Status: single, divorced, & widowed are higher ...
... S Age: suicide is higher in persons older than 50. S Gender: males higher than females S Ethnicity: white higher than Native Americans. S Marital Status: single, divorced, & widowed are higher ...
Mood Disorders
... (9) Recurrent thoughts of death and or suicidal ideation. B. The symptoms do not meet criteria for mixed episode. C. Significant impairment in social and occupational functioning. D. The symptoms are not due to GMS, or substance induced. E. The symptoms are not due to bereavement. The most recent ty ...
... (9) Recurrent thoughts of death and or suicidal ideation. B. The symptoms do not meet criteria for mixed episode. C. Significant impairment in social and occupational functioning. D. The symptoms are not due to GMS, or substance induced. E. The symptoms are not due to bereavement. The most recent ty ...
Chapter 18 - RaduegePsychology
... supermarket clerk had overcharged me a few cents on an item. She showed me that I was wrong, but that didn’t end it. I worried the rest of the day. I kept going over the incident in my mind feeling terribly embarrassed at having raised the possibility that the clerk had committed an error. The tensi ...
... supermarket clerk had overcharged me a few cents on an item. She showed me that I was wrong, but that didn’t end it. I worried the rest of the day. I kept going over the incident in my mind feeling terribly embarrassed at having raised the possibility that the clerk had committed an error. The tensi ...
File
... disturbance causes clinically significant amount of distress and last at least six months. If criteria are met specify if individual has poor insight. Interestingly enough, Allen and Hollander (2004) in their research identify three subtypes of hypochondriasis. These three subtypes have been describ ...
... disturbance causes clinically significant amount of distress and last at least six months. If criteria are met specify if individual has poor insight. Interestingly enough, Allen and Hollander (2004) in their research identify three subtypes of hypochondriasis. These three subtypes have been describ ...
Ten-year outcome: patients with schizoaffective disorders
... and 60 patients with unipolar nonpsychotic depression. The non-psychotic depression sample did not include patients with borderline diagnoses, anxiety disorders, severe anorexia, panic disorders, antisocial personality disorders, etc. The RDC diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder ...
... and 60 patients with unipolar nonpsychotic depression. The non-psychotic depression sample did not include patients with borderline diagnoses, anxiety disorders, severe anorexia, panic disorders, antisocial personality disorders, etc. The RDC diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder ...
General Education - Crites Counseling and Consultation
... He may feel energized and driven to do things that are important to him. The primary symptoms that are often seen in hypomania are sleep problems (sleep less), increased activity, hyper-sexuality, irritability, and an inflated sense of self (this is not to a dangerous level like a manic). ...
... He may feel energized and driven to do things that are important to him. The primary symptoms that are often seen in hypomania are sleep problems (sleep less), increased activity, hyper-sexuality, irritability, and an inflated sense of self (this is not to a dangerous level like a manic). ...
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
... population samples could be expected to have a manic disorder. 20-30% of children who have psychiatric problems are referred for or receive psychiatric help. Therefore, the typical clinician is likely to have a low rate of exposure to youths with mania, which makes it difficult to form a template of ...
... population samples could be expected to have a manic disorder. 20-30% of children who have psychiatric problems are referred for or receive psychiatric help. Therefore, the typical clinician is likely to have a low rate of exposure to youths with mania, which makes it difficult to form a template of ...
CHAPTER 31 for wiki
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Rare and controversial dissociative disorder in which an individual experiences two or more distinct and alternating personalities • Formerly called multiple personalities – Before the 1970s fewer than 100 cases had ever been reported. – In the 1980s alone, reports ...
... Dissociative Identity Disorder • Rare and controversial dissociative disorder in which an individual experiences two or more distinct and alternating personalities • Formerly called multiple personalities – Before the 1970s fewer than 100 cases had ever been reported. – In the 1980s alone, reports ...
Bipolar Disorder Unpacked - Samaritan Center
... the nervous system and may also underlie learning and memory functions of mature brain. Previous studies have shown an increase in dendritic spine density and/or enlargement of spines after the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP). Using twophoton time-lapse imaging of dendritic spines in acute ...
... the nervous system and may also underlie learning and memory functions of mature brain. Previous studies have shown an increase in dendritic spine density and/or enlargement of spines after the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP). Using twophoton time-lapse imaging of dendritic spines in acute ...
Utilizing Gestalt therapy in an inpatient setting with patients
... symptoms (Perälä et al., 2007). Psychotic symptoms do not just affect those with schizophrenia. Psychotic symptoms can also be present in people that are diagnosed with disorders such as bipolar I disorder, major depression, substance induced psychosis, and psychosis due to medical conditions. All o ...
... symptoms (Perälä et al., 2007). Psychotic symptoms do not just affect those with schizophrenia. Psychotic symptoms can also be present in people that are diagnosed with disorders such as bipolar I disorder, major depression, substance induced psychosis, and psychosis due to medical conditions. All o ...
RCPsych Literature Search COMORBIDITY 2007
... For diagnosis of patients with comorbid psychotic symptoms and substance use disorders (SUDs), Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, makes clear distinctions between independent psychotic disorders (eg, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia) and substance-induced syndromes ...
... For diagnosis of patients with comorbid psychotic symptoms and substance use disorders (SUDs), Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, makes clear distinctions between independent psychotic disorders (eg, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia) and substance-induced syndromes ...
Psychogenic polydipsia: a mini review with three case
... We described three cases of chronic “severe polydipsia”, the first associated with an episode of SIWI (self-induced water-intoxication) and the third associated with SIADH. PPD onset occurred late in the course of mental illness, after many years of exposure to “typical neuroleptics”, in all three c ...
... We described three cases of chronic “severe polydipsia”, the first associated with an episode of SIWI (self-induced water-intoxication) and the third associated with SIADH. PPD onset occurred late in the course of mental illness, after many years of exposure to “typical neuroleptics”, in all three c ...
NEUROPSYCHIATRY OF SEIZURES - EPILEPSY Association Of Sri
... range from 7.5 to 34 percent of patients with epilepsy. • Those with complex partial seizures and poor seizure control are more likely to have mood disorders. • Psychological studies also suggest a greater incidence of ideational orientation, self-criticism, and depression among epilepsy patients ...
... range from 7.5 to 34 percent of patients with epilepsy. • Those with complex partial seizures and poor seizure control are more likely to have mood disorders. • Psychological studies also suggest a greater incidence of ideational orientation, self-criticism, and depression among epilepsy patients ...
schizophrenia in children and young people
... symptoms. In other words, the person’s perception of reality does not conform to that of healthy individuals. The person acquires a changed sense of reality. This may be expressed in hallucinations, delusions, jumbled words and thoughts, or catatonic states. ...
... symptoms. In other words, the person’s perception of reality does not conform to that of healthy individuals. The person acquires a changed sense of reality. This may be expressed in hallucinations, delusions, jumbled words and thoughts, or catatonic states. ...
psychiatric disorders associated with cushing`s syndrome
... Bolanos 2004). Additionally, depression occurs in approximately 25% of the patients in the prodromal phase of Cushing's syndrome (Sonino 1993). It was observed that the incidence, type of mood disorders, and response to treatment are not related to the etiology of Cushing's syndrome (Sonino 2001). A ...
... Bolanos 2004). Additionally, depression occurs in approximately 25% of the patients in the prodromal phase of Cushing's syndrome (Sonino 1993). It was observed that the incidence, type of mood disorders, and response to treatment are not related to the etiology of Cushing's syndrome (Sonino 2001). A ...
Full Text
... psychiatrists are not familiar with the diagnosis of ASDs. The high prevalence of psychotic symptoms in this sample is likely to depend on the specific setting of the study, i.e., that people with more severe forms of ASD than those typically followed-up in the national health service were reaching ...
... psychiatrists are not familiar with the diagnosis of ASDs. The high prevalence of psychotic symptoms in this sample is likely to depend on the specific setting of the study, i.e., that people with more severe forms of ASD than those typically followed-up in the national health service were reaching ...
Juvenile Mood Disorders Bostic, Wilens, Spencer
... No overall improvement with treatment compared to placebo Small advantage for TCAs in adolescents, but not children Treatment with a tricyclic caused more vertigo, orthostatic hypotension, tremor and dry mouth ...
... No overall improvement with treatment compared to placebo Small advantage for TCAs in adolescents, but not children Treatment with a tricyclic caused more vertigo, orthostatic hypotension, tremor and dry mouth ...
Psychiatrists` View on the Risk Factors for Aggressive Behavior in
... regard to their opinion on the risk factors for aggression in psychosis. A survey was especially developed for investigating these issues. Factor analysis yielded four factors representing distinct types of risk factors, namely illness-related features, personality characteristics, environmental inf ...
... regard to their opinion on the risk factors for aggression in psychosis. A survey was especially developed for investigating these issues. Factor analysis yielded four factors representing distinct types of risk factors, namely illness-related features, personality characteristics, environmental inf ...