Engineering without Ethics
... Will it provide a positive source of public evaluation, enhance reputation, and build public trust? Will it enable new employees to be effectively socialized into the professional culture, know what’s expected? Is it specific enough to deter unethical behavior and provide support to the employ ...
... Will it provide a positive source of public evaluation, enhance reputation, and build public trust? Will it enable new employees to be effectively socialized into the professional culture, know what’s expected? Is it specific enough to deter unethical behavior and provide support to the employ ...
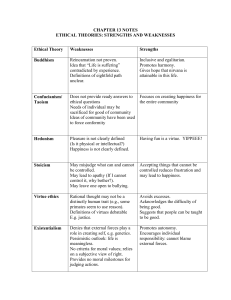
Chapter 13 Theories Strengths and Weaknesses
... Limits the development of self; ignores the responsibility we have to others. Suggests people are slaves to selfinterest and lack freedom to make choices. ...
... Limits the development of self; ignores the responsibility we have to others. Suggests people are slaves to selfinterest and lack freedom to make choices. ...
IPPTChap002 - WordPress.com
... Is Your Conscience Reliable? (Cont’d) If a person’s values are at “Level 2,” they may make decisions based on the situation and what others say and do ...
... Is Your Conscience Reliable? (Cont’d) If a person’s values are at “Level 2,” they may make decisions based on the situation and what others say and do ...
Lesson 2 Meta Ethics - mrslh Philosophy & Ethics
... Hume. Hume claimed that we cannot move logically from a statement about the way the world is to a statement about how we ought to act. This view is known as the ‘is-ought gap’ or Hume’s fork, because he made a clear cut between facts and ethics. The radical conclusion which this leads to is the idea ...
... Hume. Hume claimed that we cannot move logically from a statement about the way the world is to a statement about how we ought to act. This view is known as the ‘is-ought gap’ or Hume’s fork, because he made a clear cut between facts and ethics. The radical conclusion which this leads to is the idea ...
lecture outline
... to publicize its “social responsibility” report. See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 14.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual. ...
... to publicize its “social responsibility” report. See complete case, discussion questions, and suggested answers on page 14.Error! Bookmark not defined. of this manual. ...
Moral Reasoning and Ethical Theories
... • Religion and divine command ethics – who are those among us who know precisely what God’s commands are or are not on each issue? ...
... • Religion and divine command ethics – who are those among us who know precisely what God’s commands are or are not on each issue? ...
STEVE SMITH - Society of Corporate Compliance and Ethics
... of action, if it results in the greatest good for the greatest number of people (or at least minimum harm). Example: “Utilitarianism” There are no universal principles that can guide action, but rather likely benefits and costs associated with any action must be calculated to judge the practice eith ...
... of action, if it results in the greatest good for the greatest number of people (or at least minimum harm). Example: “Utilitarianism” There are no universal principles that can guide action, but rather likely benefits and costs associated with any action must be calculated to judge the practice eith ...
Ethics
... part of funeral service practice is derived from the idea that the funeral professional is entrusted with serving the bereaved survivors and the proper treatment and disposition of remains.” ...
... part of funeral service practice is derived from the idea that the funeral professional is entrusted with serving the bereaved survivors and the proper treatment and disposition of remains.” ...
Chapter 4
... Ability to recognize one’s own feelings and those of others Ability to self-motivate Ability to manage one’s own emotions (e.g., anger) ...
... Ability to recognize one’s own feelings and those of others Ability to self-motivate Ability to manage one’s own emotions (e.g., anger) ...
clouds
... Deontology -- “Any position in ethics which claims that the rightness or wrongness of actions depends on whether they correspond to our duty or not. The word derives from the Greek ...
... Deontology -- “Any position in ethics which claims that the rightness or wrongness of actions depends on whether they correspond to our duty or not. The word derives from the Greek ...
Lesson 14: Ethics
... “A people that values its privileges above its principles soon loses both.” -Dwight D. Eisenhower “Honesty is the first chapter of the Book of Wisdom.” -Thomas Jefferson ...
... “A people that values its privileges above its principles soon loses both.” -Dwight D. Eisenhower “Honesty is the first chapter of the Book of Wisdom.” -Thomas Jefferson ...
Lesson 14: Ethics
... “A people that values its privileges above its principles soon loses both.” -Dwight D. Eisenhower “Honesty is the first chapter of the Book of Wisdom.” -Thomas Jefferson ...
... “A people that values its privileges above its principles soon loses both.” -Dwight D. Eisenhower “Honesty is the first chapter of the Book of Wisdom.” -Thomas Jefferson ...
Medical Ethics, Part I
... would want them to treat you” Human beings should never be treated as only a ...
... would want them to treat you” Human beings should never be treated as only a ...
morals and ethics2 - Mountain View
... Actions are judged right or wrong solely by their consequences. Right actions are those that produce the greatest balance of happiness over unhappiness. Each person’s happiness is equally important. Strength--promotes human well-being and attempts to lessen human suffering. Weakness--One person’s go ...
... Actions are judged right or wrong solely by their consequences. Right actions are those that produce the greatest balance of happiness over unhappiness. Each person’s happiness is equally important. Strength--promotes human well-being and attempts to lessen human suffering. Weakness--One person’s go ...
Ethics 101 Power Point Presentation
... conduct to treat others fairly: Like cases are treated alike - fairness. Imposes unclear responsibilities on physicians - society has not sorted this out! How well are resources allocated? What is futility? ...
... conduct to treat others fairly: Like cases are treated alike - fairness. Imposes unclear responsibilities on physicians - society has not sorted this out! How well are resources allocated? What is futility? ...
Lesson 13: Ethics
... D. Making moral judgments is part of what it means to be human. E. How does one make moral judgments? 1. Religion: Involves deference to religious authority or scripture that directs decisions. 2. Mystical experience or flipping a coin. ...
... D. Making moral judgments is part of what it means to be human. E. How does one make moral judgments? 1. Religion: Involves deference to religious authority or scripture that directs decisions. 2. Mystical experience or flipping a coin. ...
Applied Ethics Introduction & Theories
... Philosophical study of certain values of human life. We also can find a reason to support moral positions ...
... Philosophical study of certain values of human life. We also can find a reason to support moral positions ...
Ethical Fading - Ethics Unwrapped
... committed. Studies show that offering people an opportunity to wash their hands after behaving immorally is often enough to restore their self-‐image. There’s a reason we talk about starting with a ...
... committed. Studies show that offering people an opportunity to wash their hands after behaving immorally is often enough to restore their self-‐image. There’s a reason we talk about starting with a ...
File - Zachary Carscaddon
... 1. Unexpected results from the release of genetically modified organisms have been extremely ...
... 1. Unexpected results from the release of genetically modified organisms have been extremely ...
Major Theories in Moral Philosophy
... deontology all belong to the type of moral philosophy called Ethics of Conduct, focusing on ”What to Do.” Virtue Ethics, going back to the time of Socrates, Plato and Aristotle, and further back in time, focuses on developing a good character: “How to Be.” Virtues, which the Greeks thought of as ...
... deontology all belong to the type of moral philosophy called Ethics of Conduct, focusing on ”What to Do.” Virtue Ethics, going back to the time of Socrates, Plato and Aristotle, and further back in time, focuses on developing a good character: “How to Be.” Virtues, which the Greeks thought of as ...
Ethical Behaviour - Unit 2.3
... Moral-rights - respect the fundamental rights of people Justice - ethical decisions treat people fairly according to rules ...
... Moral-rights - respect the fundamental rights of people Justice - ethical decisions treat people fairly according to rules ...
pers ective p Bad people do not have a monopoly on bad deeds:
... next door. Some subjects were alone, while others were working alongside a small group of strangers who were part of the study and had been instructed not to respond. Darley found that 80 percent of those working alone got up from their work to check on the individual calling for help. By contrast, ...
... next door. Some subjects were alone, while others were working alongside a small group of strangers who were part of the study and had been instructed not to respond. Darley found that 80 percent of those working alone got up from their work to check on the individual calling for help. By contrast, ...
Ethics of eating meat

In many societies, controversy and debate have arisen over the ethics of eating animals. The most commonly given ethical objection to meat-eating is that, for most people living in the developed world, it is not necessary for their survival or health; hence, it is concluded, slaying animals just because people like the taste of meat is wrong and morally unjustifiable. Ethical vegetarians may also object to the practices underlying the production of meat, or cite concerns about animal welfare, animal rights, environmental ethics, and religious scruples. In response, proponents of meat-eating have adduced various scientific, nutritional, cultural, and religious arguments in support of the practice. Some meat-eaters only object to rearing animals in certain ways, such as in factory farms, or killing them with cruelty; others avoid only certain meats, such as veal or foie gras.