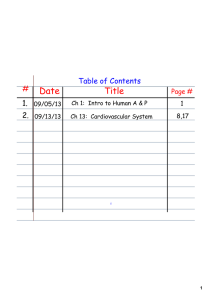
Heart Dissection Introduction Mammals have four
... reptiles, but the oxygen-rich blood is completely separated from oxygen-poor blood. The left side of the heart handles only oxygenated blood, and the right side receives and pumps only deoxygenated blood. With no mixing of the two kinds of blood, and with a double circulation that restores pressure ...
... reptiles, but the oxygen-rich blood is completely separated from oxygen-poor blood. The left side of the heart handles only oxygenated blood, and the right side receives and pumps only deoxygenated blood. With no mixing of the two kinds of blood, and with a double circulation that restores pressure ...
Organization of the Human Body
... • Integration and Coordination a. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. It integrates incoming information from receptors and sends impulses to muscles and glands. b. The endocrine system, including all of the glands that secrete hormones, helps to ...
... • Integration and Coordination a. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. It integrates incoming information from receptors and sends impulses to muscles and glands. b. The endocrine system, including all of the glands that secrete hormones, helps to ...
Heart Dissection Introduction Mammals have four
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
Heart Dissection - Sinoe Medical Association
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
Hyper Hearts
... The circulatory system is a complex organ system in the body so it is important to simplify the lesson for the appropriate age group including additional information only when necessary. Using diagrams of the body, illustrate the complete circulatory system including the heart, arteries, veins, capi ...
... The circulatory system is a complex organ system in the body so it is important to simplify the lesson for the appropriate age group including additional information only when necessary. Using diagrams of the body, illustrate the complete circulatory system including the heart, arteries, veins, capi ...
Simon`s Circulatory System
... The circulation of blood is very important for your body. Blood supplies the body with oxygen and nutrients. We need oxygen and nutrients to live. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all the different parts of our body. ...
... The circulation of blood is very important for your body. Blood supplies the body with oxygen and nutrients. We need oxygen and nutrients to live. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all the different parts of our body. ...
Wake Forest Univ heart dissection PDF
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
... 9. With your fingers, push open the heart at the cut to examine the internal structure. If there is dried blood inside the chambers, rinse out the heart. 10. Locate the right atrium. Notice the thinner muscular wall of this receiving chamber. 11. Find where the inferior & superior vena cava enter th ...
4340_cardio_1
... What is the oxygen content of the blood (high or low)? Where does the blood flow to at the end of the systemic circuit? Which side of the heart is part of the pulmonary circuit? What is the oxygen content of the blood (high or low)? Where does the blood flow to at the end of the pulmonary circuit? W ...
... What is the oxygen content of the blood (high or low)? Where does the blood flow to at the end of the systemic circuit? Which side of the heart is part of the pulmonary circuit? What is the oxygen content of the blood (high or low)? Where does the blood flow to at the end of the pulmonary circuit? W ...
healthy heart scooter tag - American Heart Association
... The heart is located in the center of the chest. An adult’s heart is a little larger than a fist with the other hand around it. A child’s heart is a little larger than the child’s fist. The heart is an involuntary muscle. It pumps blood carrying oxygen and other nutrients into the circulatory system ...
... The heart is located in the center of the chest. An adult’s heart is a little larger than a fist with the other hand around it. A child’s heart is a little larger than the child’s fist. The heart is an involuntary muscle. It pumps blood carrying oxygen and other nutrients into the circulatory system ...
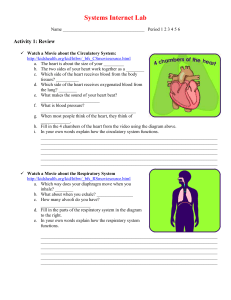
Inside the Human Body—The Respiratory System
... a. The heart is about the size of your _________ b. The two sides of your heart work together as a ________ c. Which side of the heart receives blood from the body tissues? __________ d. Which side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lung? ________ e. What makes the sound of your heart b ...
... a. The heart is about the size of your _________ b. The two sides of your heart work together as a ________ c. Which side of the heart receives blood from the body tissues? __________ d. Which side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lung? ________ e. What makes the sound of your heart b ...
Heart-rate LAB
... The overall pattern of blood flow, throughout the body, consists of two loops: heart, lungs, heart and heart, body, heart. The pulmonary circuit (heart, lung, heart loop) is where there is an exchange of gases between the alveoli of the lung and the capillaries. As blood moves into the lungs it drop ...
... The overall pattern of blood flow, throughout the body, consists of two loops: heart, lungs, heart and heart, body, heart. The pulmonary circuit (heart, lung, heart loop) is where there is an exchange of gases between the alveoli of the lung and the capillaries. As blood moves into the lungs it drop ...
Respiration System - ScienceStLaurence
... heart, trachea, esophagus, and blood vessels. The lungs are covered by a protective membrane called the pulmonary pleura. Lung function normally peaks in the late teens and early twenties. After the early twenties, lung function declines about 1 percent a year over the rest of a person's lifetime. L ...
... heart, trachea, esophagus, and blood vessels. The lungs are covered by a protective membrane called the pulmonary pleura. Lung function normally peaks in the late teens and early twenties. After the early twenties, lung function declines about 1 percent a year over the rest of a person's lifetime. L ...
A healthy heart is most essential part of human body
... body is healthy and disease free. Heart is main Human heart is a muscular organ that function to pump blood and circulate it through the whole body at all times. From one half it send blood to lungs to receive oxygen and other half of heart receive oxygen rich blood and pumps it to all body organs, ...
... body is healthy and disease free. Heart is main Human heart is a muscular organ that function to pump blood and circulate it through the whole body at all times. From one half it send blood to lungs to receive oxygen and other half of heart receive oxygen rich blood and pumps it to all body organs, ...
Lessons 3 and 4 Exercise and Heart Rate
... Your heart is really a muscle. It's located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it's about the size of your fist. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste. Your heart is sort of like a pu ...
... Your heart is really a muscle. It's located a little to the left of the middle of your chest, and it's about the size of your fist. The heart sends blood around your body. The blood provides your body with the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also carries away waste. Your heart is sort of like a pu ...
B1G Unit 5 Ch. 20 Lecture Notes
... than the ECG of a healthy younger adult. Abnormal rhythms (arrhythmias) such as atrial fibrillation are more common in older people. They may be caused by heart disease. ...
... than the ECG of a healthy younger adult. Abnormal rhythms (arrhythmias) such as atrial fibrillation are more common in older people. They may be caused by heart disease. ...
The Human Heart
... Its movement through the heart and around the body is called circulation and can be viewed as a cycle. Beginning at the left side of your heart, fresh, clean oxygen-rich blood is pumped around our bodies. The cells throughout our bodies take the oxygen from the blood and use it as fuel to work a ...
... Its movement through the heart and around the body is called circulation and can be viewed as a cycle. Beginning at the left side of your heart, fresh, clean oxygen-rich blood is pumped around our bodies. The cells throughout our bodies take the oxygen from the blood and use it as fuel to work a ...
PDF - Science Matters
... 1. Dissection with teacher: reinforce key vocabulary and have students identify parts and function. 2. Reading: students browse heart-related books and use post-its to ask questions or mark an interesting page or idea for other students to see; they also write questions/notes in their notebook. 3. P ...
... 1. Dissection with teacher: reinforce key vocabulary and have students identify parts and function. 2. Reading: students browse heart-related books and use post-its to ask questions or mark an interesting page or idea for other students to see; they also write questions/notes in their notebook. 3. P ...
MAN AWESOMELY AND WONDERFULLY MADE
... Heart rate exercise: Have children take their pulse by placing two fingers on their wrist or on their neck for 15 seconds while counting the pulse beats. Time the number of pulse beats by 4 to get the number of heartbeats in a minute. Next have the children do some physical exercises e.g. star jumps ...
... Heart rate exercise: Have children take their pulse by placing two fingers on their wrist or on their neck for 15 seconds while counting the pulse beats. Time the number of pulse beats by 4 to get the number of heartbeats in a minute. Next have the children do some physical exercises e.g. star jumps ...
Introduction to the Heart and Circulatory System
... • The Main Pump • The heart is divided into 4 chambers that are connected by valves – Valves are flap-like structures that allow blood to only flow in one direction – The audible sounds heard in the heart (Lubdub) are actually the valves closing • When a valve is not working properly the sound will ...
... • The Main Pump • The heart is divided into 4 chambers that are connected by valves – Valves are flap-like structures that allow blood to only flow in one direction – The audible sounds heard in the heart (Lubdub) are actually the valves closing • When a valve is not working properly the sound will ...
What are Heart Disease and Stroke?
... above the normal range. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against blood vessel walls. It’s written as two numbers, such as 122/78 mm Hg. The top number (systolic) is the pressure when the heart beats. The bottom number (diastolic) is the pressure when the heart rests between beats. High b ...
... above the normal range. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against blood vessel walls. It’s written as two numbers, such as 122/78 mm Hg. The top number (systolic) is the pressure when the heart beats. The bottom number (diastolic) is the pressure when the heart rests between beats. High b ...
module 3 3.1.2 transport in animals heart and circulation
... Filling phase Normal cardiac cycles (at rest) take 0.8 seconds ...
... Filling phase Normal cardiac cycles (at rest) take 0.8 seconds ...
Anatomy #01 د.محمد الحيدري 15-3
... The whole heart, like any visceral structure in the body, is surrounded by a serous membrane for protection. Of course, the lungs also have a protective covering called the pleura, GIT (stomach to rectum part of it) is surrounded by the Peritoneum (some parts are not). The one that surrounds the hea ...
... The whole heart, like any visceral structure in the body, is surrounded by a serous membrane for protection. Of course, the lungs also have a protective covering called the pleura, GIT (stomach to rectum part of it) is surrounded by the Peritoneum (some parts are not). The one that surrounds the hea ...
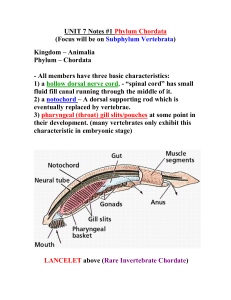
UNIT 9 Notes #1 Phylum Chordata - Mr. Lesiuk
... Example: Frog, toad, salamander, newts - Smallest of all classes, only 4000 species. - Aquatic as larvae, usually living in freshwater with the aid of gills. -Adults usually terrestrial and have inefficient lungs for respiration must get help in respiration from moist skin. - Eggs lack a shell, ther ...
... Example: Frog, toad, salamander, newts - Smallest of all classes, only 4000 species. - Aquatic as larvae, usually living in freshwater with the aid of gills. -Adults usually terrestrial and have inefficient lungs for respiration must get help in respiration from moist skin. - Eggs lack a shell, ther ...
Artificial heart

An artificial heart is a device that replaces the heart. Artificial hearts are typically used to bridge the time to heart transplantation, or to permanently replace the heart in case heart transplantation is impossible. Although other similar inventions preceded it going back to the late 1940s, the first artificial heart to be successfully implanted in a human was the Jarvik-7 in 1982, designed by a team including Willem Johan Kolff and Robert Jarvik.An artificial heart is distinct from a ventricular assist device designed to support a failing heart. It is also distinct from a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, which is an external device used to provide the functions of both the heart and lungs and are only used for a few hours at a time, most commonly during cardiac surgery.