Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Technical Information
... sustainable way. The IGCC technology uses a gasifier to convert coal to fuel gas, and then uses a combined cycle power block to generate electricity. IGCC has many advantages over traditional technologies including: higher efficiency, lower pollutant emissions, and a possibility of carbon capture an ...
... sustainable way. The IGCC technology uses a gasifier to convert coal to fuel gas, and then uses a combined cycle power block to generate electricity. IGCC has many advantages over traditional technologies including: higher efficiency, lower pollutant emissions, and a possibility of carbon capture an ...
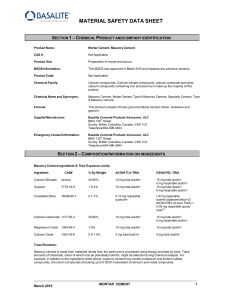
material safety data sheet
... recognize that masonry cement chemically reacts with water, and that some of the intermediate products of this reaction (that is, those present while a masonry cement product is “setting”) pose a far more severe hazard than does masonry cement itself. While the information provided in this material ...
... recognize that masonry cement chemically reacts with water, and that some of the intermediate products of this reaction (that is, those present while a masonry cement product is “setting”) pose a far more severe hazard than does masonry cement itself. While the information provided in this material ...
AS Chemistry - Crawshaw Academy
... Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on these topics, particularly if you are starting the course with a B in Science/Additional Science. A good place to start with your preparation for ...
... Chemistry Calculations’ and ‘Balancing Equations’. In order for you to settle into the course quickly it is essential that you do some background work on these topics, particularly if you are starting the course with a B in Science/Additional Science. A good place to start with your preparation for ...
5 Things You Can Do to Reduce the Risk of Kidney Stones
... 1. Drink Plenty of Water: drinking extra water dilutes the substances in urine that lead to kidney stones. Drink enough fluids to pass 2 liters (2 liters is approx. 2 quarts) of urine every 24 hours. Your work environment may also determine how much you should have to drink: example, a person workin ...
... 1. Drink Plenty of Water: drinking extra water dilutes the substances in urine that lead to kidney stones. Drink enough fluids to pass 2 liters (2 liters is approx. 2 quarts) of urine every 24 hours. Your work environment may also determine how much you should have to drink: example, a person workin ...
82KB - NZQA
... solid, CaCO3, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, carbon dioxide, CO2, and forms another white solid calcium oxide, CaO. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) When white calcium hydroxide solid, Ca(OH)2, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, water, H2O, and also forms the white solid ca ...
... solid, CaCO3, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, carbon dioxide, CO2, and forms another white solid calcium oxide, CaO. CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) When white calcium hydroxide solid, Ca(OH)2, is strongly heated it releases a colourless gas, water, H2O, and also forms the white solid ca ...
Practice Exam #2
... A) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. B) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
... A) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. B) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
11 BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS 1. 2 K + 1
... Directions - Write the following reactions equation noting the states. For example, note a gas as (g). Then balance the equation by placing coefficients in front of the formula. For example, 2 CO2. ...
... Directions - Write the following reactions equation noting the states. For example, note a gas as (g). Then balance the equation by placing coefficients in front of the formula. For example, 2 CO2. ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... f) Cr2O72-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 3Mn2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3MnO2(s) + H2O(l) 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. ...
... f) Cr2O72-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 3Mn2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3MnO2(s) + H2O(l) 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. ...
Complete the following equations
... The concentration of Mg2+ in seawater is about 0.055 M. (a) How many liters of seawater will produce 1.00 kg of magnesium. (b) How many kilograms of calcium oxide, CaO, must be added to the seawater sample of part (a) in order to precipitate all of Mg2+ as magnesium hydroxide. (c) Write a balanced e ...
... The concentration of Mg2+ in seawater is about 0.055 M. (a) How many liters of seawater will produce 1.00 kg of magnesium. (b) How many kilograms of calcium oxide, CaO, must be added to the seawater sample of part (a) in order to precipitate all of Mg2+ as magnesium hydroxide. (c) Write a balanced e ...
study packet for chapter 5
... D) condensation of water vapor E) Ammonium thiocyanate and barium hydroxide are mixed at 25 °C: the temperature drops. ...
... D) condensation of water vapor E) Ammonium thiocyanate and barium hydroxide are mixed at 25 °C: the temperature drops. ...
CHE 1401 - Summer 2012 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... When 0.721 g of titanium is combusted in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 25.00°C to 53.80°C. In a separate experiment, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is measured to be 9.84 kJ/K. The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter i ...
... When 0.721 g of titanium is combusted in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 25.00°C to 53.80°C. In a separate experiment, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is measured to be 9.84 kJ/K. The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter i ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... When 0.721 g of titanium is combusted in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 25.00°C to 53.80°C. In a separate experiment, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is measured to be 9.84 kJ/K. The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter i ...
... When 0.721 g of titanium is combusted in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 25.00°C to 53.80°C. In a separate experiment, the heat capacity of the calorimeter is measured to be 9.84 kJ/K. The heat of reaction for the combustion of a mole of Ti in this calorimeter i ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
... B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... E) 1.00 × 103 23) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are __________ joules in one Btu. 1 lb = 453.59 g; °C = (5/9)(°F - 32°); specific heat of H2O (l) = 4 ...
... E) 1.00 × 103 23) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are __________ joules in one Btu. 1 lb = 453.59 g; °C = (5/9)(°F - 32°); specific heat of H2O (l) = 4 ...
MSDS - Dudley Chemical Corporation
... representation as to its comprehensiveness or accuracy. This document is intended only as a guide to the appropriate precautionary handling of the material by a properly trained person using this. Individuals receiving the information must exercise their independent judgment in determining its appro ...
... representation as to its comprehensiveness or accuracy. This document is intended only as a guide to the appropriate precautionary handling of the material by a properly trained person using this. Individuals receiving the information must exercise their independent judgment in determining its appro ...
Chapter 17: Thermodynamics
... heat and other forms of energy. Internal energy (U): the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles making up a system. State Function: a property of a system that depends only on its present state which is determined by variables such as temperature and pressure. ...
... heat and other forms of energy. Internal energy (U): the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the particles making up a system. State Function: a property of a system that depends only on its present state which is determined by variables such as temperature and pressure. ...
Chemical Equilbrium
... If you cannot make a simplifying assumption, many times you will end up with a quadratic equation for an equilibrium constant expression. You can end up with a 3rd, 4th, 5th, etc. order polynomial, but I will not hold you responsible for being able to solve those as there is no simple formula for th ...
... If you cannot make a simplifying assumption, many times you will end up with a quadratic equation for an equilibrium constant expression. You can end up with a 3rd, 4th, 5th, etc. order polynomial, but I will not hold you responsible for being able to solve those as there is no simple formula for th ...
Thermo Practice Test
... Which one of the following statements best describes the relationship between G and temperature? A) G is independent of T; B) G varies with T; C) G is a linear function of T; D) G usually decreases with T. Hydrogen bromide gas and chlorine gas react to produce hydrogen chloride gas and liquid o ...
... Which one of the following statements best describes the relationship between G and temperature? A) G is independent of T; B) G varies with T; C) G is a linear function of T; D) G usually decreases with T. Hydrogen bromide gas and chlorine gas react to produce hydrogen chloride gas and liquid o ...
File
... As the climate becomes warmer and the ground thaws bacteria produce methane from the remains of dead plants and animals. How do scientists find the methane in the arctic? Digging a hole and igniting the gas (easier done over a lake). Methane is a hydrocarbon, a compound that is composed only of the ...
... As the climate becomes warmer and the ground thaws bacteria produce methane from the remains of dead plants and animals. How do scientists find the methane in the arctic? Digging a hole and igniting the gas (easier done over a lake). Methane is a hydrocarbon, a compound that is composed only of the ...
284
... 35. With the news that calcium deficiencies in many women’s diets may contribute td the development of osteoporosis (bone weakening), the use of dietary calcium supplements has become increasingly common. Many of these calcium supplements consist of nothing more than calcium carbonate, CaCO3. When a ...
... 35. With the news that calcium deficiencies in many women’s diets may contribute td the development of osteoporosis (bone weakening), the use of dietary calcium supplements has become increasingly common. Many of these calcium supplements consist of nothing more than calcium carbonate, CaCO3. When a ...
Specific Reactions Quiz.wpd
... a) various carbon products created due to lack of oxygen including solid carbon (black component) b) as air contacts the random carbon products (smaller hydrocarbons) created, they may further combust c) since energy is still tied up in carbon product bonds, energy is not released all at once d) the ...
... a) various carbon products created due to lack of oxygen including solid carbon (black component) b) as air contacts the random carbon products (smaller hydrocarbons) created, they may further combust c) since energy is still tied up in carbon product bonds, energy is not released all at once d) the ...
Chapter 11: Thermochemistry
... Two substances at the same temperature have the same average kinetic energy. Their velocities or speeds would therefore depend on their masses. The smaller the mass, the higher the velocity, and vice versa. If CO2 and O2 were in two different containers both at 30°C, which one would be moving faster ...
... Two substances at the same temperature have the same average kinetic energy. Their velocities or speeds would therefore depend on their masses. The smaller the mass, the higher the velocity, and vice versa. If CO2 and O2 were in two different containers both at 30°C, which one would be moving faster ...
Ministry Strand: Quantities in Chemical Reactions Teacher
... stoichiometry, percentage yield, limiting reagent, mole, and atomic mass D 2.5 - calculate the corresponding mass, or quantity in moles or molecules, for any given reactant or product in a balanced chemical equation as well as for any other reactant or product in the chemical reaction D 3.4 - explai ...
... stoichiometry, percentage yield, limiting reagent, mole, and atomic mass D 2.5 - calculate the corresponding mass, or quantity in moles or molecules, for any given reactant or product in a balanced chemical equation as well as for any other reactant or product in the chemical reaction D 3.4 - explai ...